The service temperature a brazed joint can withstand depends entirely on the filler metal used for the joint. This can range from as low as 400°F (200°C) for some silver-based alloys to well over 1800°F (980°C) for specialized nickel alloys designed for aerospace applications. The strength of any brazed joint degrades significantly as the service temperature rises and approaches the melting point of the filler alloy.
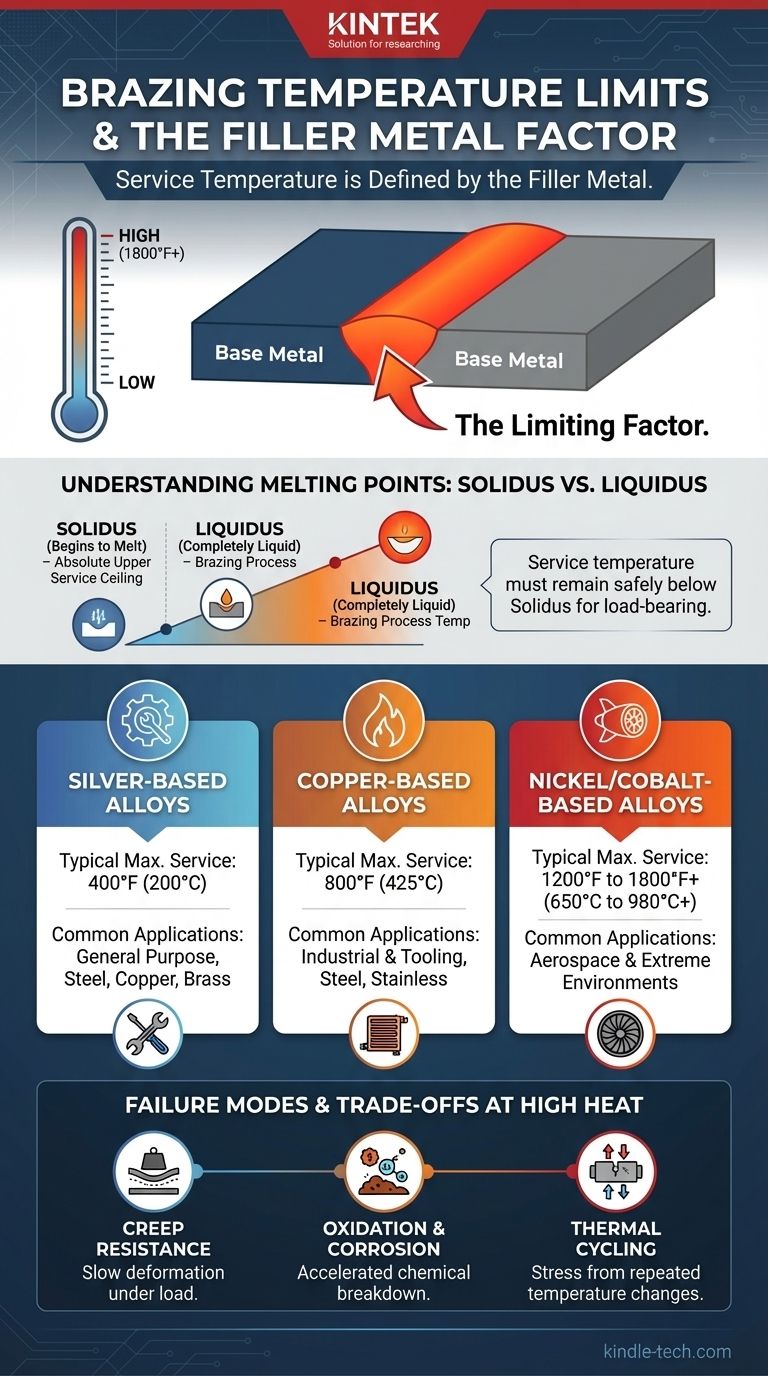
The maximum temperature a brazed joint can handle is fundamentally limited by the solidus temperature (the point where it begins to melt) of the specific filler alloy used. For any load-bearing application, the service temperature must remain safely below this point.

The Filler Metal: The Limiting Factor in High-Temp Brazing
A brazed joint is a composite of two or more base metals joined by a filler metal. To create the joint, the assembly is heated to a temperature high enough to melt the filler metal, but not the base metals. This means the filler is, by design, the component with the lowest melting point.
Why the Filler Governs Temperature Resistance
The filler alloy is the "glue" that holds the base metals together. Because it melts at a much lower temperature than the materials it joins, it will always be the first part of the assembly to soften and lose strength when heated.
The structural integrity of the joint at an elevated temperature is therefore a direct function of the filler metal's properties at that temperature.
Understanding Solidus vs. Liquidus
To properly assess temperature limits, two key terms are critical:
- Solidus: The temperature at which the filler alloy begins to melt. This is the absolute upper ceiling for a joint's service temperature. Even approaching this temperature will cause a drastic reduction in strength.
- Liquidus: The temperature at which the filler alloy is completely liquid. As the provided references note, the brazing process itself must be conducted at a temperature above the liquidus to ensure the alloy flows properly into the joint.
The difference between the solidus and liquidus temperatures is the alloy's "melting range." An alloy with a narrow melting range provides a more predictable transition from solid to liquid.
Common Brazing Alloys and Their Service Limits
The choice of filler metal is a critical engineering decision based on the intended operating environment. Alloys are typically grouped into families with distinct performance characteristics.
Silver-Based Alloys
These are extremely common for general-purpose joining of steel, copper, and brass due to their excellent flow and high strength at room temperature. However, their strength drops off relatively quickly with heat.
Typical Maximum Service Temperature: 400°F (200°C) for continuous service.
Copper-Based Alloys
Primarily used for brazing steel, stainless steel, and tungsten carbide, copper alloys offer good strength at a higher temperature range than silver alloys. They are a cost-effective choice for many industrial applications.
Typical Maximum Service Temperature: 800°F (425°C), with some variability.
Nickel and Cobalt-Based Alloys
These are high-performance alloys designed for the most demanding environments, such as jet engine turbine blades and industrial gas turbines. They offer exceptional strength, creep resistance, and oxidation resistance at extreme temperatures.
Typical Maximum Service Temperature: 1200°F to over 1800°F (650°C to 980°C+).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Failure Modes
Simply choosing an alloy with a high melting point is not enough. High-temperature applications introduce unique challenges that must be considered in the design of the joint.
Creep Resistance
Creep is the tendency of a material to slowly and permanently deform under a constant load, especially at elevated temperatures. A joint that is perfectly strong for short durations may fail over months or years due to creep if the filler alloy is not designed for that specific stress and temperature.
Oxidation and Corrosion
High temperatures dramatically accelerate chemical reactions like oxidation. The filler metal must not only hold the joint together but also resist being corroded or oxidized by its operating environment, which would weaken it over time.
Thermal Cycling
If the component is repeatedly heated and cooled, the differing thermal expansion rates of the base metals and the filler metal can induce stress. This cycling can lead to fatigue cracks and eventual failure of the joint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure reliability, you must match the brazing alloy to the demands of the operating environment.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose joining for room-temperature service: Silver-based alloys offer an excellent combination of strength, ductility, and ease of use.
- If your application involves moderate heat up to 800°F (425°C), such as in heat exchangers or tooling: Copper-based alloys provide a robust and more economical solution than high-performance options.
- If you are designing for extreme environments like aerospace or industrial turbines: You must use a high-performance nickel or cobalt-based alloy specifically engineered for high-temperature strength and creep resistance.
Ultimately, understanding that the filler alloy dictates the joint's thermal limits is the key to designing a safe and reliable brazed assembly.
Summary Table:
| Filler Metal Family | Typical Maximum Continuous Service Temperature | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Silver-Based Alloys | 400°F (200°C) | General-purpose joining of steel, copper, brass |
| Copper-Based Alloys | 800°F (425°C) | Brazing steel, stainless steel, tungsten carbide |
| Nickel/Cobalt-Based Alloys | 1200°F to 1800°F+ (650°C to 980°C+) | Aerospace turbines, industrial gas turbines |
Ensure Your Brazed Joints Withstand the Heat
Choosing the right filler metal is critical for the safety and longevity of your high-temperature assemblies. The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for reliable brazing processes. Whether you're working on general fabrication or cutting-edge aerospace components, we have the solutions to support your material joining challenges.
Let us help you select the perfect materials for your application. Contact our brazing specialists today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Laboratory ITO FTO Conductive Glass Cleaning Flower Basket
- Versatile PTFE Solutions for Semiconductor and Medical Wafer Processing
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of tungsten filament? Key Limitations in Lighting Technology
- What is the suitability of tungsten as an electrical conducting material for heating applications? Master Extreme High-Temperature Heating
- What happens when tungsten is heated? Harnessing Extreme Heat for Demanding Applications
- Why tungsten is not used in heating devices? The Critical Role of Oxidation Resistance
- What is the function of high-temperature metal filaments in HFCVD? Catalyzing Diamond Growth Success










