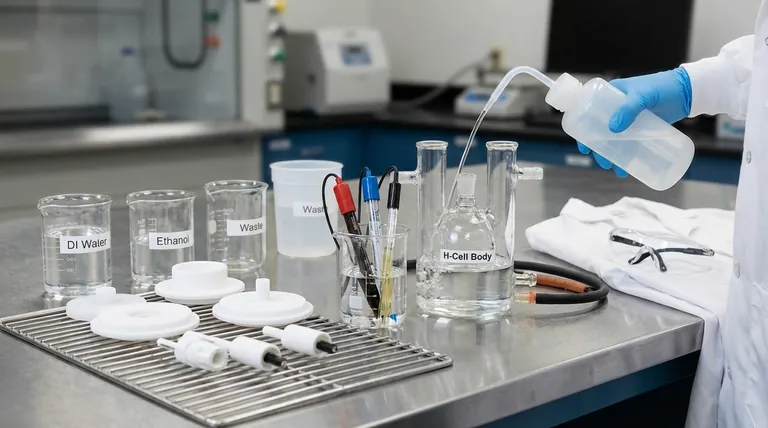
Proper post-experiment procedure is critical for maintaining the integrity of a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell and ensuring the accuracy of future work. The process involves a specific sequence of shutting down power, handling components, cleaning the cell, and storing everything correctly. This protocol protects sensitive electrodes from damage, prevents cross-contamination between experiments, and extends the life of the apparatus.
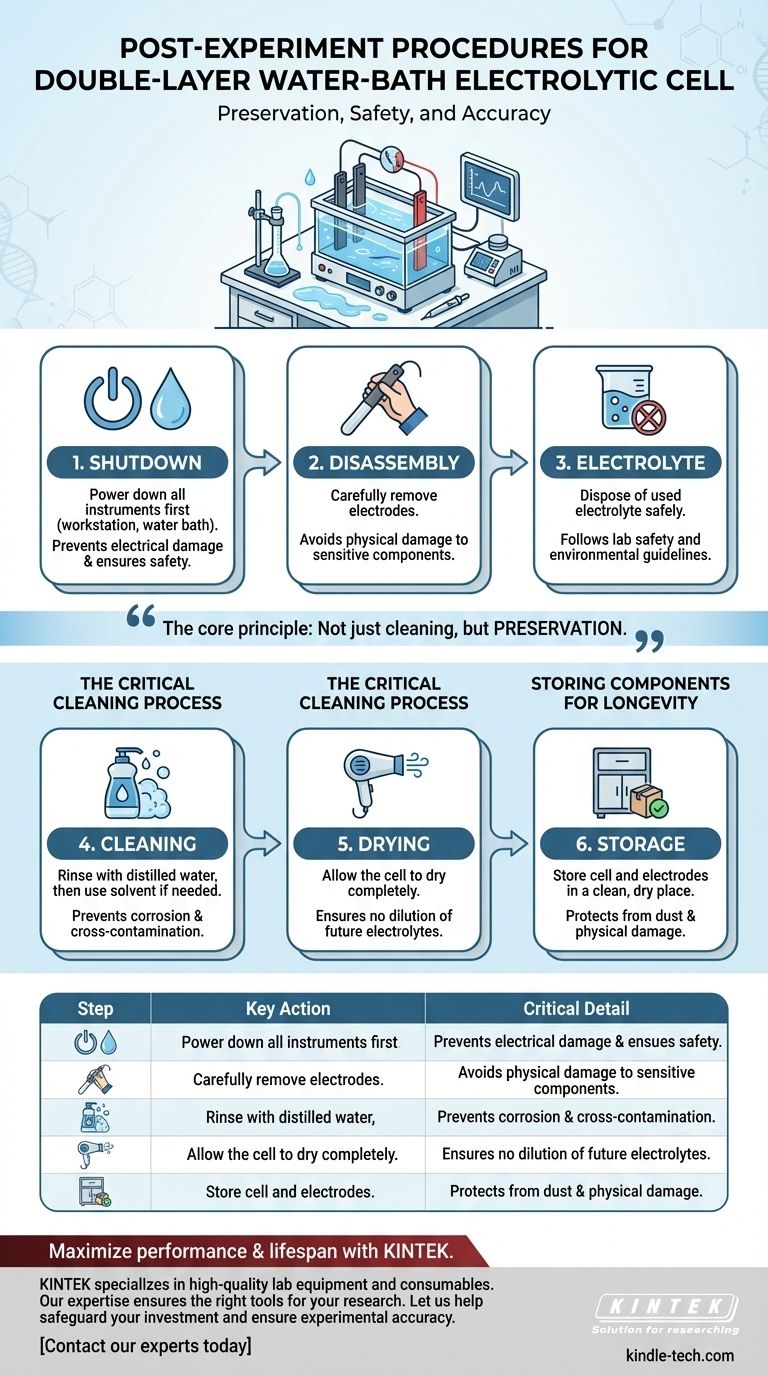
The core principle behind post-experiment procedure is not just cleaning, but preservation. A disciplined shutdown and storage routine is the most effective way to safeguard your investment in sensitive equipment and guarantee the reliability of your future data.

The Systematic Shutdown Protocol
The first priority after an experiment concludes is to safely power down the system and disassemble its core components in the correct order.
Prioritize Electrical Safety
Before touching any part of the cell, ensure all electrical energy sources are off. First, turn off the electrochemical workstation and the constant temperature water bath. Only after the power is off should you disconnect any circuits or wiring.
Handle Electrodes with Care
Once the system is powered down, carefully remove the working, reference, and counter electrodes. These components are often fragile and expensive. Avoid bumping them against the cell walls or each other during removal.
Manage the Electrolyte Safely
Properly dispose of the used electrolyte immediately after removing the electrodes. The correct disposal method depends entirely on the chemical's properties and must adhere to your lab's safety and environmental guidelines, which may involve neutralization, recycling, or specialized waste collection.
The Critical Cleaning Process
Thorough cleaning is essential to prevent residual chemicals from corroding the equipment or contaminating subsequent experiments.
The Initial Rinse
The first and most important cleaning step is to rinse the cell multiple times with distilled or deionized water. This removes the bulk of the residual electrolyte and reaction byproducts from the glass surfaces.
Advanced Cleaning for Stubborn Residues
If water is insufficient, a more potent cleaning agent may be required. You can soak the cell in a suitable solvent, such as ethanol or acetone, or use a dilute acid or base.
Crucially, you must confirm that the chosen cleaning agent will not corrode the cell body, seals, or any other components.
The Importance of Thorough Drying
After the final rinse, allow the cell to dry completely. Storing a wet cell can lead to contamination issues. This ensures that no residual water will dilute the electrolyte in your next experiment.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes during the post-use phase can be costly, leading to damaged equipment and compromised results.
Avoiding Thermal Shock and Damage
Never sterilize the fully assembled cell at high temperatures. The PTFE lid can expand when heated and may not return to its original shape, ruining the seal. While the glass parts can often be autoclaved, they should be done so separately and with care to avoid thermal shock.
Preventing Physical Damage
The most common source of damage is carelessness during disassembly and cleaning. Always handle the glass cell gently to avoid cracks and be especially delicate with electrodes, which can be easily bent or have their surfaces scratched.
The Risk of Cross-Contamination
An inadequate cleaning protocol is a primary cause of inconsistent experimental results. Even trace amounts of residue from a previous experiment can interfere with the electrochemical reactions of the next one, invalidating your data.
Storing Components for Longevity
Proper storage protects the cleaned cell and its sensitive parts from contamination and damage between uses.
Storing the Cell Body
Once clean and completely dry, store the electrolytic cell in a dry, clean, and dust-free environment. A dedicated cabinet or container is ideal to prevent contamination from ambient lab conditions.
Storing Sensitive Electrodes
Electrodes require specific storage conditions. After cleaning them according to manufacturer instructions, they must be preserved properly to prevent physical impact and contamination. Many electrodes, particularly reference electrodes, must be stored in a dedicated solution to keep them stable and ready for use.
How to Apply This to Your Lab Work
Your primary goal dictates which part of this process requires the most attention.
- If your primary focus is equipment safety and longevity: Always power down all instruments before disassembling any components to prevent electrical damage and personal injury.
- If your primary focus is experimental accuracy: Implement a rigorous, multi-stage cleaning protocol to eliminate any chance of cross-contamination that could invalidate your results.
- If your primary focus is component care: Treat electrodes as the sensitive, critical instruments they are by cleaning them gently and storing them according to their specific requirements.
Following this disciplined procedure transforms routine cleanup into a critical practice that guarantees the reliability of your research and the longevity of your equipment.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Critical Detail |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Shutdown | Power down all instruments first. | Prevents electrical damage and ensures safety. |
| 2. Disassembly | Carefully remove electrodes. | Avoids physical damage to sensitive components. |
| 3. Electrolyte | Dispose of used electrolyte safely. | Follows lab safety and environmental guidelines. |
| 4. Cleaning | Rinse with distilled water, then use solvent if needed. | Prevents corrosion and cross-contamination. |
| 5. Drying | Allow the cell to dry completely. | Ensures no dilution of future electrolytes. |
| 6. Storage | Store cell and electrodes in a clean, dry place. | Protects from dust and physical damage. |
Maximize the performance and lifespan of your lab equipment with KINTEK.
Proper maintenance is key to reliable results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including electrochemical cells and accessories. Our expertise ensures you have the right tools and support for your research.
Let us help you safeguard your investment and ensure experimental accuracy.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double-Layer Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
- Optical Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
People Also Ask
- When is professional repair required for a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Protect Your Lab's Precision and Safety
- How can water and gas leaks be prevented in a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? A Guide to Proactive Maintenance
- What are the key features of a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Achieve Precise Temperature Control for Your Experiments
- What does the routine maintenance of a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell involve? A Guide to Ensuring Precision and Longevity
- What is the overall structure of the H-type double-layer optical water bath electrolytic cell? Precision Design for Controlled Experiments



















