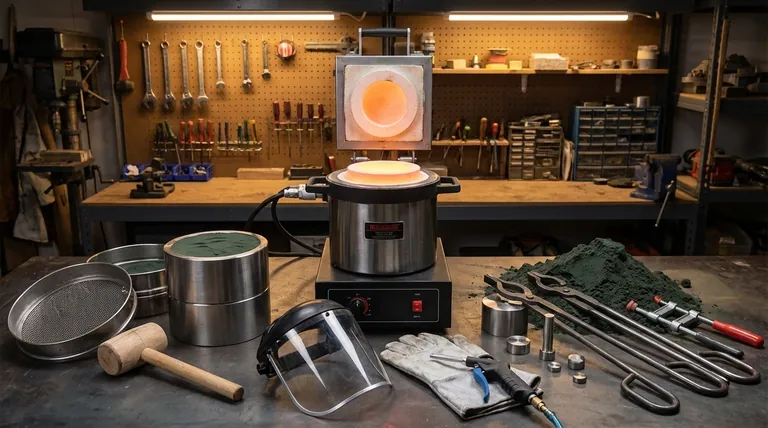
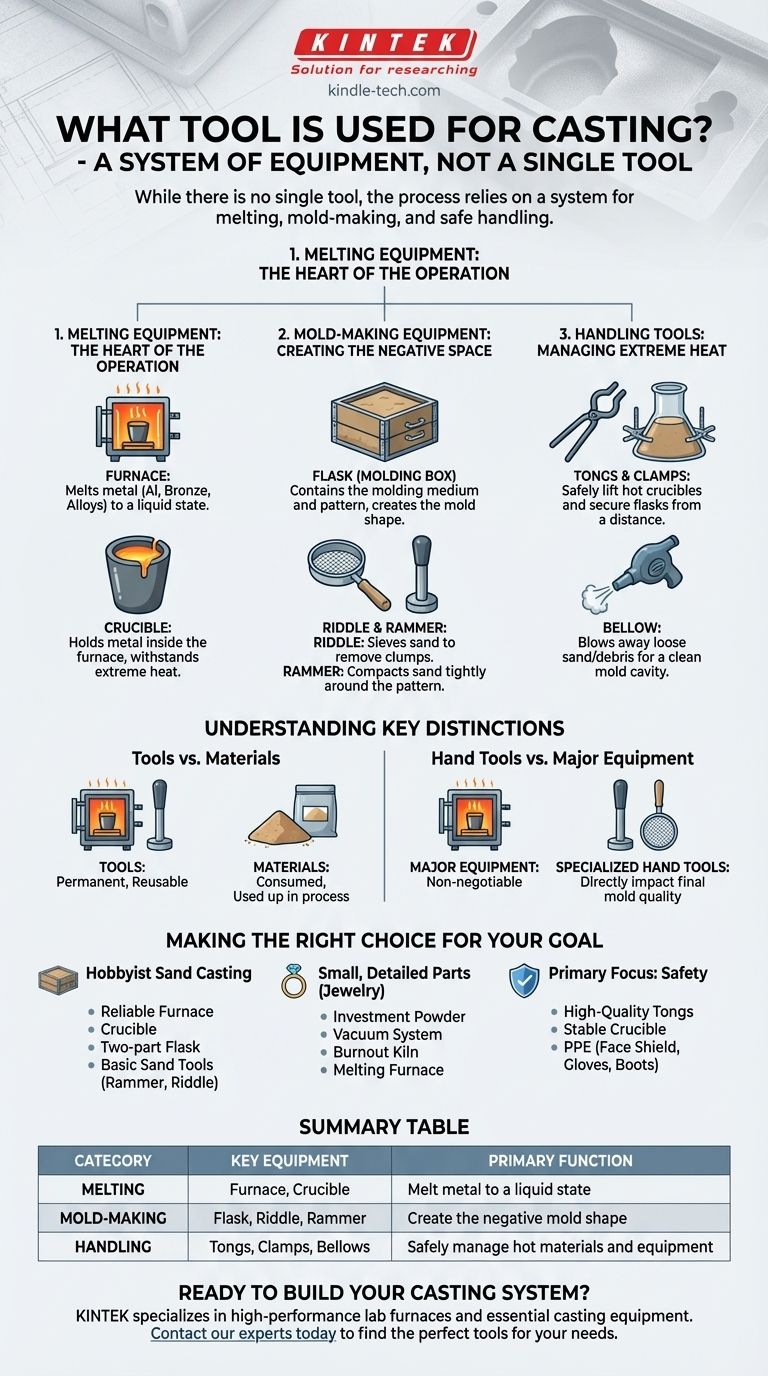
While there is no single tool for casting, the process relies on a system of equipment designed for melting metal, creating a mold, and safely handling the materials. The most critical pieces of equipment are the furnace, which melts the metal, and the flask or molding box, which contains the mold itself. These are supported by various hand tools used to shape and prepare the mold.
The essential tools for casting are not a single item but a collection of components that fall into three main categories: melting equipment (furnace), mold-making equipment (flasks, rammers), and material handling tools (tongs, clamps).

The Core Components of a Casting System
Thinking of casting in terms of a system, rather than a single tool, is the key to understanding the process. Each category of equipment performs a distinct and necessary function.
Melting Equipment: The Heart of the Operation
The primary task in casting is to transform solid metal into a liquid state. This is accomplished with specialized high-temperature equipment.
The furnace is the most important piece of equipment. Its sole purpose is to generate enough heat to melt your chosen metal, whether it's aluminum, bronze, or another alloy.
A crucible is a ceramic or graphite container that holds the metal inside the furnace. It is designed to withstand extreme thermal shock and remain stable at high temperatures.
Mold-Making Equipment: Creating the Negative Space
Before you can pour metal, you must first create a negative space—the mold—that will give the final object its shape.
A flask, often referred to as a molding box, is a frame (typically two-part) that holds the molding medium, most commonly sand. It contains the pattern and the packed sand securely during the pouring process.
Hand tools are used to work the molding medium. A riddle is a specialized sieve used to remove clumps from the sand, while a rammer is used to compact the sand tightly around the pattern.
Other tools like vent wires are pushed through the packed sand to create small channels. These vents allow hot gases to escape when the molten metal is poured, preventing defects in the final casting.
Handling Tools: Managing Extreme Heat
Working with molten metal is inherently dangerous. Specialized tools are required to handle the hot equipment safely and effectively.
Tongs and clamps are essential for lifting the hot crucible out of the furnace and for securely holding the flask together during the pour. These tools provide a safe distance and a secure grip.
A bellow or air blower can be used to blow away loose sand or debris from the mold cavity before it is closed, ensuring a cleaner final product.
Understanding Key Distinctions
For someone new to the process, it's easy to confuse the different types of items used in casting. Clarifying these roles is crucial.
Tools vs. Materials
It is important to distinguish between reusable tools and consumable materials. A furnace, flask, and rammer are permanent tools.
In contrast, investment powder or casting sand are materials that are consumed or used up as part of the mold-making process itself.
Hand Tools vs. Major Equipment
While a furnace is a non-negotiable piece of major equipment, the importance of specific hand tools can vary. A mallet or clamps are fundamental workshop tools.
However, specialized tools like a rammer or riddle are designed specifically for the sand casting process and directly impact the quality of the final mold.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific casting project will determine which tools are most critical for you to acquire first.
- If your primary focus is hobbyist sand casting: Begin with a reliable furnace, a crucible, a two-part flask, and basic sand-working tools like a rammer and riddle.
- If your primary focus is small, detailed parts (like jewelry): You will need tools for investment casting, which centers on investment powder, a vacuum system, and a burnout kiln in addition to a melting furnace.
- If your primary focus is safety: Your first purchases should always be high-quality tongs, a stable crucible, and proper personal protective equipment (PPE), including a face shield, heat-resistant gloves, and appropriate boots.
Understanding the role of each tool transforms casting from a list of equipment into a manageable, systematic process.
Summary Table:
| Category | Key Equipment | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Melting | Furnace, Crucible | Melt metal to a liquid state |
| Mold-Making | Flask, Riddle, Rammer | Create the negative mold shape |
| Handling | Tongs, Clamps, Bellows | Safely manage hot materials and equipment |
Ready to build your casting system? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and essential equipment for metal casting. Whether you're a hobbyist or a professional, our reliable tools ensure precise melting and safe operation. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace and casting equipment for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- What are the specific functions of graphite molds in the vacuum hot-press sintering process? Expert Insights for Ceramics
- What role does a high-purity graphite mold play during hot pressing? Optimize Boron Carbide Sintering at 1850°C
- What role do high-strength graphite molds play during vacuum hot pressing? Enhance Precision in CuAlMn Composites
- What technical requirements must specialized pressure-bearing molds meet? Optimize Sulfide Electrolyte Densification














