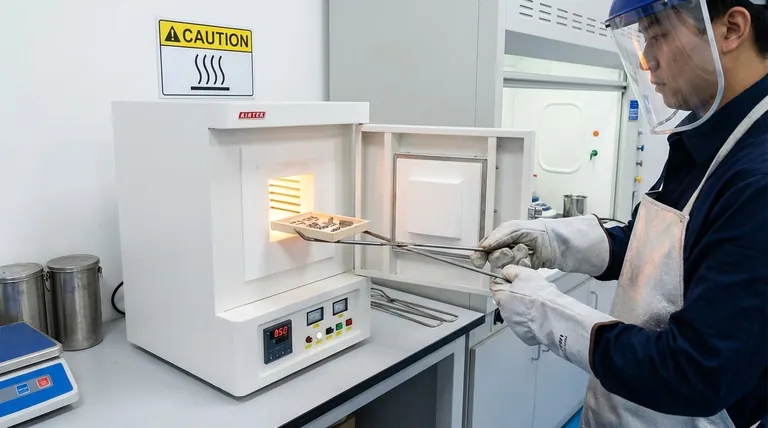
Proper precautions during heat treatment are essential for protecting personnel, equipment, and the material itself. The primary areas of concern involve managing extreme temperatures, handling potentially hazardous atmospheric gases, and executing the quenching process safely to prevent injury and ensure the desired metallurgical outcome is achieved without damaging the part.
Heat treatment safety is not merely a checklist of rules, but a comprehensive strategy. It requires a deep understanding of the risks to personnel, the limitations of the equipment, and the metallurgical sensitivity of the material being processed.

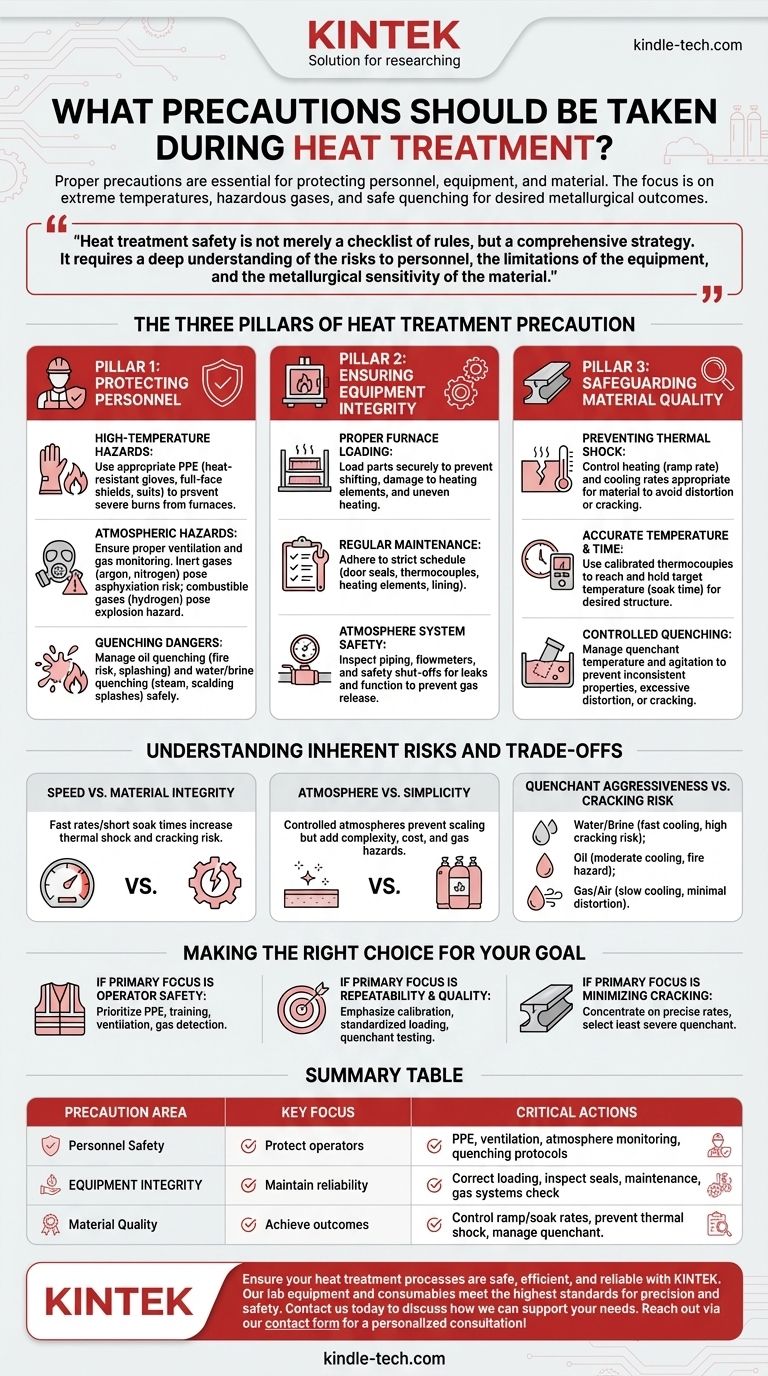
The Three Pillars of Heat Treatment Precaution
Effective safety and quality control in heat treatment rest on three foundational pillars. Neglecting any one of them introduces significant risk to the entire operation.
Pillar 1: Protecting Personnel
The most immediate risks in heat treatment are those to the operator and any nearby staff.
High-Temperature Hazards Furnaces operate at temperatures that can cause severe, life-threatening burns instantly. All personnel must wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including heat-resistant gloves, aprons or suits, and full-face shields.
Atmospheric Hazards Many heat treatment processes use controlled atmospheres to prevent oxidation. These can involve inert gases like argon or nitrogen, which pose an asphyxiation risk in enclosed spaces, or combustible gases like hydrogen, which create an explosion hazard. Proper ventilation and gas monitoring systems are non-negotiable.
Quenching Dangers The quenching stage, where a hot part is rapidly cooled, is particularly hazardous. Submerging a part in oil can cause violent splashing and presents a significant fire risk. Quenching in water or brine can create large volumes of steam, causing splashes of scalding water.
Pillar 2: Ensuring Equipment Integrity
The equipment itself requires careful handling and maintenance to operate safely and reliably.
Proper Furnace Loading Parts must be loaded securely within the furnace. Improperly placed components can shift or fall, damaging the furnace's heating elements or insulation. Overloading the furnace can lead to uneven heating and potential equipment strain.
Regular Maintenance A strict maintenance schedule is critical. This includes inspecting door seals, thermocouples (for temperature accuracy), heating elements, and the integrity of the furnace lining or retort.
Atmosphere System Safety For controlled atmosphere furnaces, all piping, flowmeters, and safety shut-offs must be regularly inspected for leaks and proper function to prevent the release of flammable or toxic gases.
Pillar 3: Safeguarding Material Quality
A core precaution is ensuring the process doesn't ruin the workpiece, which is the entire point of the procedure. The benefits of changing a material's properties are only realized if the process is precisely controlled.
Preventing Thermal Shock Heating or cooling a part too quickly can induce internal stresses, leading to distortion or catastrophic cracking. This is known as thermal shock. The heating rate (ramp rate) and cooling rate must be appropriate for the material's geometry and composition.
Accurate Temperature and Time Holding the material at the wrong temperature or for an incorrect duration (soak time) will fail to produce the desired metallurgical structure. Using calibrated thermocouples and control systems is essential to guarantee the part reaches and holds the target temperature accurately.
Controlled Quenching The speed of the quench determines the final hardness. An uncontrolled quench can lead to inconsistent properties across the part, excessive distortion, or quench cracking. The quenchant's temperature and agitation must be carefully managed.
Understanding Inherent Risks and Trade-offs
Choosing a heat treatment process involves balancing desired outcomes with inherent risks.
Speed vs. Material Integrity
Rushing the process by using excessively fast ramp rates or short soak times can save energy and time. However, this dramatically increases the risk of thermal shock, leading to cracking, and can result in incomplete metallurgical transformation, failing to achieve the desired strength or hardness.
Atmosphere vs. Simplicity
Using a controlled atmosphere prevents surface scaling and decarburization, yielding a cleaner, higher-quality part. The trade-off is significant complexity and cost, along with the safety hazards of storing and handling industrial gases.
Quenchant Aggressiveness vs. Cracking Risk
Different quenching mediums offer a trade-off between cooling power and severity.
- Water/Brine: Provides very rapid cooling for maximum hardness but carries the highest risk of distortion and cracking.
- Oil: Cools less severely, reducing cracking risk, but is a fire hazard and produces smoke and fumes.
- Gas/Air: Offers the slowest, most gentle quench, minimizing distortion but may not be fast enough to harden many steel alloys.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific precautions should be prioritized based on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is operator safety and compliance: Prioritize comprehensive PPE, rigorous training on emergency procedures, and robust ventilation and gas detection systems.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and quality: Emphasize the calibration of all control instrumentation (thermocouples, timers), standardized part-loading procedures, and regular testing of quenchant condition.
- If your primary focus is minimizing material cracking and distortion: Concentrate on developing and validating precise heating and cooling rates and carefully selecting the least severe quenchant that can still achieve the required properties.
By treating these precautions as integrated principles rather than a simple list, you ensure safety, preserve equipment, and guarantee control over your final material properties.
Summary Table:
| Precaution Area | Key Focus | Critical Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Personnel Safety | Protect operators from burns, gases, and quenching hazards. | Use heat-resistant PPE, ensure ventilation, monitor atmospheres, follow quenching protocols. |
| Equipment Integrity | Maintain furnace and system reliability. | Load parts correctly, inspect seals/thermocouples, schedule maintenance, check gas systems. |
| Material Quality | Achieve desired metallurgical outcomes without damage. | Control ramp/soak rates, prevent thermal shock, manage quenchant temperature/agitation. |
Ensure your heat treatment processes are safe, efficient, and reliable with KINTEK.
Our lab equipment and consumables are designed to meet the highest standards for precision and safety. Whether you need furnaces with precise temperature control, quenching systems, or atmosphere management solutions, KINTEK provides the tools to protect your personnel, maintain your equipment, and achieve consistent material properties.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific heat treatment needs and help you implement these essential precautions. Reach out via our contact form for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between a furnace and oven? Understanding Their Unique Heating Purposes
- What is maintenance and how can you maintain the laboratory? Boost Lab Reliability & Data Integrity
- What is the heat capacity of a muffle furnace? Understanding Thermal Mass for Optimal Performance
- Is a muffle furnace an oven? A Guide to High-Temperature vs. Low-Temperature Heating
- How do you check the temperature of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Precise Monitoring



















