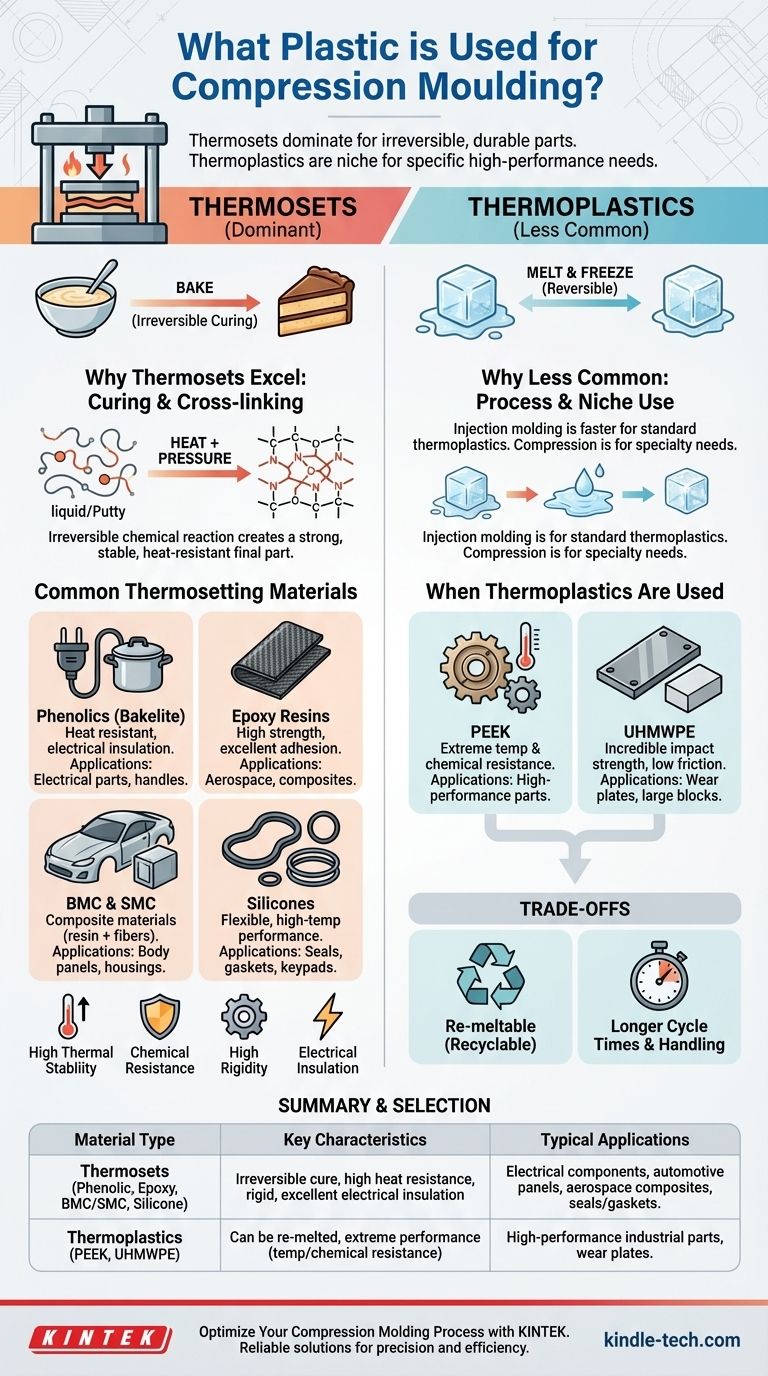
The primary materials used for compression molding are thermosetting plastics, though some high-performance thermoplastics are also suitable. Thermosets, such as Epoxy, Phenolic (Bakelite), and polyester resins found in Bulk Molding Compound (BMC) and Sheet Molding Compound (SMC), are ideal because they undergo an irreversible chemical reaction (curing) under heat and pressure, forming a strong, rigid, and heat-resistant final part.
The critical insight is not which specific plastic to use, but understanding why compression molding is fundamentally aligned with thermosetting polymers. These materials transform from a pliable state to a permanently solid one, making the process perfect for creating durable, dimensionally stable components that cannot be re-melted.
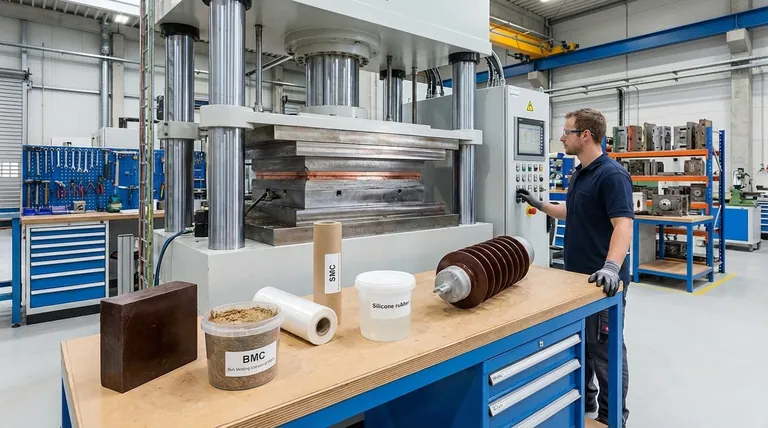

The Foundation: Why Thermosets Dominate Compression Molding
To choose the right material, you must first understand the core principle that makes this process unique. Compression molding is defined by applying heat and immense pressure to a material placed directly into the mold cavity.
What is a Thermoset?
A thermoset is a polymer that is irreversibly cured by heat. Before molding, it exists as a liquid, putty, powder, or pre-formed charge.
Think of it like baking a cake. Once you bake the liquid batter into a solid cake, you cannot turn it back into batter by reheating it. This is a permanent chemical change.
In contrast, a thermoplastic is like an ice cube. You can melt it into water and refreeze it back into an ice cube repeatedly. Most common plastics, like PET in water bottles, are thermoplastics.
The Curing Process Advantage
The compression molding process is perfectly suited for the slow, deliberate curing of thermosets. The material is placed in the heated mold, and as the press closes, the material flows to fill the cavity.
The sustained heat and pressure are held not just to form the part, but to initiate and complete the cross-linking reaction. This reaction creates a powerful, three-dimensional network of chemical bonds throughout the material, locking it into its final shape.
Key Properties of Thermoset Parts
This cross-linking gives parts made from thermosets their signature characteristics:
- High Thermal Stability: They do not soften or melt when reheated.
- High Rigidity and Dimensional Stability: They hold their shape exceptionally well under load and across a range of temperatures.
- Excellent Chemical Resistance: The strong chemical bonds make them resistant to solvents and other corrosive agents.
- Good Electrical Insulation: Many thermosets are natural insulators.
Common Thermosetting Plastics for Compression Molding
While the category is broad, a few key materials cover the majority of applications.
Phenolics (PF)
Often called by its trade name, Bakelite, this was one of the first synthetic plastics. It is a cost-effective choice known for its exceptional heat resistance and electrical insulating properties. You find it in electrical components, automotive distributor caps, and heat-resistant handles for cookware.
Epoxy Resins (EP)
Epoxy is renowned for its superior mechanical strength, low shrinkage, and excellent adhesion. When reinforced with fibers like glass or carbon, it is used to create high-strength, lightweight composite parts for aerospace and high-performance automotive applications.
Bulk and Sheet Molding Compounds (BMC & SMC)
These are not single plastics but composite materials. They consist of an unsaturated polyester (UP) or vinyl ester (VE) resin, mixed with fillers, catalysts, and chopped glass fibers.
- BMC is a putty-like "bulk" material.
- SMC is a flexible, leather-like "sheet."
They are workhorses of the industry, used to create large, strong, and relatively low-cost parts like automotive body panels, electrical enclosures, and appliance housings.
Silicones and Elastomers
For applications requiring flexibility and high-temperature performance, thermosetting elastomers like silicone are compression molded. This is the process used to create seals, gaskets, O-rings, and flexible keypads.
What About Thermoplastics?
While less common, some high-performance thermoplastics are also compression molded, typically when their unique properties are required and other processes are less suitable.
Why Thermoplastics Are Less Common
For most standard thermoplastics (like Polypropylene or ABS), injection molding is a much faster and more economical process. Compression molding's longer cycle times make it less competitive for high-volume thermoplastic parts.
When Thermoplastics Are Used
Compression molding is reserved for specialty thermoplastics that are difficult to process otherwise.
- PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone): An ultra-high-performance material with extreme temperature and chemical resistance.
- UHMWPE (Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene): Known for its incredible impact strength and low-friction surface, it is often compression molded into large blocks or wear plates.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material for compression molding involves balancing performance with process limitations.
Irreversibility: The Thermoset Downside
The greatest strength of a thermoset is also its biggest weakness. Because the curing process is irreversible, thermoset parts cannot be melted down and recycled like thermoplastics. This has significant environmental and end-of-life considerations.
Longer Cycle Times
The time required for the material to cure within the mold can range from one to several minutes. This is significantly longer than the seconds-long cycle times of injection molding, making compression molding less suitable for extremely high-volume production.
Material Form and Handling
Thermosets require careful handling. They arrive as powders, pre-forms, or compounds (BMC/SMC) that must be precisely measured and placed into the mold for each cycle, a step that is often more labor-intensive than the automated feeding of an injection molding machine.
How to Select the Right Material
Your choice depends entirely on the performance demands and cost constraints of your final application.
- If your primary focus is high heat and electrical insulation at a low cost: Phenolics are the classic and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is large, strong structural components for automotive or industrial use: Start with Sheet Molding Compound (SMC) or Bulk Molding Compound (BMC).
- If your primary focus is ultimate mechanical strength and performance in a composite: Epoxy resin, often reinforced with carbon fiber, is the premium option.
- If your primary focus is creating flexible, high-temperature seals or gaskets: Look to Silicone and other thermosetting elastomers.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical and temperature resistance beyond what most thermosets offer: Consider a high-performance thermoplastic like PEEK.
By matching the material's fundamental properties to your specific engineering needs, you can fully leverage the power of compression molding.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Examples | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermosets | Phenolic (Bakelite), Epoxy, BMC/SMC, Silicone | Irreversible cure, high heat resistance, rigid, excellent electrical insulation | Electrical components, automotive panels, aerospace composites, seals/gaskets |
| Thermoplastics | PEEK, UHMWPE | Can be re-melted, extreme performance (temp/chemical resistance) | High-performance industrial parts, wear plates |
Optimize Your Compression Molding Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right plastic is critical for achieving durable, high-performance parts. Whether you're working with robust thermosets like Phenolic and Epoxy or specialized thermoplastics like PEEK, KINTEK is your trusted partner for all your lab equipment and consumable needs.
We provide reliable solutions that ensure precision and efficiency in your material testing and processing workflows. Let our expertise help you enhance product quality and accelerate your development cycle.
Ready to elevate your compression molding projects? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP for Small Workpiece Production 400Mpa
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- What makes a press hydraulic? The Power of Fluid Mechanics for Unmatched Force
- What is the primary function of a hydraulic press in SiC/Al-Zn-Mg-Cu extrusion? Mastering Material Deformation
- Can hydraulic systems that run too hot or too cold cause severe problems over time? Yes, and here's how to prevent it.
- What is the function of a laboratory uniaxial hydraulic press in preparation of green pellets? Expert Compaction Guide
- What material can break a hydraulic press? Discover the Limits of Crushing Force
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press used to apply 800 MPa for magnetic powder cores? Achieve Peak Material Density
- How does the axial pressure provided by a laboratory hydraulic system influence weld formation? Master Precision Bonding
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press required for BZY20 ceramic green bodies? Mastering SSRS at 375 MPa









