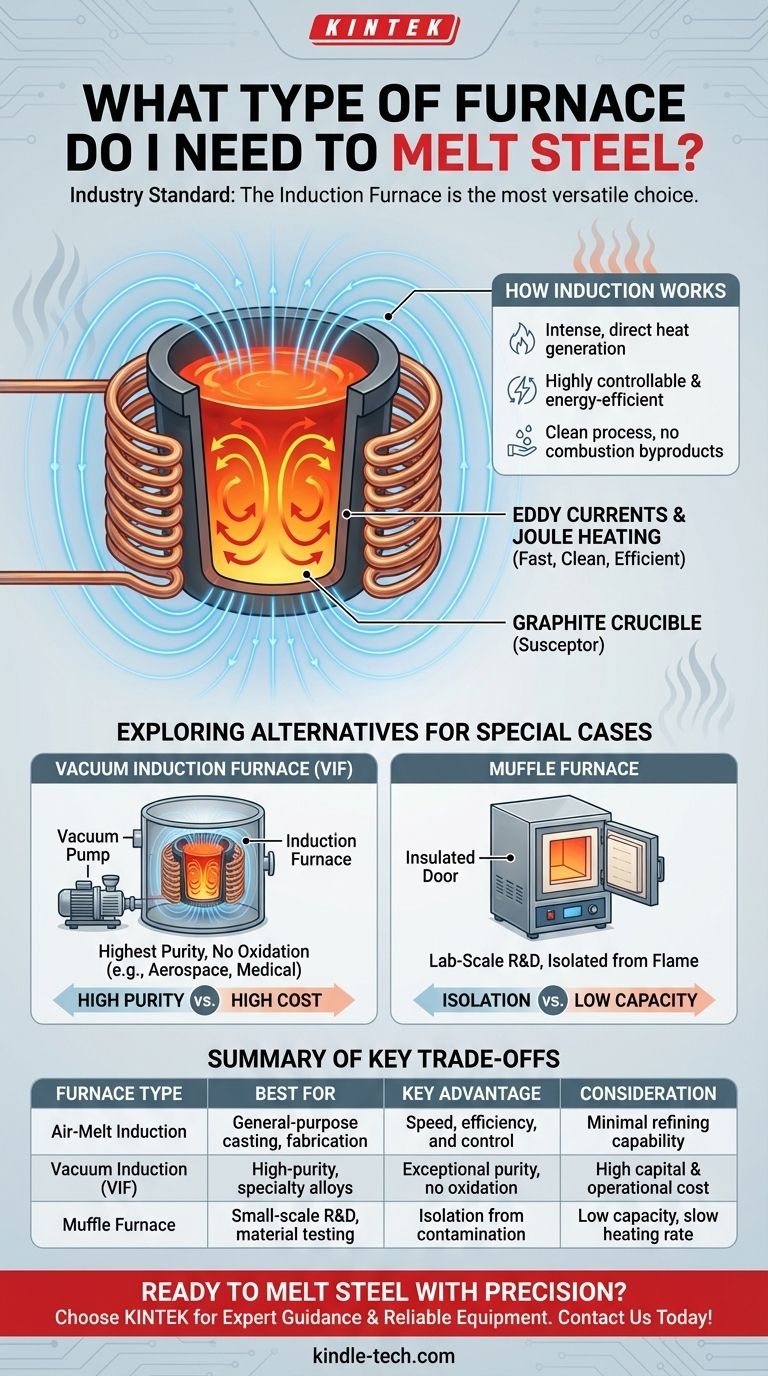
For melting steel, the industry standard and most versatile option is an induction furnace. This type of furnace does not use flames or external heating elements. Instead, it uses powerful, high-frequency magnetic fields to generate intense heat directly within the steel itself or within a conductive crucible, resulting in a fast, clean, and highly efficient melt.
While several furnace types can reach the necessary temperatures, the core decision is not just about heat. The choice hinges on a trade-off between melt purity, operational scale, and cost, with induction furnaces offering the best balance for the widest range of steel melting applications.
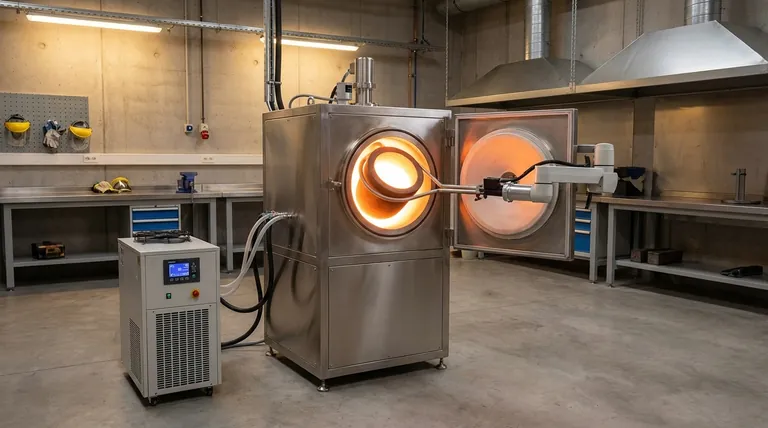

How an Induction Furnace Works for Steel
An induction furnace operates on a principle that is both elegant and powerful. It is fundamentally different from a traditional fuel-burning or resistance furnace.
The Principle of Electromagnetic Induction
The furnace uses a coil of copper tubing, through which a powerful alternating current is passed. This creates a rapidly changing magnetic field around and within the coil.
When a conductive material like steel or a graphite crucible is placed inside this field, the magnetic field induces powerful electrical currents within it, known as eddy currents.
Due to the material's natural electrical resistance, these swirling currents generate immense heat. This process, called Joule heating, melts the metal from the inside out.
The Role of the Crucible
For melting steel, the metal is held in a container called a crucible. This crucible is often made of graphite.
Graphite is an ideal material because it is a susceptor—it readily absorbs the electromagnetic energy and converts it into heat, which is then transferred to the steel. This ensures a uniform and controlled melt.
Why This Method is Ideal for Steel
Induction heating is highly controllable and energy-efficient. Because the heat is generated directly within the charge material, very little energy is wasted.
This method is also very clean, as there are no byproducts of combustion to contaminate the metal. This is critical for maintaining the specific properties of steel alloys.
Exploring Other Furnaces for Special Cases
While standard induction furnaces are the workhorse, specialized applications may demand different technology. These are often variations of induction or are used for very specific, non-production goals.
Vacuum Induction Furnaces
For the highest purity applications, such as aerospace or medical-grade steel, a Vacuum Induction Furnace (VIF) is used. This is an induction furnace housed inside a chamber from which all air is removed.
Melting in a vacuum prevents the liquid steel from reacting with oxygen and other gases, eliminating impurities and allowing for the creation of extremely clean, high-performance alloys.
Muffle Furnaces
A muffle furnace is typically used for lab-scale applications, not bulk steel production. It works by heating a chamber (the "muffle") externally.
The key benefit is that the material inside is completely isolated from any flame or heating element, preventing direct contamination. However, its heating rate and capacity are far too low for most practical steel melting tasks.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace is an exercise in balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" furnace, only the best one for a specific goal.
Purity vs. Cost
A standard air-melt induction furnace is cost-effective and efficient for most commercial and industrial steel.
A vacuum induction furnace produces exceptionally pure metal but comes at a significantly higher capital and operational cost due to the complexity of the vacuum system.
Efficiency vs. Refining
Induction furnaces are supremely efficient at melting, but they offer minimal refining capability. The composition of the metal you put in is largely what you get out.
Other industrial methods, like an Electric Arc Furnace (not covered in the references but relevant for context), are less controlled but can be used to refine steel by burning out impurities like carbon.
Scale vs. Complexity
Induction furnaces are highly scalable. Small, benchtop units are available for hobbyists and labs, while massive multi-ton furnaces are used in industrial foundries.
As the scale increases, so does the complexity. Large systems require sophisticated power supplies, water cooling circuits, and often robotic systems for loading and pouring.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Goal
Your choice should be directly informed by the intended outcome of your melting process.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose steel casting or fabrication: An air-melt induction furnace provides the best combination of speed, efficiency, and control.
- If your primary focus is creating high-purity or specialty steel alloys: A vacuum induction furnace is the required tool to control the melt atmosphere and eliminate gaseous impurities.
- If your primary focus is small-scale R&D or material testing: A small benchtop induction furnace or a high-temperature muffle furnace offers the precise control needed for small samples.
Understanding these core technologies empowers you to invest in the right tool for the job, ensuring both efficiency and quality in your work.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Best For | Key Advantage | Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air-Melt Induction | General-purpose casting, fabrication | Speed, efficiency, and control | Minimal refining capability |
| Vacuum Induction (VIF) | High-purity, specialty alloys (aerospace, medical) | Exceptional purity, no oxidation | High capital and operational cost |
| Muffle Furnace | Small-scale R&D, material testing | Isolation from contamination | Low capacity, slow heating rate |
Ready to Melt Steel with Precision and Efficiency?
Choosing the right furnace is critical to your project's success. Whether you're in R&D, producing specialty alloys, or running a fabrication shop, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your needs.
Why choose KINTEK for your lab equipment?
- Expert Guidance: Our specialists will help you select the perfect induction or vacuum furnace tailored to your specific steel melting requirements.
- Proven Reliability: From benchtop units to industrial-scale systems, our furnaces are built for durability and precise performance.
- Full Support: We provide comprehensive service, from installation to maintenance, ensuring your operations run smoothly.
Don't leave your melting results to chance. Contact us today for a consultation and let KINTEK empower your laboratory with the right technology. Get in touch via our Contact Form to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys



















