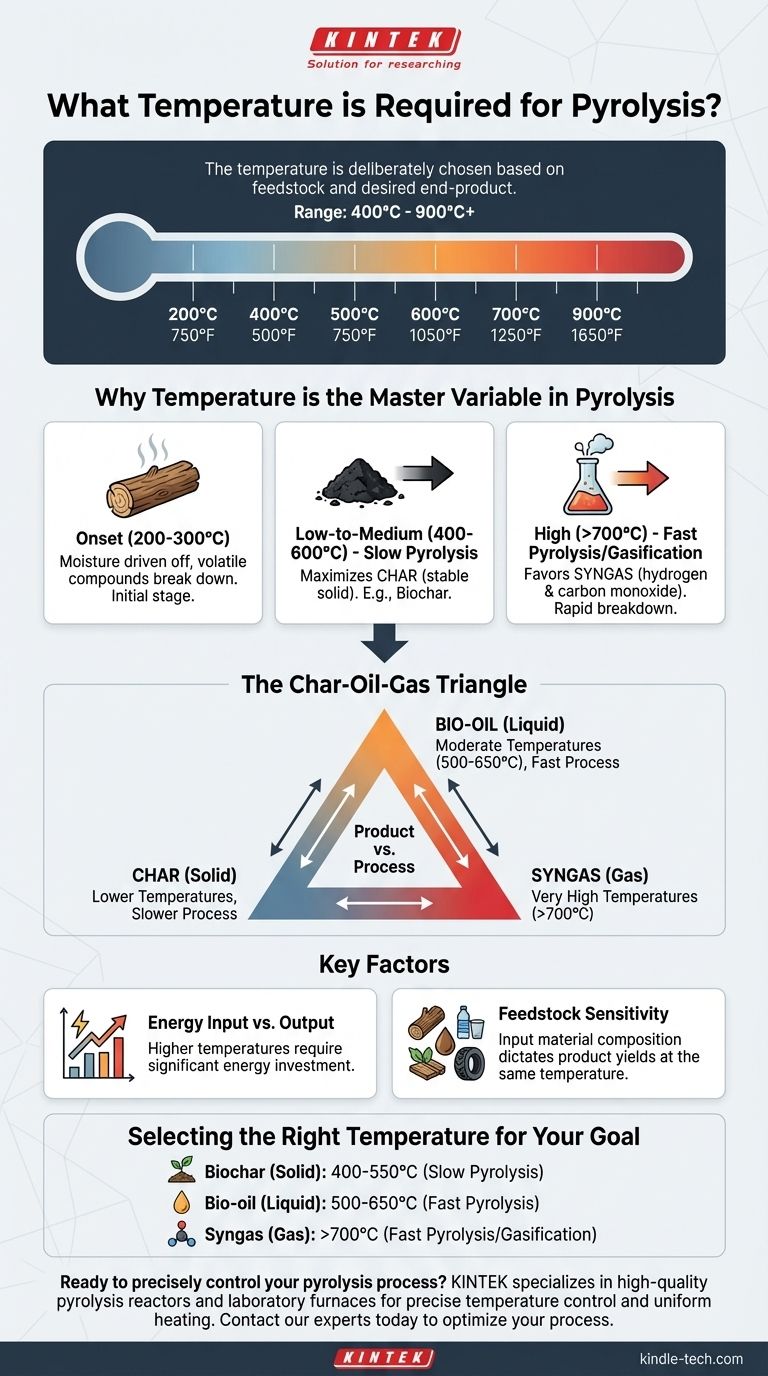
In short, pyrolysis requires a wide range of temperatures. The process typically operates between 400°C and 900°C (750°F to 1650°F), but the specific temperature is deliberately chosen based on the starting material, known as feedstock, and the desired end-product. For some organic materials like wood, the initial stages of decomposition can begin at temperatures as low as 200°C.
The central takeaway is that there is no single temperature for pyrolysis. Instead, temperature is the primary control lever used to determine whether the process yields more solid char, liquid bio-oil, or flammable gas.
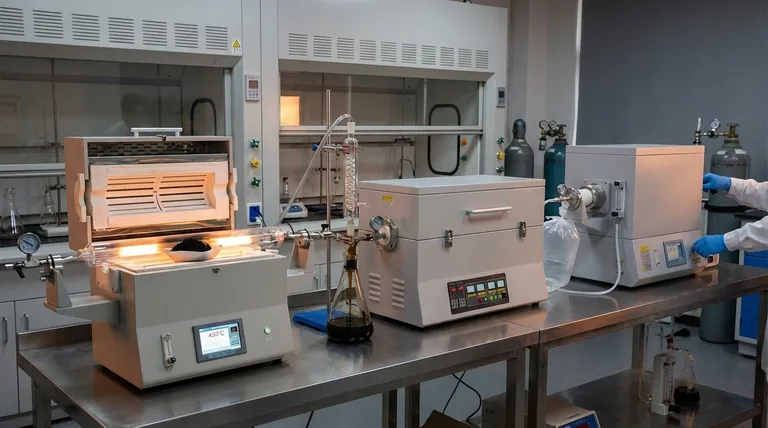

Why Temperature is the Master Variable in Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an oxygen-deprived environment. Temperature directly governs the speed of the reaction and dictates the chemical composition of the final products. Understanding this relationship is key to controlling the outcome.
The Onset of Pyrolysis (200-300°C)
For many types of biomass, like wood, the process begins at relatively low temperatures. In this range, moisture is driven off, and the most volatile organic compounds begin to break down. This initial stage sets the foundation for the more intense reactions to follow.
Low-to-Medium Temperature (400-600°C)
This range is often associated with "slow pyrolysis." The slower heating rates and more moderate temperatures maximize the production of char, a stable, carbon-rich solid. This is the preferred method for creating products like biochar for agricultural use.
High Temperature (600-900°C)
As the temperature increases, the reaction speed accelerates dramatically. This range, particularly above 700°C, favors the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler, gaseous compounds. This "fast pyrolysis" or "gasification" is used to maximize the yield of syngas, a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Product vs. Process
Choosing a temperature is an exercise in balancing competing priorities. The ideal temperature for one goal is often suboptimal for another, creating a fundamental set of trade-offs.
The Char-Oil-Gas Triangle
Think of the products as a triangle. Lower temperatures and slower processes favor the solid corner (char). Fast pyrolysis at moderate temperatures (around 500-650°C) favors the liquid corner (bio-oil). Very high temperatures favor the gas corner (syngas). You can't maximize all three at once.
Energy Input vs. Energy Output
Reaching and maintaining higher temperatures requires a significant energy investment. A high-temperature process designed to produce syngas must yield enough energy value in the gas to justify the high energy cost of running the reactor itself.
Feedstock Sensitivity
The chemical structure of the input material matters. Wood, plastics, tires, and agricultural waste all have different compositions and will break down into different products at the same temperature. The process must be tuned specifically for the feedstock being used.
Selecting the Right Temperature for Your Goal
Your objective determines the correct operational temperature. The process is not one-size-fits-all; it is a precise tool engineered for a specific outcome.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar for soil amendment: Target a slower pyrolysis process in the lower temperature range, typically between 400°C and 550°C, to maximize solid carbon output.
- If your primary focus is generating bio-oil for liquid fuel production: Utilize a fast pyrolysis method in a moderate temperature range, often around 500°C to 650°C, to quickly vaporize and condense the organic matter.
- If your primary focus is creating syngas for fuel or chemical synthesis: Employ a high-temperature process, generally above 700°C, to ensure the complete thermal cracking of materials into simple gas molecules.
Ultimately, temperature is the dial you turn to deliberately transform waste into a valuable resource.
Summary Table:
| Goal / Primary Product | Recommended Temperature Range | Process Type |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar (Solid) | 400°C - 550°C | Slow Pyrolysis |
| Bio-oil (Liquid) | 500°C - 650°C | Fast Pyrolysis |
| Syngas (Gas) | Above 700°C | Fast Pyrolysis / Gasification |
Ready to precisely control your pyrolysis process?
The right lab equipment is essential for achieving your target product yields. KINTEK specializes in high-quality pyrolysis reactors and laboratory furnaces that deliver the precise temperature control and uniform heating required for consistent, reliable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you optimize your pyrolysis process for maximum efficiency and product value.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of tube furnace? Unlock Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What is the role of corundum tubes in oxygen permeation testing? Ensure Integrity for Bi-doped Membranes
- What is the function of a tube furnace? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Processing in a Controlled Atmosphere
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab



















