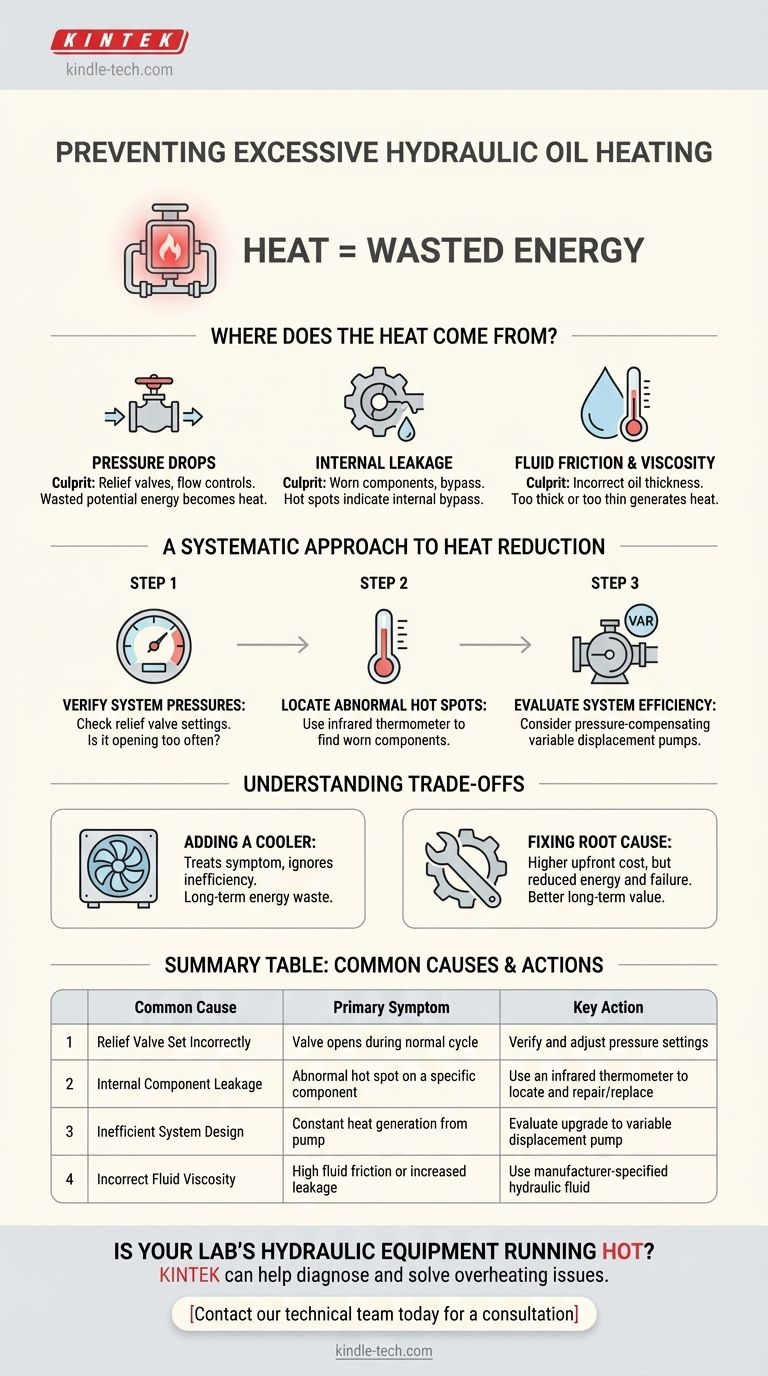
To prevent excessive heating of hydraulic oil, you must either reduce the system's heat load or increase its capacity for heat dissipation. The most effective strategy is to identify and correct the sources of inefficiency causing the heat, such as unnecessary pressure drops or internal component leakage, before simply adding a larger cooling system.
The core principle to understand is that heat in a hydraulic system is a direct symptom of wasted energy. Every component that creates a pressure drop without performing useful work is essentially a small electric heater, converting hydraulic power into thermal energy. Your primary goal is to find and minimize these sources of waste.

Where Does the Heat Come From?
Understanding the origin of heat is the first step in controlling it. Heat is generated anytime hydraulic fluid flows from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure without producing mechanical work.
The Impact of Pressure Drops
A pressure drop is the single largest source of heat in most hydraulic systems. This occurs when fluid is forced through a restriction.
The most common culprit is a relief valve. When a fixed-displacement pump moves more fluid than the system requires, the excess is sent over the relief valve, converting all of its potential energy directly into heat.
Other components like flow controls, proportional valves, and even undersized hoses or fittings also create pressure drops and subsequent heat.
The Effect of Internal Leakage
As components wear, their internal seals and tolerances degrade. This allows high-pressure fluid to leak past its intended path and return directly to a low-pressure reservoir.
This internal bypass or "slippage" in pumps, motors, and cylinders does no useful work. It is a major source of heat, especially in older, high-hour equipment. An unusually hot component is often a clear sign of significant internal leakage.
Fluid Friction and Viscosity
The viscosity of the hydraulic fluid itself plays a role. If the oil is too thick (high viscosity) for the operating temperature, it increases fluid friction within pipes and components, generating heat.
Conversely, if the oil is too thin (low viscosity), it can increase internal leakage in components, which also generates heat. Using the manufacturer-specified fluid is critical.
A Systematic Approach to Heat Reduction
Instead of immediately assuming the cooler is too small, a systematic diagnosis will often reveal an underlying issue that is cheaper and more effective to fix.
Step 1: Verify System Pressures
Check the settings on your relief valves. Are they set higher than the manufacturer's specification? A valve set too high can cause unnecessary heat generation across the entire system.
Also, determine if the relief valve is opening during a normal machine cycle. If it is, the system is inefficiently dumping energy as heat.
Step 2: Locate Abnormal Hot Spots
Use a non-contact infrared thermometer to scan system components immediately after operation.
A component that is significantly hotter than the surrounding lines—like a specific valve, cylinder, or pump—is a strong indicator of excessive internal leakage that needs to be addressed.
Step 3: Evaluate Overall System Efficiency
Consider the system's design. A simple system using a fixed-displacement pump with a relief valve is inherently inefficient if the actuator is often idle or requires variable flow.
Upgrading to a pressure-compensating or load-sensing variable displacement pump can dramatically reduce heat generation by only producing the flow and pressure the system actually needs.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Solving a heat problem involves balancing cost, complexity, and performance. There is no single "best" solution for every application.
Adding a Cooler vs. Fixing the Root Cause
Installing a larger heat exchanger is often seen as a quick fix. It treats the symptom (excess heat) but ignores the disease (system inefficiency).
This approach may solve the overheating problem, but the underlying inefficiency continues to waste energy, increasing operational costs over the life of the machine.
Cost vs. Efficiency in Design
A highly efficient hydraulic circuit, such as one using a load-sensing pump and proportional valves, has a higher upfront cost.
However, the long-term savings from reduced energy consumption and the elimination of heat-related component failures often justify the initial investment, especially in continuous-duty applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your strategy should be guided by your specific operational needs and constraints.
- If your primary focus is immediate troubleshooting: Use an infrared thermometer to find hot spots and a pressure gauge to verify relief valve settings, as these are the most common and easily fixable issues.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: Focus on fixing the root cause of the heat by repairing or replacing worn components that show signs of internal leakage.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Analyze the fundamental system design to see if a more efficient pump or control method can be implemented to stop generating the heat in the first place.
Ultimately, viewing excess heat as a measurable indicator of wasted power is the key to building a more reliable and cost-effective hydraulic system.
Summary Table:
| Common Cause of Heat | Primary Symptom | Key Action |
|---|---|---|
| Relief Valve Set Incorrectly | Valve opens during normal cycle | Verify and adjust pressure settings |
| Internal Component Leakage | Abnormal hot spot on a specific component | Use an infrared thermometer to locate and repair/replace |
| Inefficient System Design | Constant heat generation from pump | Evaluate upgrade to variable displacement pump |
| Incorrect Fluid Viscosity | High fluid friction or increased leakage | Use manufacturer-specified hydraulic fluid |
Is your lab's hydraulic equipment running hot and inefficiently?
Excessive heat is a sign of wasted energy and can lead to premature equipment failure. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you diagnose the root cause of overheating in your hydraulic systems—whether it's a worn component or an inefficient design—and provide the right solutions to enhance reliability and reduce operational costs.
Boost your lab's efficiency and protect your investment. Contact our technical team today for a consultation to discuss your specific hydraulic system challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the lifespan of a filter media? Understand the 3 Types for Optimal Filtration
- What is the number one cause of failure in hydraulic systems? The Silent Killer of Your Equipment
- What happens if a hydraulic system leaks? Prevent Costly Damage and Safety Hazards
- What are the preventive maintenance of hydraulic systems? Extend Equipment Life and Maximize Uptime
- What is a major cause of hydraulic system and component failures? Prevent Costly Downtime with Clean Fluid












