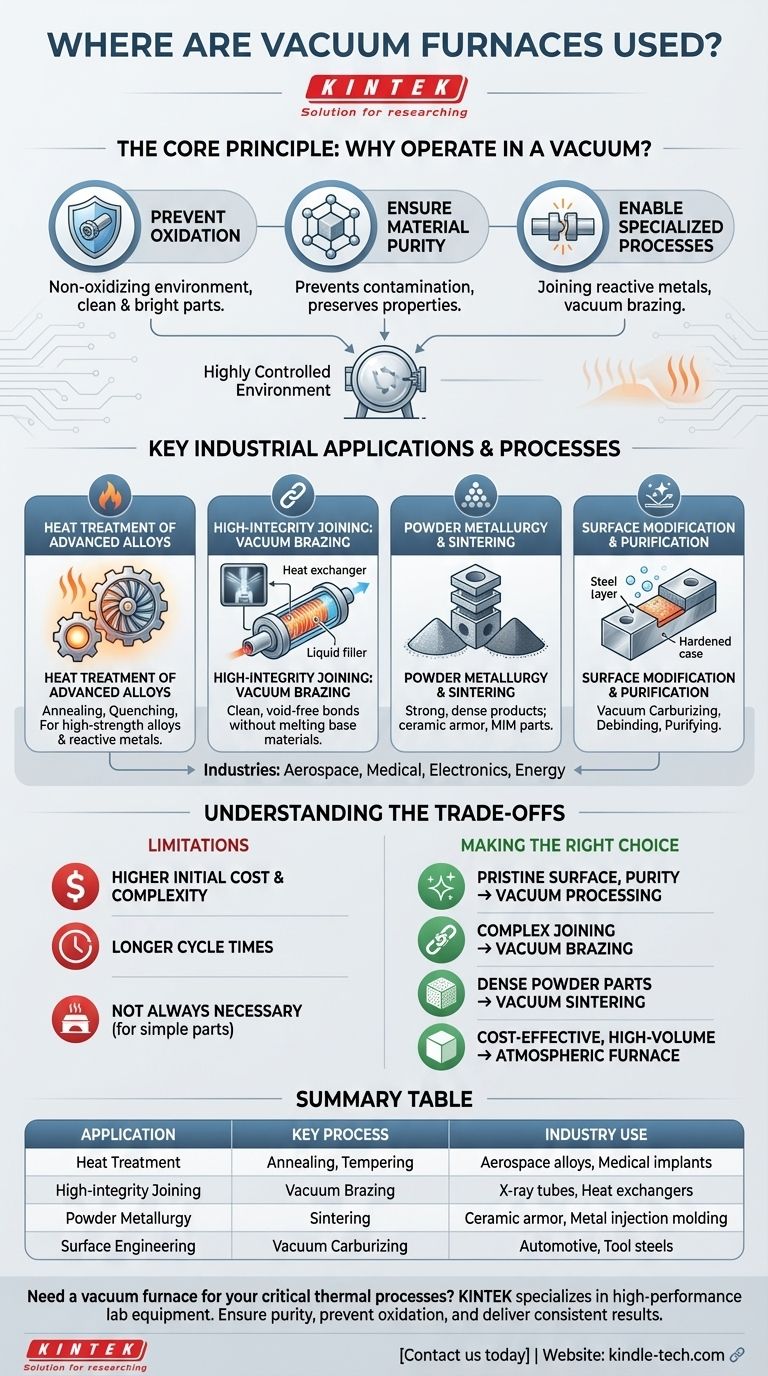
At their core, vacuum furnaces are used for high-temperature thermal processes where controlling the atmosphere is critical to the final product's quality. They are essential in industries like medical, aerospace, electronics, and energy for applications such as the heat treatment of advanced alloys, high-purity brazing, and the sintering of powdered metals and ceramics. The primary function is to protect materials from the negative effects of reactive gases present in the air.
The crucial takeaway is that a vacuum furnace is not just a heater; it is a highly controlled environment. Its use is dictated by the need to prevent chemical reactions—primarily oxidation—that would compromise a material's structural integrity, surface finish, or performance at elevated temperatures.

The Core Principle: Why Operate in a Vacuum?
Heating a material makes it more chemically reactive. When done in a normal atmosphere, elements like oxygen and water vapor can aggressively attack the workpiece, leading to undesirable outcomes. A vacuum furnace solves this by removing the atmosphere before applying heat.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
At high temperatures, oxygen readily bonds with most metals, forming a layer of oxide on the surface. This can lead to discoloration, scaling, and a compromised surface finish.
By removing the air, a vacuum furnace creates a non-oxidizing environment, resulting in clean, bright parts that often require no secondary cleaning.
Ensuring Material Purity and Integrity
For high-performance alloys used in aerospace or medical implants, even minor contamination can drastically alter their metallurgical properties.
A vacuum ensures that no unwanted elements from the atmosphere can diffuse into the material, preserving its intended strength, ductility, and fatigue resistance.
Enabling Specialized Processes
Certain advanced processes are only possible in a vacuum. For example, joining reactive metals or achieving a perfect bond in vacuum brazing requires an environment free of oxides that would otherwise inhibit the process.
Key Industrial Applications and Processes
The principle of atmospheric control makes vacuum furnaces indispensable for a wide range of critical manufacturing and research tasks.
Heat Treatment of Advanced Alloys
This includes processes like annealing, quenching, tempering, and solution heat treating.
While these can be done in air for common steels, a vacuum is necessary for high-strength steel alloys, superalloys, and reactive metals (like titanium) to achieve precise properties without surface degradation.
High-Integrity Joining: Vacuum Brazing
Brazing uses a filler metal to join two components without melting them. In a vacuum, the surfaces to be joined remain perfectly clean and oxide-free.
This allows the filler metal to flow evenly and create a strong, void-free bond, which is essential for manufacturing components like X-ray tubes, medical implants, and microchannel heat exchangers.
Powder Metallurgy and Sintering
Sintering is the process of heating compacted powders (metal or ceramic) to bond the particles together, forming a solid object.
A vacuum prevents contamination between the fine particles and ensures a strong, dense final product. This is critical for producing ceramic ballistic armor, cermets, and complex parts via metal injection molding (MIM).
Surface Modification and Purification
Processes like vacuum carburizing (low-pressure carburizing) are used to harden the surface of steel parts. The vacuum allows for precise control of the carbon-rich atmosphere, leading to uniform case depth and superior part quality.
They are also used for debinding, a process to remove binder materials from "green" parts before sintering, and for purifying high-temperature materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum furnaces are not the solution for every thermal processing need. Understanding their limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Initial Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces, with their vacuum pumps, sealed chambers, and sophisticated control systems, represent a significantly higher capital investment than traditional atmospheric furnaces. They also require more specialized knowledge to operate and maintain.
Longer Cycle Times
The process of pumping the chamber down to the required vacuum level before heating and backfilling it with an inert gas before cooling adds time to each cycle. For high-volume production of simple parts, this can be a bottleneck.
Not Always Necessary
For many general-purpose heat treatments on low-carbon steels where a slight surface oxide layer is acceptable (or will be removed by subsequent machining), a simpler and more cost-effective atmospheric furnace is often the more practical choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace hinges entirely on the required quality and properties of the final component.
- If your primary focus is a pristine surface finish and absolute material purity: Vacuum processing is essential to prevent oxidation and ensure a bright, clean final part.
- If your primary focus is joining complex, high-performance components: Vacuum brazing provides the cleanest, strongest, and most reliable joints possible, especially for sensitive or reactive materials.
- If your primary focus is creating dense parts from powdered metals or advanced ceramics: Vacuum sintering is non-negotiable to prevent contamination and achieve the desired final properties.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume heat treatment of non-critical parts: A traditional atmospheric furnace is likely the more economical and efficient solution.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum furnace is a strategic decision to invest in environmental control for applications where nothing less than perfect material integrity will suffice.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Process | Industry Use |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, Tempering | Aerospace alloys, Medical implants |
| High-Integrity Joining | Vacuum Brazing | X-ray tubes, Heat exchangers |
| Powder Metallurgy | Sintering | Ceramic armor, Metal injection molding |
| Surface Engineering | Vacuum Carburizing | Automotive, Tool steels |
Need a vacuum furnace for your critical thermal processes? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum furnaces designed for precision heat treatment, brazing, and sintering. Our solutions ensure material purity, prevent oxidation, and deliver consistent results for industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics. Contact us today to discuss how we can meet your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can I vacuum the inside of my furnace? A Guide to Safe DIY Cleaning vs. Professional Service
- What are the advantages of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Precision and Cleanliness for Critical Components
- How does argon and nitrogen cooling compare in vacuum furnaces? A Guide to Faster, Cheaper Quenching
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment



















