In short, you use injection molding to mass-produce plastic parts. This manufacturing process is the engine behind a vast number of everyday items, chosen for its ability to create identical, often complex, plastic components at an extremely high speed and low per-unit cost once production is running. It's how we get everything from simple bottle caps and combs to intricate automotive components and toy building blocks.
Injection molding is the definitive solution for manufacturing plastic parts in high volumes with high precision. The decision to use it hinges on a trade-off: a significant upfront investment in tooling in exchange for an exceptionally low cost for each part produced at scale.
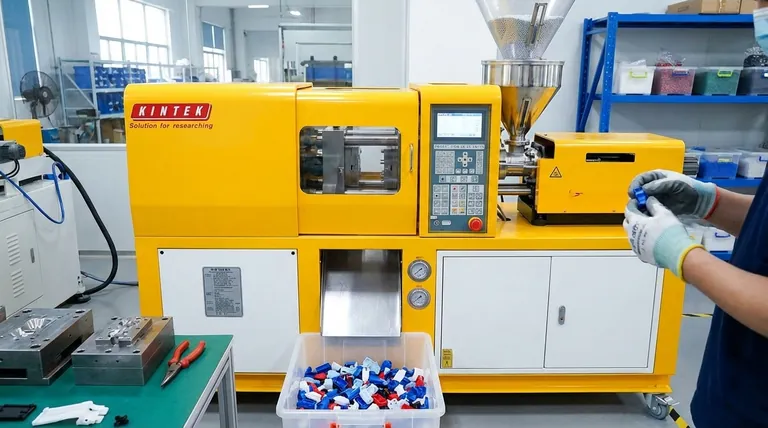

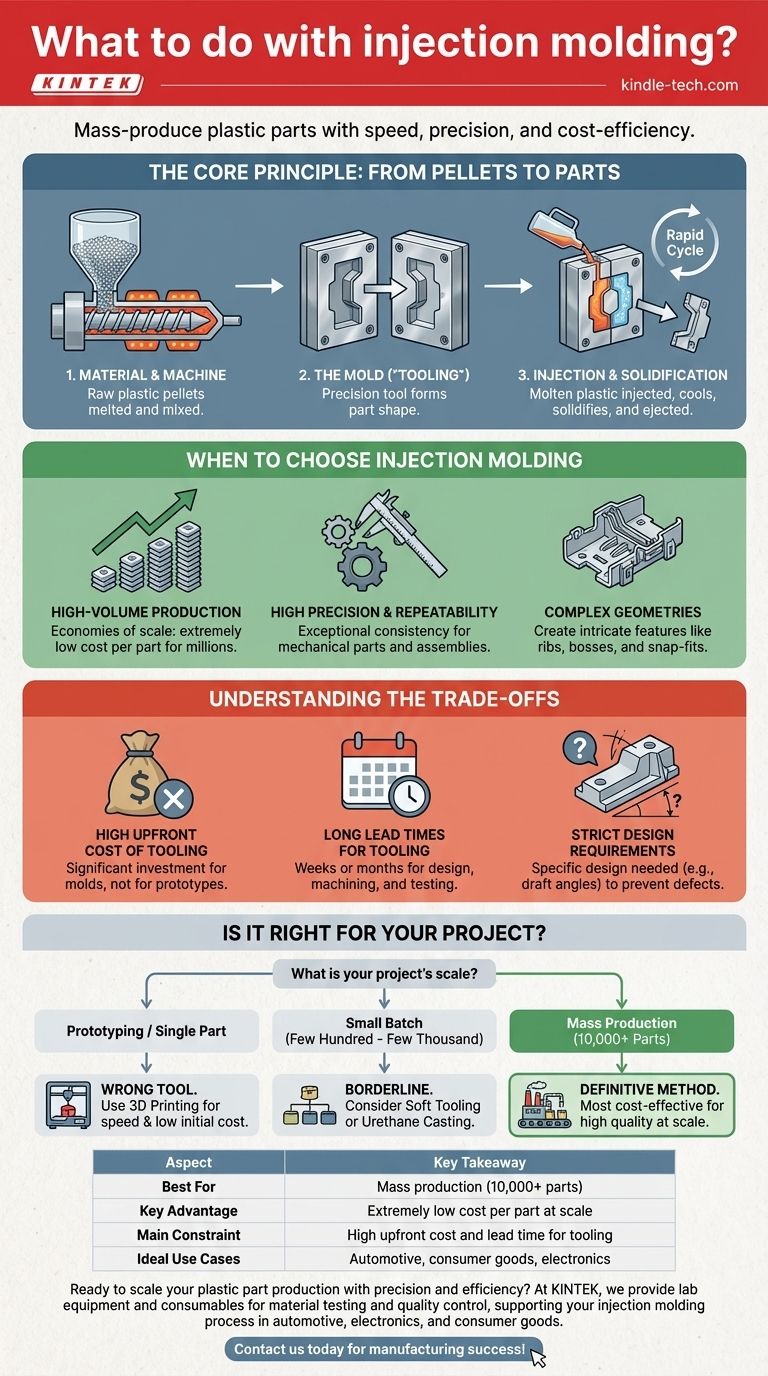
The Core Principle: From Pellets to Parts
Understanding why injection molding is so dominant requires a quick look at how it works. The process is a rapid cycle of melting, injecting, and cooling plastic.
The Material and Machine
It all begins with raw plastic, typically in the form of small pellets. These pellets are fed into a heated barrel, where a screw melts and mixes them into a homogenous molten liquid.
The Mold (The "Tooling")
The heart of the process is the mold, a precision-machined tool usually made from steel. It consists of two halves that clamp together to form a negative space—a "cavity"—in the exact shape of the desired part.
Injection and Solidification
The machine injects the molten plastic under immense pressure into the mold's cavity. The plastic fills the space completely, and after a brief cooling period, it solidifies. The mold then opens, and the finished part is ejected, ready for the cycle to begin again, often in just a matter of seconds.
When to Choose Injection Molding
Injection molding is not a universal solution. It is a specialized tool that excels under specific conditions, making it the clear choice for certain goals.
For High-Volume Production
The process is defined by its economies of scale. While the initial mold is expensive, it can be used to produce hundreds of thousands, or even millions, of parts. This amortizes the upfront cost, making the price per part incredibly low.
For High Precision and Repeatability
Because every part is formed in the same steel mold, injection molding delivers exceptional consistency. This is critical for mechanical parts like gears or components that must fit together perfectly in a larger assembly, such as in automotive or electronic applications.
For Complex Geometries
Molding allows for the creation of intricate features that are difficult or cost-prohibitive to achieve with other methods. Details like reinforcing ribs, mounting bosses for screws, and snap-fit closures can be integrated directly into the part design.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The power of injection molding comes with significant constraints that are crucial to understand before committing to this process.
The High Upfront Cost of Tooling
The primary barrier to entry is the cost of the mold itself. A high-quality production mold is a complex piece of engineering that can cost anywhere from a few thousand to hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on its complexity and size. This makes the process completely unsuitable for one-off prototypes or very small production runs.
Long Lead Times for Tooling
Creating that precision mold is not a fast process. The design, machining, and testing of a new tool can take weeks or even months. This initial time investment must be factored into any project timeline.
Strict Design Requirements
Parts must be designed specifically for injection molding. This involves considerations like maintaining consistent wall thickness to prevent warping, and adding "draft angles" (slight tapers on the walls) so the part can be cleanly ejected from the mold. Failure to follow these design principles can lead to costly defects and production failures.
Is Injection Molding Right for Your Project?
Your choice of manufacturing process must align with your project's scale, budget, and timeline.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or creating a single part: Injection molding is the wrong tool. Use 3D printing for its speed and low initial cost.
- If your primary focus is a small batch (a few hundred to a few thousand parts): This is a borderline case. Consider "soft tooling" (simpler, less durable molds) or alternative processes like urethane casting, as the cost per part for injection molding may still be too high.
- If your primary focus is mass production (over 10,000 parts): Injection molding is the definitive, most cost-effective method for achieving high quality at scale.
By understanding its core strengths and limitations, you can leverage injection molding to turn a concept into millions of identical, high-quality products.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Best For | Mass production (10,000+ parts) |
| Key Advantage | Extremely low cost per part at scale |
| Main Constraint | High upfront cost and lead time for tooling |
| Ideal Use Cases | Automotive components, consumer goods, electronic housings |
Ready to scale your plastic part production with precision and efficiency?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed to support your injection molding process, from material testing to quality control. Whether you're in automotive, electronics, or consumer goods, our solutions help ensure your parts meet the highest standards of consistency and performance.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your manufacturing success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Assemble Square Lab Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Multi-Punch Rotary Tablet Press Mold Ring for Rotating Oval and Square Molds
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
People Also Ask
- What is the manufacturing process of rubber molding? Injection, Compression, or Transfer Molding?
- What is a positive of injection moulding? Achieve High-Volume Production with Unmatched Efficiency
- What is molding technique? A Guide to High-Volume, Complex Part Manufacturing
- What is short capacity of injection Moulding machine? Optimize Your Shot Size for Flawless Parts
- What is the application of injection moulding machine? Powering Mass Production for Complex Parts


















