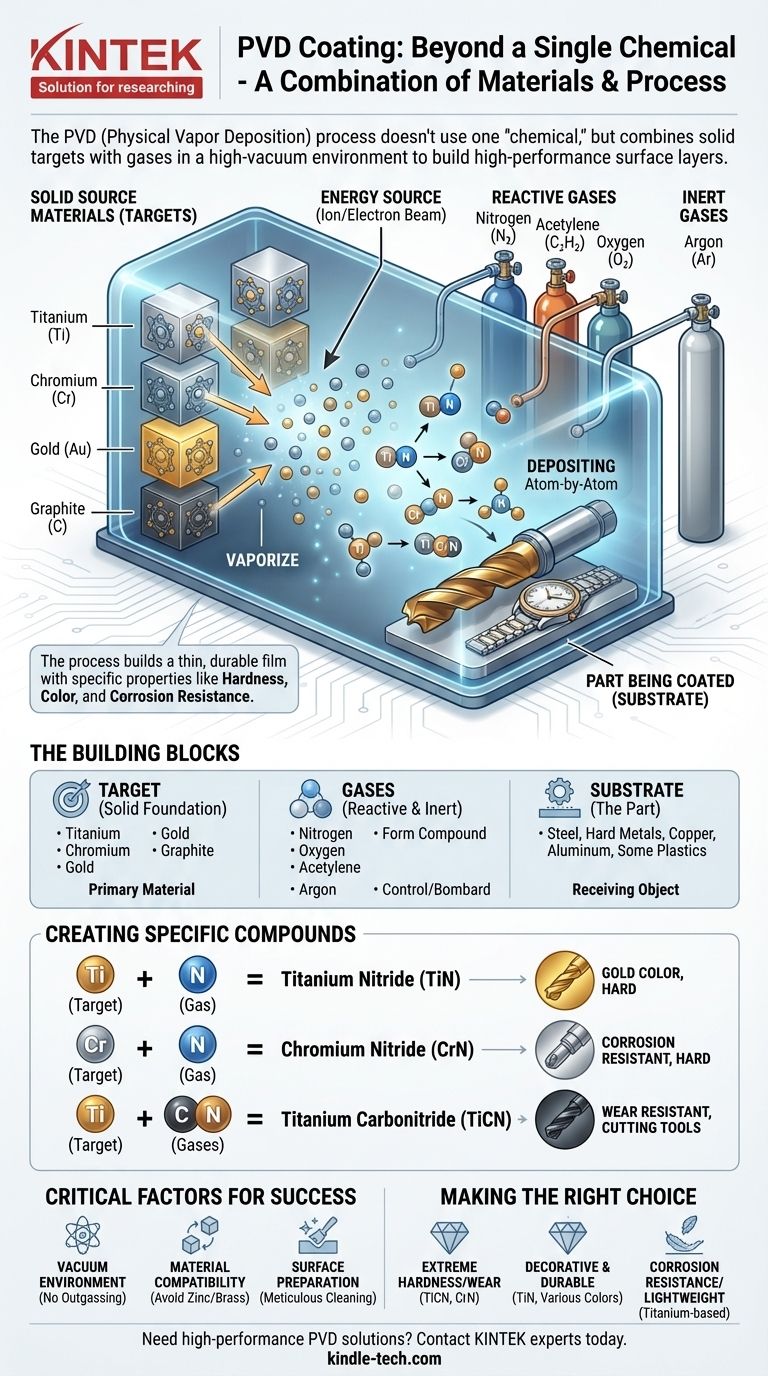
In PVD coating, there is no single "chemical" used. Instead, the process combines solid source materials, known as targets, with specific reactive gases in a high-vacuum environment. Common solid targets include metals like Titanium (Ti), Chromium (Cr), and Gold (Au), while reactive gases like Nitrogen (N₂) and Acetylene (C₂H₂) are used to form the final coating compound on the part's surface.
The core principle of PVD is not about applying a liquid chemical, but about building a new, high-performance surface layer. This is achieved by vaporizing a solid metal and reacting it with a gas to deposit a thin, durable film with specific properties like hardness, color, and corrosion resistance.

The Building Blocks of a PVD Coating
Physical Vapor Deposition is a material-building process, not a simple application. It requires three key components: the target, the gas, and the substrate.
The Solid Source Material (The "Target")
The foundation of any PVD coating is the target, a solid block of the primary material you wish to deposit.
This target is placed inside a vacuum chamber and bombarded with energy (such as ions or an electron beam) to convert it from a solid into a vapor.
Common target materials include Titanium, Chromium, Gold, and even non-metals like Graphite (a source of carbon).
Reactive and Inert Gases
Gases are introduced into the vacuum chamber to create the final coating compound and control the environment.
Reactive gases combine with the vaporized target material to form new compounds. This is what determines many of the coating's final properties. Key examples include Nitrogen, Oxygen, and carbon-source gases like Acetylene.
Inert gases, most commonly Argon, are used to create a stable, non-reactive environment and are also used to bombard the target to create the vapor.
The Part Being Coated (The "Substrate")
The substrate is the object receiving the coating. PVD is compatible with a vast range of materials.
This includes all types of steel (especially stainless and high-speed steels), hard metals, non-ferrous metals like copper and aluminum, and even some plastics.
How Materials Combine to Form a Coating
The "chemical" of a PVD coating is the compound formed when the vaporized target reacts with the gas and deposits onto the substrate.
The Basic Process
First, the substrate is thoroughly cleaned. It is then placed in a chamber with the target material, and the air is evacuated to create a high vacuum.
The target is then vaporized. As the vaporized metal travels through the chamber, it mixes with the intentionally introduced reactive gas.
This new compound deposits atom-by-atom onto the substrate, forming a thin, dense, and highly-adherent film.
Creating Specific Compounds
The final coating is a direct result of the target-gas combination.
- Titanium (target) + Nitrogen (gas) = Titanium Nitride (TiN), a very common, hard coating with a distinctive gold color.
- Chromium (target) + Nitrogen (gas) = Chromium Nitride (CrN), known for its excellent corrosion resistance and hardness.
- Titanium (target) + Carbon/Nitrogen (gases) = Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN), an even harder coating valued for its wear resistance on cutting tools.
Common Pitfalls and Limitations
While powerful, the PVD process has specific requirements that must be respected for a successful outcome.
The Critical Role of Vacuum
PVD is fundamentally a vacuum-based process. This means any material that releases gasses under vacuum ("outgassing") is unsuitable.
Unsuitable Substrates
Materials like galvanized steel or un-plated brass are generally not compatible with PVD. The zinc in these materials vaporizes in the vacuum, contaminating the chamber and preventing a good coating.
Surface Preparation is Everything
The final coating is only as good as the surface it is applied to. Any contaminants like oils, dirt, or oxides must be meticulously removed before the process begins, or the coating will not adhere properly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The combination of target material and reactive gas is chosen based on the desired outcome for the final product.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance: A coating like Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN) or Chromium Nitride (CrN) is the superior choice, often used on industrial tooling.
- If your primary focus is a decorative and durable finish: Titanium Nitride (TiN) provides a classic gold color, while other combinations can produce a range of colors for jewelry, watches, and fixtures.
- If your primary focus is corrosion resistance and light weight: Titanium-based coatings are a leading option, making them ideal for aerospace and medical implant applications.
Ultimately, the "chemical" of PVD is a carefully engineered compound, built atom-by-atom to meet a specific performance demand.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in PVD Coating | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Target (Solid) | The primary material to be vaporized and deposited. | Titanium (Ti), Chromium (Cr), Gold (Au), Graphite |
| Reactive Gas | Combines with the vaporized target to form the final coating compound. | Nitrogen (N₂), Acetylene (C₂H₂), Oxygen (O₂) |
| Resulting Coating | The high-performance compound formed on the substrate. | TiN (Gold, Hard), CrN (Corrosion Resistant), TiCN (Wear Resistant) |
Need a high-performance PVD coating for your laboratory equipment or components? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced PVD coating solutions that enhance hardness, corrosion resistance, and durability for your specific application. Our expertise ensures your lab tools, implants, or industrial parts achieve superior performance and longevity. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can engineer the perfect coating for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















