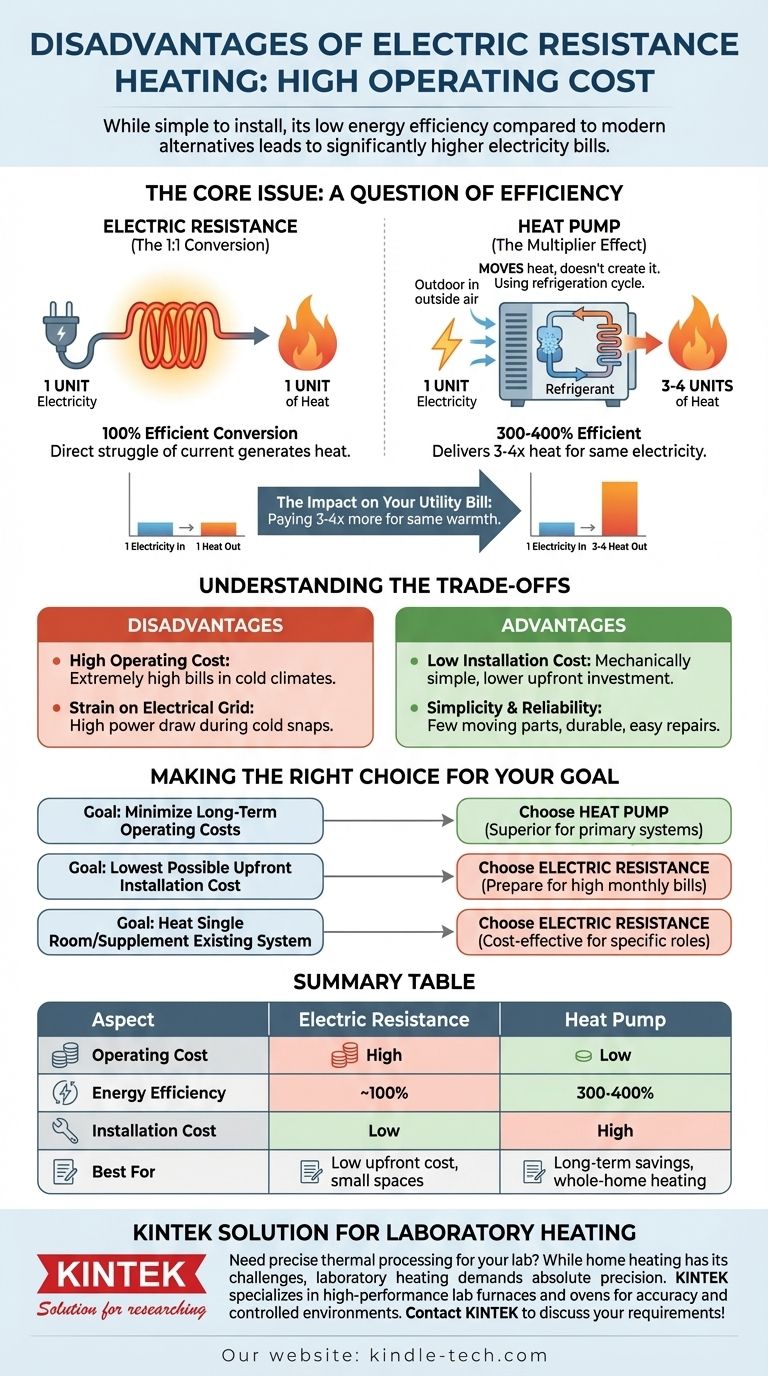
While simple and inexpensive to install, the single greatest disadvantage of electric resistance heating is its high operating cost. This is a direct result of its relatively low energy efficiency when compared to modern alternatives like heat pumps, leading to significantly higher electricity bills during the heating season.
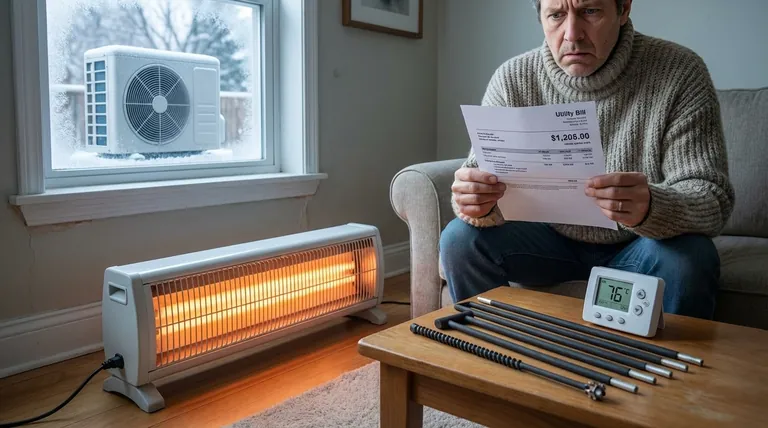
The core issue isn't that electric resistance is "bad" at making heat—it's nearly 100% efficient at converting electricity into heat. The problem is that other technologies, like heat pumps, can deliver 3 to 4 units of heat for every 1 unit of electricity, making them 300-400% efficient and far cheaper to operate.

The Core Issue: A Question of Efficiency
To understand the cost, you must first understand the fundamental difference in how heating systems use electricity. This distinction is the root of the high cost associated with electric resistance.
The 1:1 Conversion of Resistance Heat
Electric resistance heating works exactly as its name implies. An electric current is forced through a material that resists it (a heating element), and this struggle generates heat.
For every one unit of electrical energy you purchase from the utility, you get approximately one unit of heat energy in your room. In physics, this is considered 100% efficient conversion.
The Multiplier Effect of a Heat Pump
A heat pump operates on a different principle. It doesn't primarily create heat; it moves it.
Using a refrigeration cycle, a heat pump extracts heat from the outside air (even when it's cold) and transfers it inside. This process is far more efficient, allowing it to deliver three to four units of heat for every one unit of electricity it consumes. This is often expressed as an efficiency of 300% to 400%.
The Direct Impact on Your Utility Bill
Because a heat pump can deliver 3x to 4x the heat for the same amount of electricity, its operating cost is proportionally lower. Choosing electric resistance as a primary heat source is like paying three to four times more for the same level of warmth.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology exists in a vacuum. The high operating cost of electric resistance is balanced by a few key advantages, which explains why it is still used in certain applications.
Disadvantage: High Operating Cost
This is the most significant drawback. In climates with cold winters, relying solely on electric resistance heating for an entire home will result in extremely high utility bills compared to natural gas or a heat pump.
Disadvantage: Strain on the Electrical Grid
The high power draw of resistance heaters, especially when many are used simultaneously during a cold snap, can put a significant load on the local electrical infrastructure.
Advantage: Low Installation Cost
This is the primary reason people choose this technology. Electric resistance systems, like baseboard heaters or electric furnaces, are mechanically simple. They have a very low upfront purchase and installation cost compared to the complexity of a furnace or heat pump system.
Advantage: Simplicity and Reliability
With few or no moving parts, electric resistance heaters are exceptionally reliable and durable. When a failure does occur, repairs are typically simple and inexpensive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be guided by how you balance upfront investment against long-term running costs.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term operating costs: A heat pump is the superior choice for a primary heating system due to its vast efficiency advantage.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible upfront installation cost: Electric resistance heating is the clear winner, but you must be prepared for much higher monthly utility bills.
- If you need to heat a single, small room or supplement an existing system: An electric resistance heater (like a baseboard or portable unit) offers a simple, targeted, and cost-effective solution for that specific role.
Understanding the fundamental trade-off between installation cost and operational efficiency is the key to selecting the right heating system for your needs.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Electric Resistance Heating | Heat Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Cost | High | Low |
| Energy Efficiency | ~100% | 300-400% |
| Installation Cost | Low | High |
| Best For | Low upfront cost, small spaces | Long-term savings, whole-home heating |
Need precise thermal processing for your lab? While home heating has its challenges, laboratory heating demands absolute precision and reliability. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces, ovens, and heating elements designed for accuracy, durability, and controlled environments. Let our experts help you select the ideal heating solution for your research or quality control needs.
Contact KINTALK today to discuss your laboratory heating requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What material is used for making heating element? Choose the Right Alloy for Your Application
- What is silicon carbide rod heated to high temperature used as? A Premier Heating Element for Extreme Environments
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution
- What is a silicon carbide heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat for Industrial Processes

















