At its core, sample preparation encompasses all the steps performed to transform a raw sample into a refined form that is suitable for analysis by an instrument. These methods range from simple filtration and dilution to complex multi-step extraction and concentration procedures designed to isolate specific compounds. The ultimate goal is to remove interferences and present the target analyte to the instrument in a way that ensures an accurate and reliable measurement.
The most sophisticated analytical instrument in the world cannot produce good data from a poorly prepared sample. Sample preparation is not a preliminary chore; it is the most critical step in the analytical process, directly governing the quality, accuracy, and reliability of your final results.
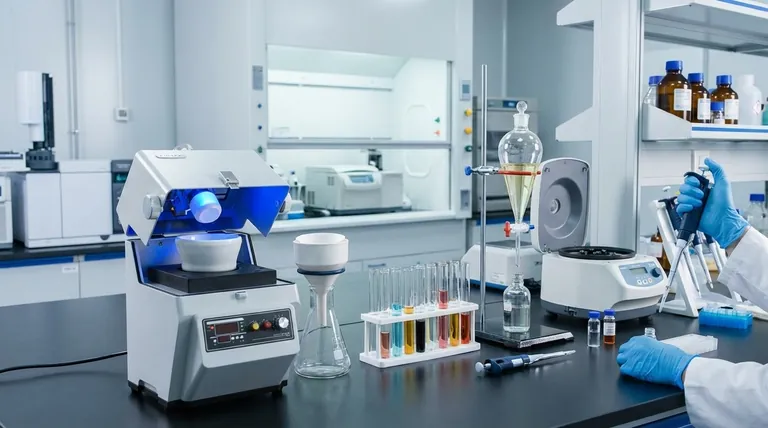

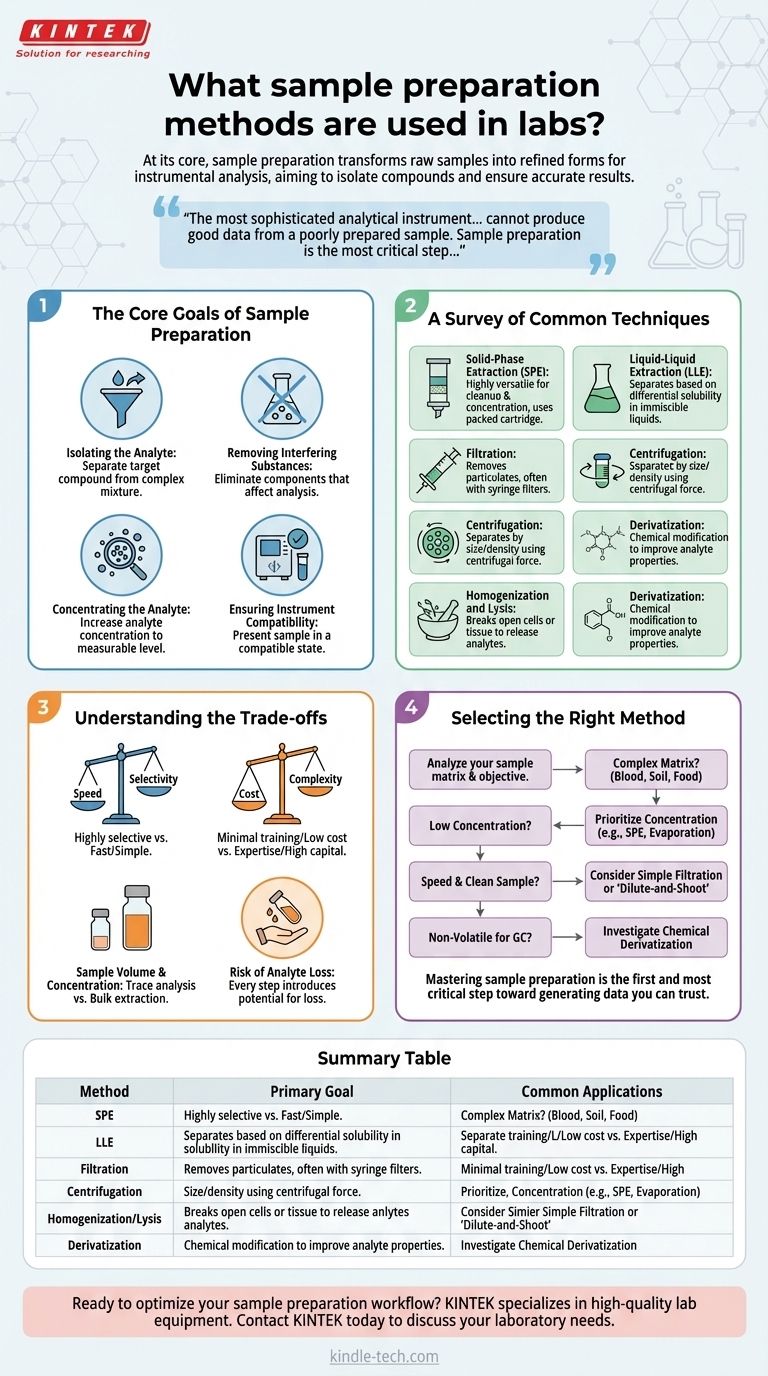
The Core Goals of Sample Preparation
Before choosing a specific technique, it is essential to understand why sample preparation is necessary. Every method is designed to achieve one or more of four fundamental objectives.
Isolating the Analyte of Interest
Your target compound, or analyte, is often just one component within a complex mixture. The primary goal is to separate this analyte from everything else in the original sample matrix, such as proteins, lipids, salts, or pigments.
Removing Interfering Substances
A sample matrix contains many components that can interfere with your analysis. These interferences might suppress the instrument's signal, create false positive signals, or even damage sensitive instrument components like an analytical column. A good preparation method eliminates these substances.
Concentrating the Analyte
In many cases, the analyte is present at a concentration too low for the instrument to detect reliably. Preparation techniques like solid-phase extraction or solvent evaporation are used to increase the analyte's concentration to a measurable level.
Ensuring Instrument Compatibility
The final prepared sample must be in a solvent or state that is compatible with the analytical instrument. For example, a sample for gas chromatography (GC) must be volatile, and a sample for liquid chromatography (LC) must be fully dissolved in a mobile-phase-compatible solvent.
A Survey of Common Techniques
Labs use a wide array of techniques, often in combination, to achieve the goals outlined above. The choice depends on the sample type, the target analyte, and the analytical instrument.
Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE)
SPE is a highly versatile and widely used technique for sample cleanup and concentration. It works by passing a liquid sample through a packed cartridge (a sorbent) that selectively retains either the analyte or the interferences, allowing them to be separated. It is a workhorse in environmental, clinical, and pharmaceutical labs.
Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE)
LLE is a classic method that separates compounds based on their differential solubilities in two immiscible liquids, typically water and an organic solvent. The sample is mixed with the two solvents, and the analyte partitions into the solvent in which it is more soluble, leaving interferences behind.
Filtration
Filtration is a fundamental physical separation process used to remove solid particulates from a liquid or gas. In a lab setting, this is commonly done with syringe filters to protect sensitive instruments like an HPLC from clogging.
Centrifugation
This technique uses centrifugal force to separate components of a mixture based on their size, density, and shape. It is commonly used to pellet cells, precipitate DNA, or separate immiscible liquids after an extraction step.
Homogenization and Lysis
When the analyte is inside cells or tissue, the first step is to break them open. Homogenization involves mechanically disrupting tissue, while lysis refers to the breakdown of the cell membrane, often using chemical detergents or physical methods like sonication (high-frequency sound waves).
Derivatization
Sometimes, an analyte isn't well-suited for a particular analysis (e.g., not volatile enough for GC). Derivatization is a chemical reaction that modifies the analyte to give it more favorable properties, such as increased volatility or a structure that is more easily detected.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single method is perfect for every situation. Choosing the right one involves balancing several key factors.
Speed vs. Selectivity
Highly selective methods like multi-step SPE provide an exceptionally clean sample but can be time-consuming and complex. In contrast, a simple "dilute-and-shoot" approach is very fast but only works for relatively clean samples where interferences and concentration are not major concerns.
Cost and Complexity
Simple filtration is inexpensive and requires minimal training. Conversely, automated SPE systems represent a significant capital investment and require more expertise to develop and validate methods, though they offer much higher throughput and reproducibility.
Sample Volume and Analyte Concentration
The amount of sample you have and the expected concentration of your analyte are critical factors. Techniques like Solid-Phase Microextraction (SPME) are excellent for trace-level analysis from small volumes, while LLE is often better suited for bulk extractions from larger sample volumes.
The Risk of Analyte Loss
Every manipulation step—from transferring a liquid to evaporating a solvent—introduces the risk of losing some of your target analyte. More complex procedures with more steps have a higher potential for analyte loss, which can negatively impact the accuracy and precision of your final quantification.
Selecting the Right Method for Your Analysis
Your choice of sample preparation should be directly guided by your sample matrix and your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is analyzing complex matrices (blood, soil, food): You need a method with powerful cleanup capabilities, making Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE) an excellent starting point.
- If your primary focus is detecting very low concentrations: Prioritize a technique that includes a concentration step, such as SPE or solvent evaporation following an extraction.
- If your primary focus is speed with a relatively clean sample: A simple filtration followed by direct injection or a "dilute-and-shoot" protocol may be sufficient.
- If your primary focus is analyzing non-volatile compounds by Gas Chromatography: You must investigate chemical derivatization to make your analyte suitable for the instrument.
Mastering sample preparation is the first and most critical step toward generating data you can trust.
Summary Table:
| Method | Primary Goal | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE) | Cleanup & Concentration | Environmental, Pharmaceutical, Clinical |
| Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE) | Separation by Solubility | Bulk Sample Extractions |
| Filtration | Remove Particulates | Protecting HPLC, General Clarification |
| Centrifugation | Separate by Density | Pellet Cells, Separate Liquids |
| Homogenization/Lysis | Release Cellular Analytes | Tissue, Cell Analysis |
| Derivatization | Modify for Instrument Suitability | GC Analysis of Non-Volatiles |
Ready to optimize your sample preparation workflow? The right equipment is fundamental to achieving precise, reliable results. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for every step of your process, from filtration and homogenization to extraction and concentration. Our experts can help you select the perfect tools to enhance your lab's efficiency and data integrity. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how we can support your analytical success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the function of using an agate mortar during the precursor mixing stage of sulfide solid electrolyte synthesis?
- What is the particle size for XRD analysis? Optimize Your Results with the Right Preparation
- Why is an alumina mortar used for grinding dried Yttrium Oxide precursor materials? Ensure Maximum Purity and Quality
- What is the primary purpose of using grinding tools like agate mortars? Optimize LTO Electrode Performance
- What is a mortar and pestle used for in a lab? A Guide to Precision Grinding and Mixing



















