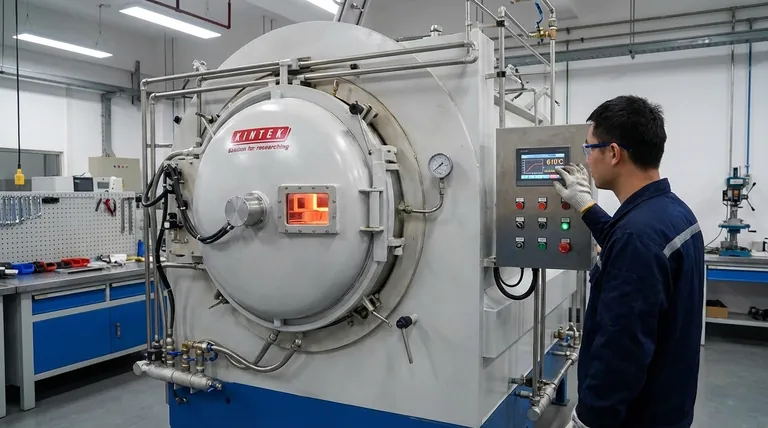
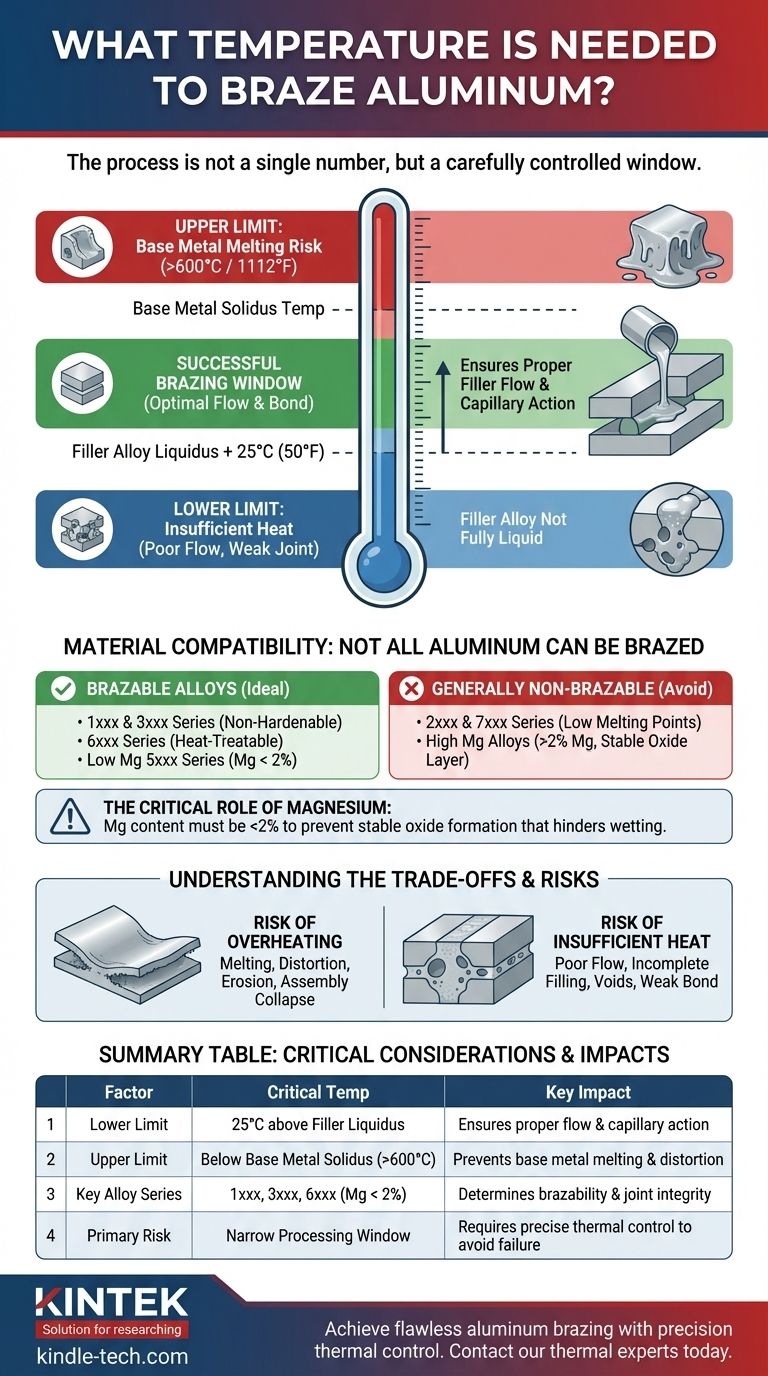
To successfully braze aluminum, the process temperature is not a single number but a carefully controlled window. The temperature must be high enough to melt the filler alloy but low enough to keep the base aluminum solid. Generally, the base aluminum alloy's solidus temperature must be above 600°C (1112°F) to be considered brazable.
The core challenge of aluminum brazing is maintaining a temperature that is slightly above the melting point of your filler material, yet safely below the melting point of the aluminum parts you are joining. This critical temperature window is the key to a strong, successful joint.

The Core Principle: The Brazing Temperature Window
Successful brazing happens within a specific thermal range. Understanding the upper and lower limits of this window, defined by your materials, is essential for process control.
The Lower Limit: Melting the Filler Alloy
The minimum temperature for the process is dictated by the filler metal, also known as the braze alloy.
You must heat the assembly to at least 25°C (50°F) above the liquidus temperature of this filler alloy. The liquidus point is the temperature at which the alloy becomes completely liquid and can flow into the joint via capillary action.
The Upper Limit: Protecting the Base Metal
The maximum allowable temperature is determined by the aluminum parts being joined.
The solidus temperature of the base aluminum—the point at which it begins to melt—must be higher than the brazing temperature. This ensures the structural integrity of the parts is maintained throughout the process.
Material Compatibility: Not All Aluminum Can Be Brazed
The specific alloy of your base metal is the most important factor in determining if brazing is even possible. The key is a sufficiently high melting point and controlled magnesium content.
Brazable Aluminum Alloys
Alloys with a solidus temperature safely above the filler's liquidus point are ideal.
This includes most non-hardenable 1xxx and 3xxx series alloys, as well as heat-treatable 6xxx series alloys. Some 5xxx series alloys are also suitable, but only if their magnesium content is low.
Generally Non-Brazable Alloys
Many common high-strength alloys have melting points that are too low for conventional brazing methods.
This includes most 2xxx and 7xxx series alloys. Their solidus temperatures are often below the liquidus point of standard aluminum filler metals, creating an impossible processing window.
The Critical Role of Magnesium
Magnesium content must be carefully controlled, ideally below 2%.
Higher levels of magnesium form a very stable and tenacious oxide layer on the aluminum surface. This oxide film prevents the filler metal from wetting the surface and flowing into the joint, resulting in a failed bond.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Achieving the correct temperature is a balancing act. Deviating from the ideal window introduces significant risks that can compromise the entire assembly.
The Risk of Overheating
If the temperature is too high or held for too long, you risk melting the base metal.
This can lead to distortion of the parts, erosion at the joint, or even a complete collapse of the assembly. The margin for error can be quite small.
The Risk of Insufficient Heat
If the temperature is too low, the filler alloy will not become fully liquid.
This results in poor flow and incomplete filling of the joint, creating voids and weak spots. The resulting bond will be unreliable and will not meet its designed strength.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right materials and controlling your process temperature are paramount. Your goal determines your material choice.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: Use brazable, heat-treatable alloys like the 6xxx series, which allow for post-braze strengthening.
- If your primary focus is general fabrication or heat exchange: Use common non-hardenable alloys like the 1xxx or 3xxx series, which are known for their excellent brazability.
- If your primary focus is avoiding failure: Always verify the specific alloy designation and confirm its magnesium content is below 2% before attempting to braze.
Ultimately, successful aluminum brazing depends on precise thermal control within the window defined by your specific materials.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Critical Temperature / Consideration | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | 25°C (50°F) above filler alloy liquidus point | Ensures proper filler metal flow and capillary action. |
| Upper Limit | Below base aluminum alloy solidus temperature (>600°C / 1112°F) | Prevents base metal melting and part distortion. |
| Key Alloy Series | 1xxx, 3xxx, 6xxx (with Mg < 2%) | Determines brazability and joint integrity. |
| Primary Risk | Narrow processing window | Requires precise temperature control to avoid failure. |
Achieve flawless aluminum brazing with precision thermal control.
Navigating the narrow temperature window for aluminum brazing is critical for creating strong, reliable joints without damaging your components. The right equipment ensures the precise and uniform heating necessary for success.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and thermal processing solutions designed for demanding applications like aluminum brazing. Our equipment delivers the accuracy and consistency your laboratory needs to avoid the risks of overheating or insufficient heat.
Let us help you optimize your brazing process. Contact our thermal experts today to discuss your specific application requirements and discover the ideal solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory vacuum annealing furnace play in HEA treatment? Ensure Purity and Phase Stability
- How does a vacuum heat treat furnace work? Achieve Pristine, Oxide-Free Metal Parts
- Why are glove boxes or vacuum equipment indispensable for ZrO2-Li2ZrCl6 preparation? Protect Air-Sensitive Materials
- Which factors must be controlled during sintering? Master Temperature, Atmosphere, and Material for Optimal Results
- What temperature is aluminum sintering? Master the 550°C-650°C Window for Strong Parts
- What is the sintering process of stainless steel? Transform Powder into Dense, Strong Components
- What temperature is a heat treatment furnace? The Key to Precise Material Transformation
- What role does a high-temperature experimental furnace play in the carbonization process of Magnetic Composite Carbon?



















