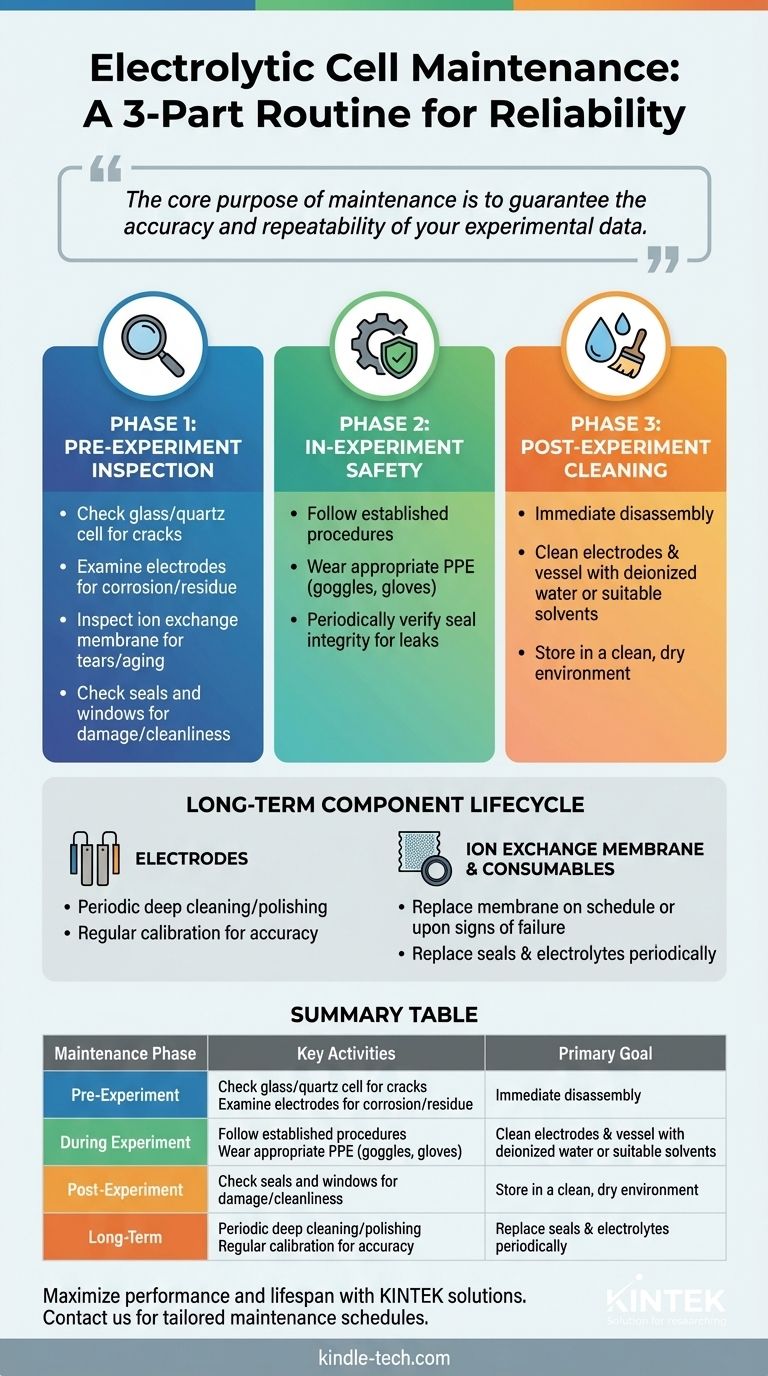
Proper maintenance of an electrolytic cell requires a three-part routine: a thorough visual inspection before each use, immediate and meticulous cleaning after each experiment, and periodic replacement of consumable components based on wear and usage. This disciplined approach ensures the integrity of your results, the safety of the operator, and the longevity of the equipment.
The core purpose of electrolytic cell maintenance is not just to prevent breakage, but to guarantee the accuracy and repeatability of your experimental data. Consistent inspection and cleaning are the foundation of reliable electrochemical analysis.
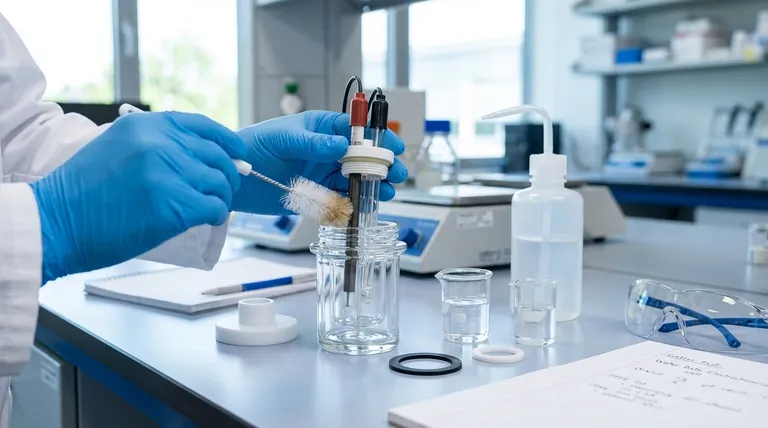

The Three Phases of Cell Maintenance
A robust maintenance plan can be broken down into a simple, repeatable rhythm: tasks you perform before, during, and after every experiment. This structure ensures nothing is overlooked.
Phase 1: Pre-Experiment Inspection
Before assembling the cell, conduct a careful visual inspection of every component. Catching a problem here prevents a failed experiment and potential damage.
- Cell Body & Lid: Check the glass or quartz cell body for any cracks or chips, as it is fragile. Ensure the lid creates a tight, secure seal.
- Electrodes: Examine the electrodes for visible signs of corrosion, physical damage, or residue from a previous experiment.
- Ion Exchange Membrane: Inspect the membrane for any tears, discoloration, or signs of aging and blockage. A compromised membrane will invalidate your results.
- Seals and Windows: Check all sealing rings to ensure they are pliable and free of nicks or damage. If your cell has quartz windows, confirm they are clean and unscratched.
Phase 2: In-Experiment Safety and Monitoring
Safe operation is an integral part of maintenance. Your primary responsibility during an experiment is to ensure the system is operating as intended and safely.
- Follow Procedures: Adhere strictly to the established operating procedures for your experiment to prevent accidents.
- Use Protective Equipment: Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as safety goggles and gloves, when handling electrolytes and cell components.
- Check for Leaks: Periodically verify the integrity of all seals to ensure there are no electrolyte leaks during operation.
Phase 3: Post-Experiment Cleaning & Storage
This is arguably the most critical step for ensuring long-term performance. Cleaning must be performed immediately after the experiment is complete.
- Immediate Cleaning: Disassemble and clean the electrodes and the reaction vessel right away. This prevents residues from drying and adhering to the surfaces, which can be difficult to remove later.
- Appropriate Solvents: Use deionized water or ethanol for general cleaning. For stubborn residues, a dilute acid or base may be necessary, but always check for compatibility with your cell materials.
- Proper Storage: After cleaning and drying, store all components in a clean, dry, and moisture-free environment to prevent corrosion and degradation.
Understanding the Long-Term Component Lifecycle
Beyond daily checks, some components have a finite lifespan and require periodic attention based on cumulative use.
Assessing the Electrodes
The electrodes are central to your experiment's success. Their condition must be actively managed.
- Periodic Deep Cleaning: Depending on your application, electrodes may require periodic deep cleaning or polishing to remove stubborn oxides or contaminants.
- Calibration: For many analytical applications, electrodes must be calibrated regularly to ensure accurate measurements.
Evaluating the Ion Exchange Membrane
The ion exchange membrane is a critical consumable part that directly impacts cell performance.
- Signs of Failure: Look for signs of aging, such as brittleness or blockage, that would impede ion flow.
- Scheduled Replacement: It is often best practice to replace the membrane on a schedule based on hours of use, rather than waiting for it to fail.
Replacing Consumables
Sealing rings and electrolytes are also consumables that degrade over time.
- Seals: If a sealing ring appears compressed, brittle, or damaged in any way, replace it immediately to prevent leaks.
- Electrolyte: The electrolyte should be replaced periodically based on the demands of your experiments and signs of contamination or depletion.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your maintenance strategy should align with your primary experimental objective.
- If your primary focus is high-precision analytics: Your highest priority is the condition of the electrodes and ion exchange membrane, so focus on regular calibration and a strict membrane replacement schedule.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening: Your priority is minimizing cross-contamination and downtime, so implement an efficient post-experiment cleaning protocol and keep spare membranes and seals readily available.
- If your primary focus is long-term stability and safety: Your priority is the physical integrity of the apparatus, so emphasize rigorous pre-use inspection of the cell body, seals, and wiring.
A disciplined maintenance routine transforms your electrolytic cell from a piece of glassware into a reliable, high-performance scientific instrument.
Summary Table:
| Maintenance Phase | Key Activities | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Experiment | Inspect cell body, electrodes, membrane, and seals. | Prevent failure and ensure experiment integrity. |
| During Experiment | Monitor for leaks, follow safety procedures, wear PPE. | Ensure safe operation and immediate issue detection. |
| Post-Experiment | Immediate disassembly and cleaning with appropriate solvents. | Prevent residue buildup and cross-contamination. |
| Long-Term | Schedule electrode calibration, membrane replacement, and seal checks. | Maintain performance and plan for consumable lifecycle. |
Maximize the performance and lifespan of your laboratory equipment. A consistent maintenance routine is key to reliable data and operational safety. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including electrolytic cells, electrodes, and ion exchange membranes. Our experts can help you establish a tailored maintenance schedule and ensure you have the right components for your specific application—whether it's high-precision analytics, high-throughput screening, or long-term stability studies.
Let us help you achieve unparalleled accuracy and efficiency in your lab. Contact our team today to discuss your needs and discover how KINTEK solutions can support your research goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Double-Layer Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
People Also Ask
- When is professional repair required for a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Protect Your Lab's Precision and Safety
- How can the electrochemical reaction be controlled when using this electrolytic cell? Master Voltage, Current & Electrolyte
- What are the key features of a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Achieve Precise Temperature Control for Your Experiments
- What are the typical volumes and aperture configurations for a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Optimize Your Electrochemical Setup
- What are the procedures for after using a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Ensure Equipment Longevity and Data Accuracy



















