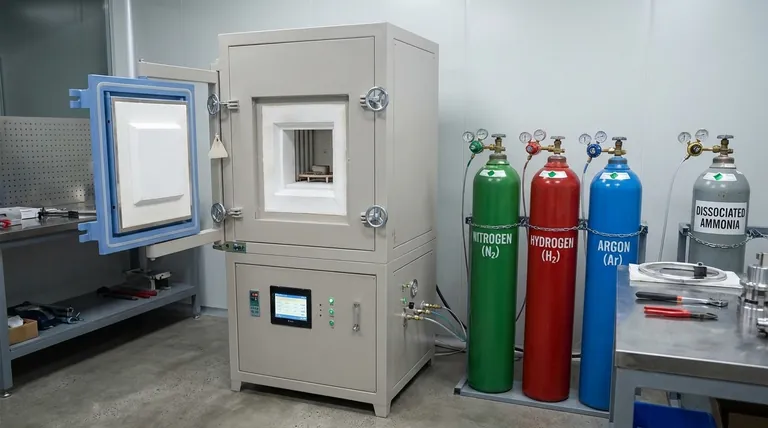
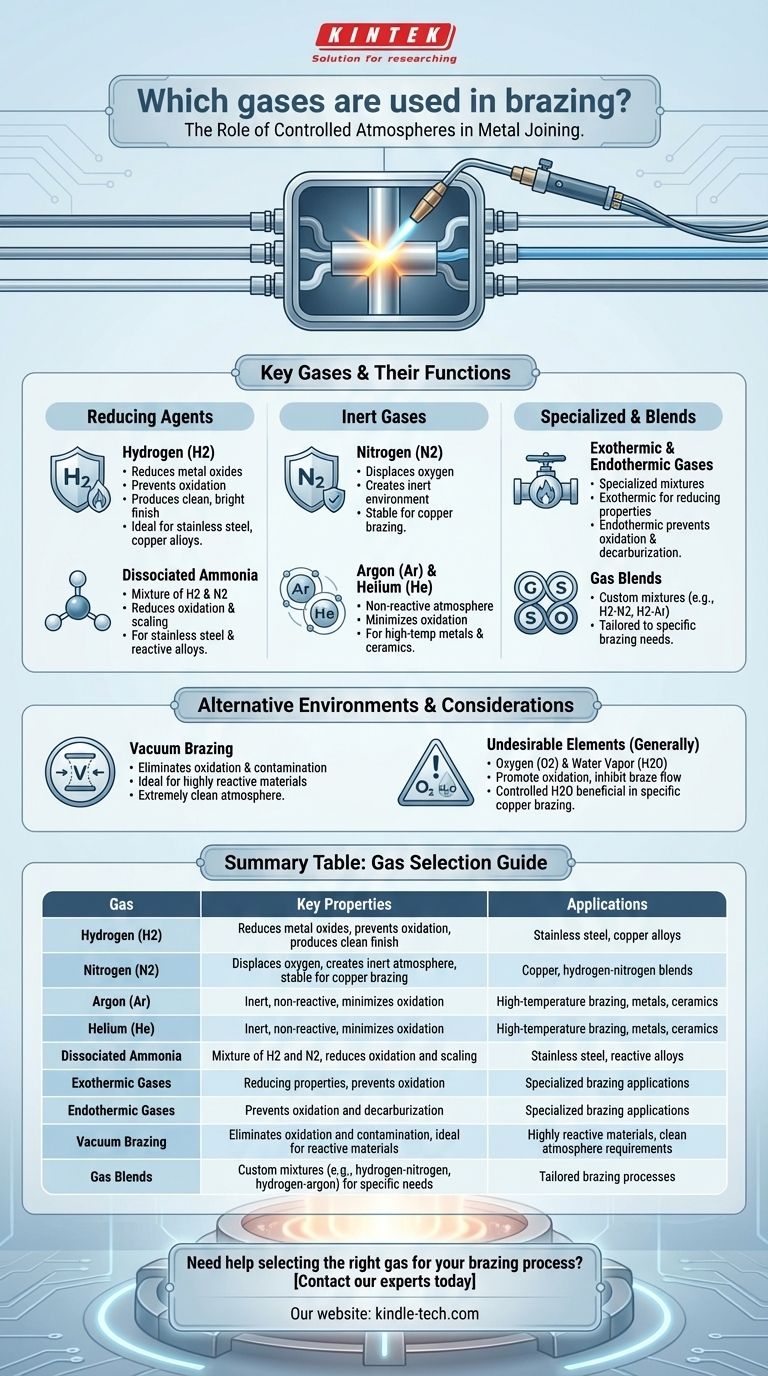
Brazing is a metal-joining process that requires a controlled atmosphere to ensure high-quality results. The gases used in brazing play a critical role in preventing oxidation, reducing scaling, and ensuring proper braze flow. Commonly used gases include hydrogen, nitrogen, argon, helium, and dissociated ammonia. These gases are selected based on the materials being joined and the desired outcomes, such as a clean, bright finish or the prevention of carbon buildup. Additionally, vacuum environments or blends of these gases can be used depending on the specific requirements of the brazing process.

Key Points Explained:
-
Hydrogen (H2)
- Hydrogen is an active agent used to reduce metal oxides, which helps prevent oxidation during brazing.
- It is particularly effective in producing a clean and bright finish on the brazed product.
- Hydrogen is often used in combination with other inert gases to create a protective atmosphere.
- It is suitable for brazing materials that are prone to oxidation, such as stainless steel and copper alloys.
-
Nitrogen (N2)
- Nitrogen is used to displace oxygen in the furnace atmosphere, creating an inert environment that prevents oxidation.
- It is especially effective for brazing copper, as it does not react with the metal and maintains a stable atmosphere.
- Nitrogen is often blended with hydrogen or other inert gases to optimize the brazing process.
-
Argon (Ar) and Helium (He)
- Argon and helium are inert gases that provide a non-reactive atmosphere, ideal for brazing metals and ceramics.
- These gases are used when a completely inert environment is required to prevent any chemical reactions during brazing.
- They are particularly useful for high-temperature brazing applications where oxidation must be minimized.
-
Dissociated Ammonia
- Dissociated ammonia (a mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen) is commonly used to reduce oxidation and scaling.
- It provides a reducing atmosphere that helps produce a clean and bright finish.
- This gas is often preferred for brazing stainless steel and other alloys that require a controlled, reactive atmosphere.
-
Exothermic and Endothermic Gases
- These are specialized gas mixtures used in specific brazing applications.
- Exothermic gases are generated by burning natural gas with air and are used for their reducing properties.
- Endothermic gases are produced by heating natural gas with air in the presence of a catalyst and are used to prevent oxidation and decarburization.
-
Vacuum Brazing
- In some cases, a vacuum environment is used instead of gases to eliminate oxidation and contamination.
- Vacuum brazing is ideal for materials that are highly reactive or require an extremely clean atmosphere.
-
Oxygen (O2) and Water Vapor (H2O)
- Oxygen and water vapor are generally undesirable in brazing atmospheres because they promote oxidation and inhibit braze flow.
- However, in specific applications, such as copper brazing, controlled amounts of water vapor can be beneficial.
-
Gas Blends
- Many brazing processes use blends of gases to achieve the desired atmosphere.
- Common blends include hydrogen-nitrogen mixtures and hydrogen-argon mixtures, which provide a balance of reducing and inert properties.
By carefully selecting the appropriate gas or gas mixture, manufacturers can ensure optimal brazing conditions, resulting in strong, high-quality joints with minimal defects. The choice of gas depends on the materials being joined, the specific requirements of the brazing process, and the desired outcome, such as a clean finish or oxidation prevention.
Summary Table:
| Gas | Key Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H2) | Reduces metal oxides, prevents oxidation, produces clean finish | Stainless steel, copper alloys |
| Nitrogen (N2) | Displaces oxygen, creates inert atmosphere, stable for copper brazing | Copper, hydrogen-nitrogen blends |
| Argon (Ar) | Inert, non-reactive, minimizes oxidation | High-temperature brazing, metals, ceramics |
| Helium (He) | Inert, non-reactive, minimizes oxidation | High-temperature brazing, metals, ceramics |
| Dissociated Ammonia | Mixture of hydrogen and nitrogen, reduces oxidation and scaling | Stainless steel, reactive alloys |
| Exothermic Gases | Reducing properties, prevents oxidation | Specialized brazing applications |
| Endothermic Gases | Prevents oxidation and decarburization | Specialized brazing applications |
| Vacuum Brazing | Eliminates oxidation and contamination, ideal for reactive materials | Highly reactive materials, clean atmosphere requirements |
| Gas Blends | Custom mixtures (e.g., hydrogen-nitrogen, hydrogen-argon) for specific needs | Tailored brazing processes |
Need help selecting the right gas for your brazing process? Contact our experts today for personalized guidance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does an inert gas flow system protect Magnetic Composite Carbon? Ensure Yield and Magnetic Utility
- How does a high-temperature atmosphere furnace ensure the active structure of calcium-aluminum catalysts?
- What is the role of a high-temperature atmosphere sintering furnace in MOF-derived catalysts? | Precision Pyrolysis
- What is the hydrogen annealing process? Achieve Clean, Strong, and Stress-Free Metal Parts
- What are the two types of exothermic atmospheres and their applications? Rich vs. Lean Atmospheres Explained
- What is the importance of argon? Unlocking the Power of an Inert Gas
- Is the atmosphere oxidizing or reducing? Discover the Chemical Engine of Our Planet
- What type of gases is used in a heat treat furnace? Control Your Metal's Final Properties



















