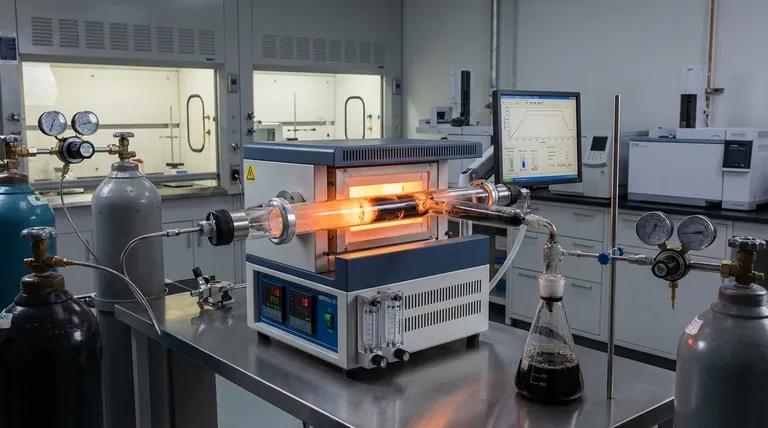
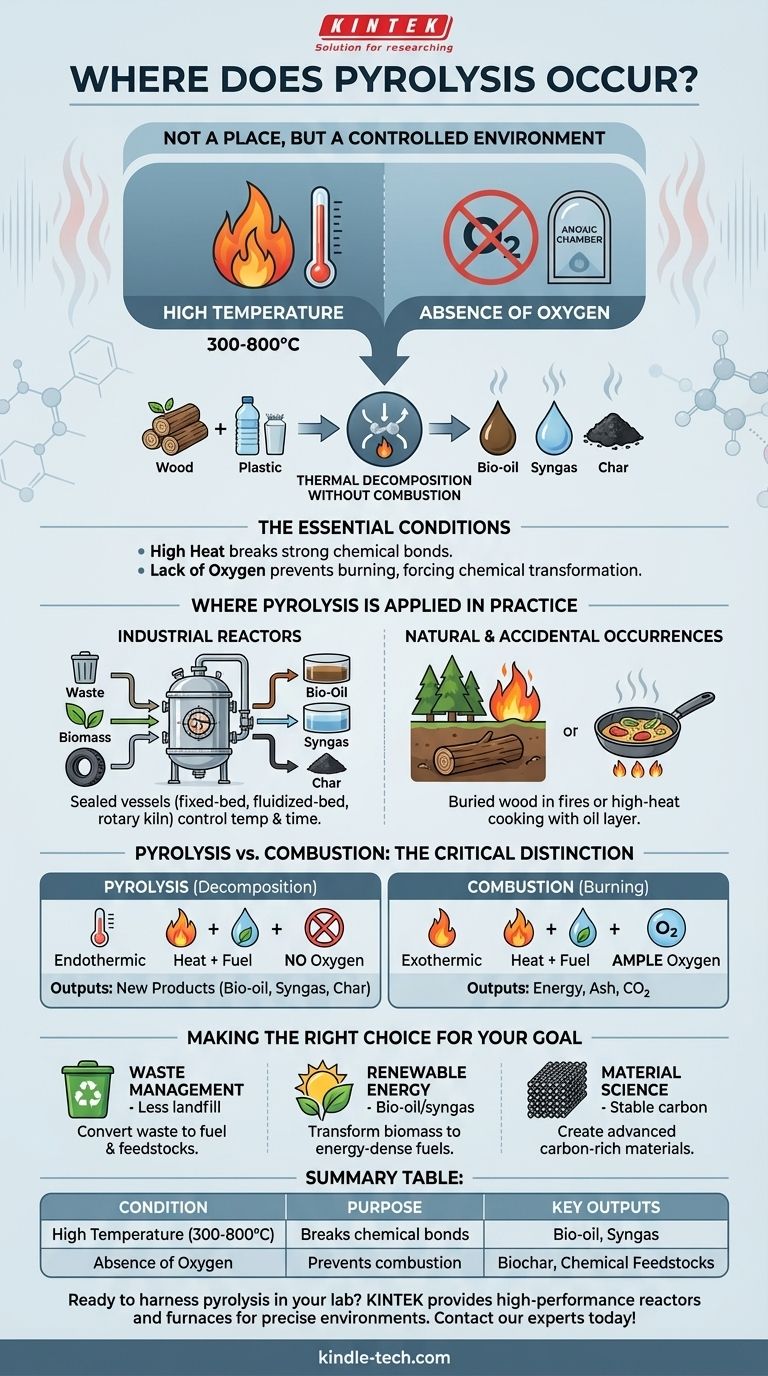
In short, pyrolysis does not occur in a specific geographical place, but rather within a specific, controlled environment. The process happens wherever a material, such as wood or plastic, is subjected to high temperatures in the absence or near-absence of oxygen. This lack of oxygen is the critical factor that prevents the material from burning (combusting) and instead causes it to chemically decompose.
The core principle to understand is that pyrolysis is thermal decomposition without combustion. It's not about where it happens, but under what conditions: high heat forces complex materials to break down, while the lack of oxygen ensures they transform into new substances (char, oil, gas) instead of simply turning to ash.

The Essential Conditions for Pyrolysis
To fully grasp where pyrolysis occurs, you must understand the two non-negotiable conditions that define the process. These two factors work together to transform matter rather than simply destroy it.
The Role of High Temperature
Pyrolysis is fundamentally a thermal process. Sufficient heat—typically ranging from 300°C to over 800°C (570°F to 1470°F)—provides the energy needed to break the strong chemical bonds holding large, complex molecules together.
This is why the process is called "pyro" (fire) "lysis" (separation). The heat literally shakes the molecules apart into smaller, often more valuable, components.
The Critical Absence of Oxygen
This is the single most important condition. In the presence of oxygen, high heat causes combustion (burning), an oxidation reaction that releases energy and produces carbon dioxide, water, and ash.
By removing oxygen, you create an anoxic environment. This starves the fire of the fuel it needs to burn, forcing the thermal energy to do something else: break the material down into a solid residue (char), a liquid condensate (bio-oil or pyrolysis oil), and various gases (syngas).
Where Pyrolysis is Applied in Practice
While the conditions are chemical, the locations are typically highly engineered systems designed to maintain those conditions precisely.
Industrial Pyrolysis Reactors
The vast majority of controlled pyrolysis takes place inside specialized equipment called a pyrolysis reactor. These are sealed, industrial vessels designed to heat materials safely without allowing oxygen to enter.
Engineers use various designs, such as fixed-bed, fluidized-bed, and rotary kiln reactors, to control temperature and processing time for different feedstocks like plastic waste, biomass, or old tires.
Natural and Accidental Occurrences
Pyrolysis also occurs in nature, though less commonly. During a forest fire, a log buried under soil or a dense pile of other logs can be heated intensely while being deprived of oxygen, causing it to turn into natural charcoal.
Similarly, when food is cooked at a very high temperature in a pan with a thin layer of oil, the side touching the hot pan can pyrolyze, creating the blackened, "charred" crust that is chemically distinct from burnt ash.
Understanding the Key Distinction: Pyrolysis vs. Combustion
Confusing these two processes is the most common pitfall. Understanding their difference is essential to understanding the value of pyrolysis.
Combustion (Burning)
Combustion is an exothermic oxidation reaction. It requires heat, fuel, and ample oxygen. Its purpose is to release the maximum amount of thermal energy from a material, leaving behind simple inorganic byproducts like ash.
Pyrolysis (Decomposition)
Pyrolysis is an endothermic decomposition reaction. It requires heat and fuel but a near-total absence of oxygen. Its purpose is not to release energy, but to transform the chemical structure of a material into new, often valuable products.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying this understanding depends on your objective, whether it's related to energy, waste, or materials.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Pyrolysis is a method for converting low-value waste (like mixed plastics) into higher-value commodities like fuel oil and chemical feedstocks, reducing landfill volume.
- If your primary focus is renewable energy: The process is used to transform biomass (like wood or agricultural residue) into energy-dense bio-oil, syngas, and stable biochar.
- If your primary focus is material science: Pyrolysis is the fundamental process for creating highly stable, carbon-rich materials, from simple wood charcoal to advanced carbon fibers.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a powerful tool of controlled chemical transformation driven by heat and defined by the absence of oxygen.
Summary Table:
| Condition | Purpose | Key Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| High Temperature (300-800°C) | Breaks chemical bonds | Bio-oil, Syngas |
| Absence of Oxygen | Prevents combustion | Biochar, Chemical Feedstocks |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including reactors and furnaces, designed to create the precise anoxic, high-temperature environments required for effective pyrolysis. Whether your goal is waste valorization, renewable energy research, or material science, our solutions deliver the control and reliability you need. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between a tubular furnace and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Application
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness



















