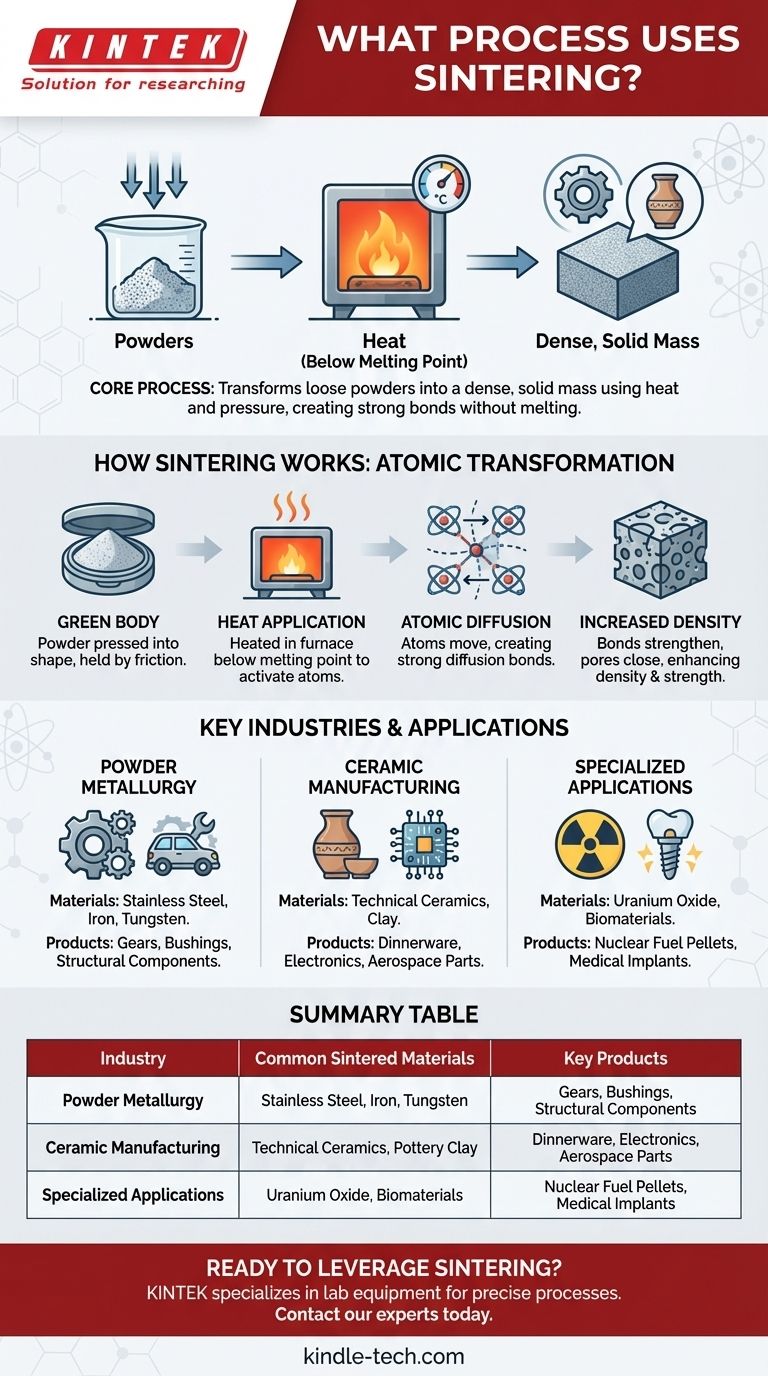
At its core, sintering is a manufacturing process that transforms loose powders into a dense, solid mass. It achieves this by applying heat—at a temperature below the material's melting point—and often pressure, causing the individual particles to bond together and compact. This technique is fundamental to powder metallurgy for creating metal parts and to the ceramics industry for producing everything from pottery to advanced components.
Sintering is the essential bridge between a powdery raw material and a strong, dense final product. Its unique value lies in its ability to create solid objects from materials with extremely high melting points, accomplishing fusion without liquefaction.

How Sintering Fundamentally Works
Sintering is a process of atomic-level transformation. Understanding the stages reveals how it achieves such remarkable results without melting the base material.
The Starting Point: A "Green Body"
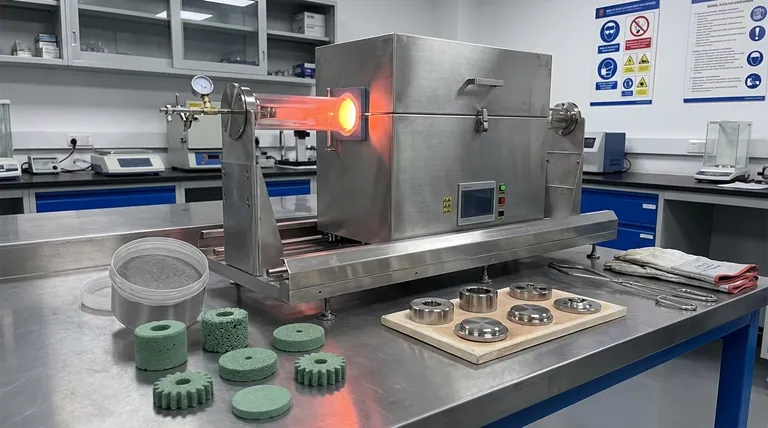
The process begins by pressing a powder into a desired shape, often called a "green body" or compact. At this stage, the object is fragile, with its particles held together only by mechanical friction.
The Role of Heat
The green body is then heated in a high-temperature furnace. Critically, the temperature remains below the material's melting point. This heat provides the energy needed to activate the atoms within the particles.
Atomic Diffusion and Bonding
At these elevated temperatures, atoms at the contact points between particles begin to diffuse, or move, across the particle boundaries. This movement creates strong diffusion bonds, effectively welding the particles together at their points of contact.
The Result: Increased Density and Strength
As these bonds form and strengthen, the contact areas between particles grow. This pulls the particle centers closer together, systematically eliminating the tiny pores and gaps between them. The result is a significant increase in the object's density, hardness, and overall strength.
Key Industries That Rely on Sintering
Sintering is not a niche process; it is a cornerstone of several major manufacturing sectors due to its versatility and unique capabilities.
Powder Metallurgy
This is one of the largest applications of sintering. It is used to create complex parts from powders of stainless steel, iron-based materials, and refractory metals like tungsten and molybdenum. This is how many gears, bushings, and structural components for automobiles and machinery are made.
Ceramic Manufacturing
From traditional pottery to advanced technical ceramics, sintering is essential. It gives ceramic products their hardness and durability. This includes everything from dinnerware to the high-performance ceramic components used in electronics and aerospace.
Specialized and High-Tech Applications
The power of sintering extends to highly specialized fields. It is used in the nuclear fuel industry to create dense uranium oxide pellets. It is also a key processing route for developing new biomaterials for medical implants in laboratory settings.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, the decision to use sintering is based on a clear set of advantages and practical realities. It is chosen specifically because other methods are less suitable.
The Primary Advantage: High-Melting-Point Materials
Sintering's greatest strength is its ability to fabricate parts from materials with exceptionally high melting points. Trying to melt and cast materials like tungsten or molybdenum is often impractical or prohibitively expensive, making sintering the superior choice.
Driving Forces and Process Variations
The efficiency of sintering is driven by forces seeking to lower the material's energy state, such as reducing surface free energy. To enhance this, different methods have been developed, including Conventional Sintering, Microwave Sintering, and Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), each offering unique benefits for specific materials.
The Necessity of Post-Sintering Finishing
A sintered part is rarely the final product. Due to inherent microscopic porosity, many parts undergo finishing processes. These can include oil impregnation for self-lubricating bearings, resin impregnation to seal pores, or galvanizing and plating to improve corrosion resistance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right approach to sintering depends entirely on the material and the desired outcome of the final part.
- If your primary focus is producing standard industrial parts from metal or ceramic: Conventional high-temperature furnace sintering is the most established and widely used method.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research or creating biomaterials: Specialized techniques like Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) provide faster processing and unique properties required for cutting-edge development.
- If your primary focus is maximizing durability and performance: You must plan for post-sintering finishing processes like impregnation or plating to achieve the required surface characteristics and integrity.
Ultimately, sintering is a foundational process that enables the creation of robust components from materials that would otherwise be nearly impossible to form.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Common Sintered Materials | Key Products |
|---|---|---|
| Powder Metallurgy | Stainless Steel, Iron, Tungsten | Gears, Bushings, Structural Components |
| Ceramic Manufacturing | Technical Ceramics, Pottery Clay | Dinnerware, Electronics, Aerospace Parts |
| Specialized Applications | Uranium Oxide, Biomaterials | Nuclear Fuel Pellets, Medical Implants |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's material development? KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables needed for precise sintering processes, from research to production. Our expertise can help you create stronger, denser components from high-melting-point materials. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What is the role of a tube furnace in the thermal treatment of argyrodite electrolytes? Master Ionic Conductivity
- What is the primary function of quartz tubes in halide electrolyte synthesis? Ensure Purity & Precise Stoichiometry
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- How does an industrial tube furnace ensure the required process conditions for supercritical fluid experimental devices?



















