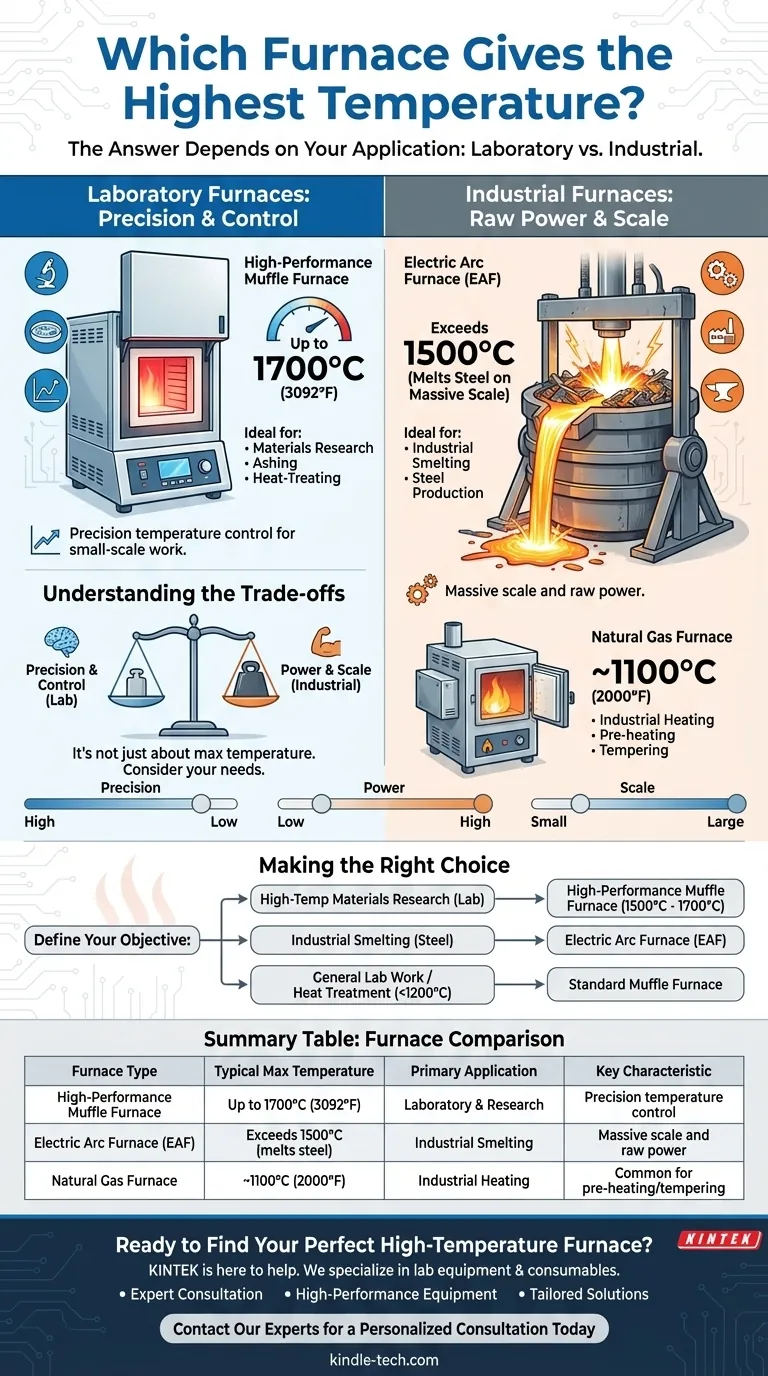
The answer depends entirely on your application, as the highest temperature furnaces are highly specialized. For laboratory and research purposes, high-performance muffle furnaces can reach 1700°C (3092°F). For heavy industrial processes like producing steel, an Electric Arc Furnace is used, reaching temperatures hot enough to melt tons of metal, far exceeding what is possible in a lab setting.
The question is not simply "which furnace is hottest," but "which type of furnace provides the necessary temperature and control for my specific task?" The choice is a trade-off between maximum heat, precision, and operational scale.

Differentiating Furnaces by Application
Not all furnaces are designed for the same purpose. The primary distinction is between furnaces built for controlled, small-scale laboratory work and those designed for massive, high-volume industrial production.
Laboratory Furnaces: Precision and Control
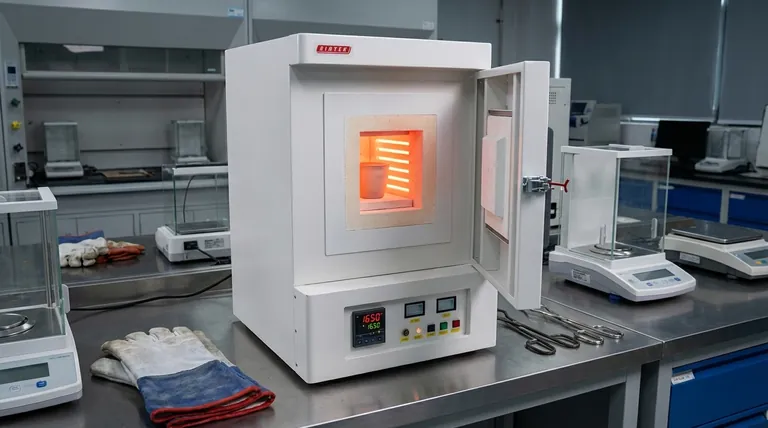
A muffle furnace is a common type of laboratory furnace used for high-temperature applications like ashing samples, heat-treating materials, or conducting materials research.
These furnaces are defined by an insulated outer chamber that heats a separate inner chamber, or "muffle," preventing the material inside from being contaminated by combustion byproducts.
The maximum temperature of a muffle furnace varies significantly by model, with basic units reaching around 1100-1200°C (2012-2192°F). However, high-performance models designed for advanced materials science can achieve up to 1700°C (3092°F).
Industrial Furnaces: Raw Power and Scale
Industrial furnaces prioritize throughput and raw heating power over the fine control of a lab furnace.
An Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) represents the pinnacle of industrial heat. It uses a high-power electric arc to melt materials like scrap steel. While a specific maximum temperature isn't a useful metric, its purpose is to create and maintain molten steel, requiring temperatures well in excess of 1500°C on a massive scale.
A natural gas furnace is another common industrial unit but operates at lower temperatures. It is often used for processes like pre-heating or tempering, typically reaching maximum temperatures around 1093°C (2000°F).
Understanding the Trade-offs: Beyond Max Temperature
Selecting a furnace based on its maximum advertised temperature alone is a common mistake. Several other factors are equally, if not more, important.
Precision vs. Power
Modern laboratory furnaces are often equipped with sophisticated controllers (PLCs) that allow for precise temperature regulation. For scientific experiments, the ability to hold a specific temperature with minimal deviation is often more critical than reaching an extreme maximum.
Scale and Suitability
The different furnace types are not interchangeable. An Electric Arc Furnace is entirely unsuitable for a laboratory, while a lab-scale muffle furnace lacks the capacity and power to perform industrial smelting. The physical size and energy consumption are designed for vastly different environments.
Operational Factors
Practical considerations heavily influence the right choice. The time a furnace takes to heat up to its maximum temperature, its power requirements, and the construction materials all impact its suitability and cost-effectiveness for a given task.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct equipment, you must first define your objective.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature materials research in a lab: Seek a high-performance laboratory or muffle furnace specifically rated to achieve temperatures in the 1500°C to 1700°C range.
- If your primary focus is industrial smelting of steel or other high-melting-point metals: An Electric Arc Furnace is the industry standard for achieving the necessary temperatures at scale.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work or heat treatment below 1200°C: A standard muffle furnace offers the best balance of control, cost, and performance.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace is about matching the tool's capabilities to your specific requirements.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Typical Max Temperature | Primary Application | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Performance Muffle Furnace | Up to 1700°C (3092°F) | Laboratory & Research | Precision temperature control for small-scale work |
| Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) | Exceeds 1500°C (melts steel) | Industrial Smelting | Massive scale and raw power for melting tons of metal |
| Natural Gas Furnace | ~1100°C (2000°F) | Industrial Heating | Common for processes like pre-heating and tempering |
Ready to Find Your Perfect High-Temperature Furnace?
Choosing the right furnace is critical to your project's success. The wrong choice can lead to inaccurate results, operational inefficiencies, and unnecessary costs.
KINTEK is here to help. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance to match you with the ideal furnace for your specific temperature, precision, and scale requirements.
We provide:
- Expert Consultation: Our specialists will help you navigate the trade-offs between maximum temperature, control, and capacity.
- High-Performance Equipment: From standard muffle furnaces to advanced models reaching 1700°C for demanding research.
- Tailored Solutions: We ensure the equipment you choose fits your lab's workflow and budget perfectly.
Don't leave your results to chance. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how the right furnace can enhance your work's efficiency and accuracy.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How thick is vacuum deposition? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings
- What is deposition of a vapor? A Guide to High-Precision Thin Film Coating
- What is the VAR process for titanium? Achieve Unmatched Purity for Critical Applications
- How do you make sintered metal? A Step-by-Step Guide to Powder Metallurgy
- What is the critical point of heat treatment? Master the Key to Steel Transformation
- How does a high-temperature steam oxidation device ensure experimental accuracy? Precision for LOCA Simulation Success
- Does increasing the insulation thickness increase the rate of heat transfer? The Critical Radius Explained
- What are the disadvantages of a continuous furnace? High Costs and Inflexibility Explained



















