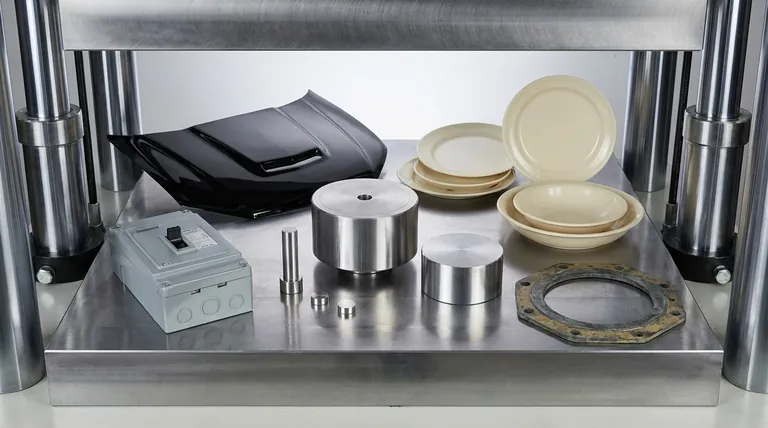
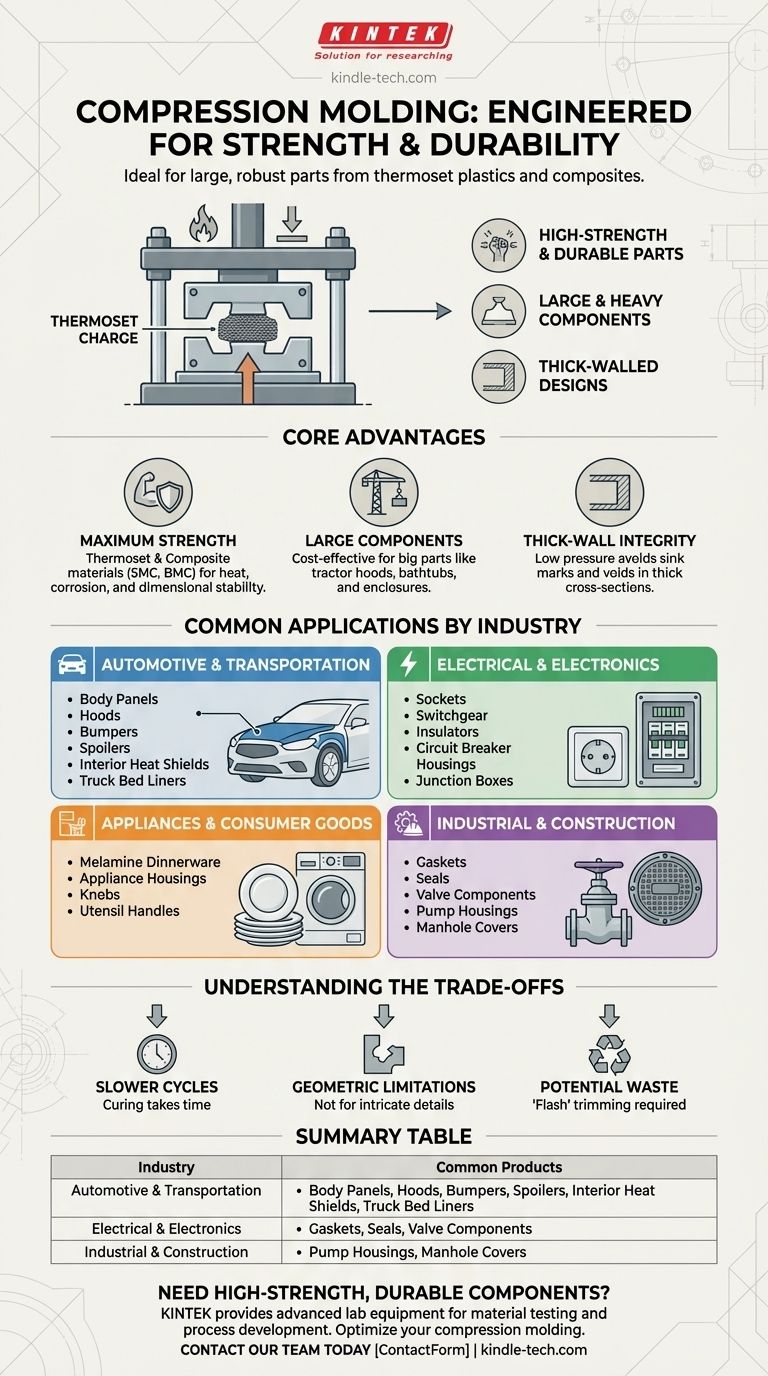
Compression molding is used to manufacture a vast range of high-strength, durable products, particularly large components for the automotive, aerospace, appliance, and electrical industries. Common examples include vehicle body panels and hoods, electrical enclosures, sturdy dinnerware, and industrial gaskets.
The key to understanding compression molding's applications is recognizing its ideal fit for producing large, strong, and dimensionally stable parts from thermoset plastics and composite materials, where material strength and heat resistance are more critical than intricate design details.

Why Compression Molding is Chosen: The Core Advantages
To understand which products use this method, you must first understand its fundamental strengths. Manufacturers choose compression molding when the final part's material properties and structural integrity are the primary concern.
High-Strength and Durable Parts
The process is exceptionally well-suited for thermoset plastics and high-strength composites like Sheet Molding Compound (SMC) and Bulk Molding Compound (BMC).
These materials undergo an irreversible chemical curing process under heat and pressure, creating parts that are extremely rigid, dimensionally stable, and resistant to heat and corrosion.
Ideal for Large and Heavy Components
Compression molding is one of the most cost-effective methods for producing very large parts. The lower pressures involved mean tooling doesn't have to withstand the extreme forces of high-pressure injection molding.
This makes it the go-to process for items like tractor hoods, bathtubs, boat hulls, and large equipment enclosures.
Excellent for Thick-Walled Designs
Because the material charge fills the mold cavity relatively slowly and under consistent pressure, the process excels at creating thick-walled components.
This avoids common defects like sink marks and internal voids that can plague other molding processes when attempting to create parts with thick cross-sections.
Common Applications by Industry
By combining these advantages, you can see a clear pattern in the types of products made with compression molding across various sectors.
Automotive and Transportation
This is a primary user of compression molding for parts that need to be both strong and relatively lightweight.
Examples include body panels, hoods, spoilers, bumpers, and interior heat shields. The process is also used for heavy-duty components like truck bed liners and fender housings.
Electrical and Electronics
The excellent heat resistance and insulating properties of thermoset materials make them ideal for electrical applications.
You will find compression molded electrical sockets, switchgear, insulators, circuit breaker housings, and large junction boxes.
Appliances and Consumer Goods
Durability and heat resistance are key drivers in this sector.
The most famous example is Melamine dinnerware (plates and bowls), known for its durability. Other applications include appliance housings, knobs, and utensil handles.
Industrial and Construction
For demanding environments, compression molding delivers robust parts that can withstand wear and chemical exposure.
Common products include gaskets, seals, valve components, pump housings, and even composite manhole covers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No manufacturing process is perfect for every application. Trustworthy analysis requires acknowledging the limitations.
Slower Cycle Times
The curing process for thermoset materials takes time, often several minutes per part. This makes compression molding less suitable for the extremely high-volume production demands where injection molding excels.
Geometric Limitations
While it can produce complex shapes, compression molding is not ideal for parts with very intricate details, sharp internal corners, or undercuts. The material does not flow as easily as molten thermoplastic in an injection mold.
Potential for Material Waste
Excess material, known as "flash," is squeezed out between the two halves of the mold when it closes. This flash must be manually or automatically trimmed from the finished part, creating a secondary operation and material waste.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a manufacturing process depends entirely on your product's specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and heat resistance for a large part: Compression molding with thermoset composites is almost certainly your best option.
- If your primary focus is producing a thick-walled component without defects: The low-pressure nature of compression molding makes it a superior choice to high-pressure alternatives.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing millions of small, complex parts from thermoplastic: You should investigate injection molding as a more suitable process.
By understanding its unique strengths in handling robust materials for large and durable applications, you can confidently determine if compression molding is the right process to engineer your product.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Common Compression Molded Products |
|---|---|
| Automotive & Transportation | Body panels, hoods, bumpers, truck bed liners, spoilers |
| Electrical & Electronics | Sockets, switchgear, circuit breaker housings, insulators |
| Appliances & Consumer Goods | Melamine dinnerware, appliance housings, knobs, utensil handles |
| Industrial & Construction | Gaskets, seals, pump housings, valve components, manhole covers |
Need to manufacture high-strength, durable components? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for material testing and process development, including solutions for thermoset and composite materials. Let our expertise help you optimize your compression molding process for superior results. Contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory and production needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What technical requirements must specialized pressure-bearing molds meet? Optimize Sulfide Electrolyte Densification
- Why is hot press molding preferred over traditional solution casting? Expert Comparison for Polymer Electrolytes
- What is the role of graphite molds during the hot pressing of LSLBO ceramics? Essential for High-Density Electrolytes
- What roles do graphite molds play during vacuum hot pressing of Al-Sc alloys? Ensure Precision & Purity
- What are the specific functions of graphite molds in the vacuum hot-press sintering process? Expert Insights for Ceramics



















