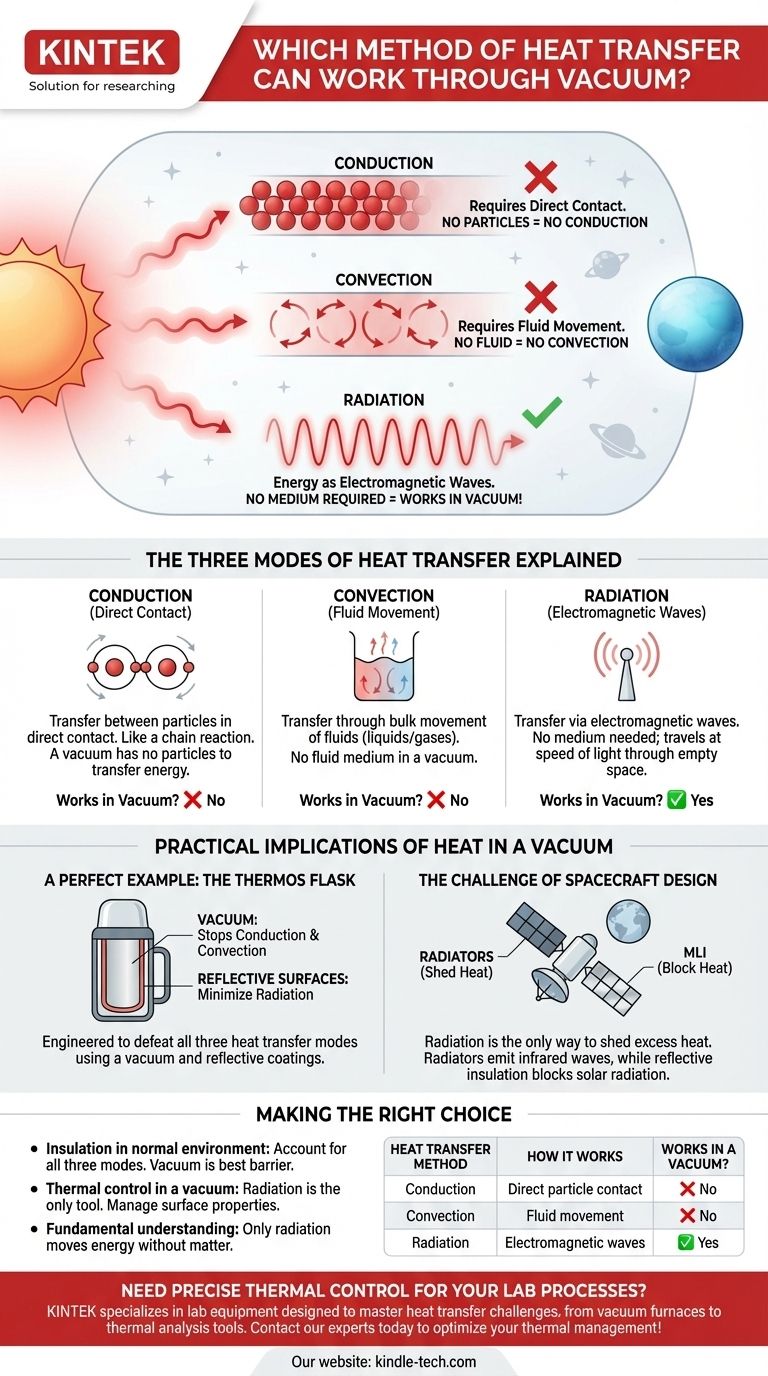
The only method of heat transfer that can work through a vacuum is thermal radiation. Unlike conduction and convection, which require a physical medium of particles to transfer energy, radiation transmits energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. These waves can travel through the emptiness of space, which is precisely how the Sun's heat reaches Earth.
The critical distinction is that conduction and convection transfer energy through matter, while radiation transfers energy as electromagnetic waves. Because these waves do not require a medium, radiation is the sole method of heat transfer possible in a perfect vacuum.
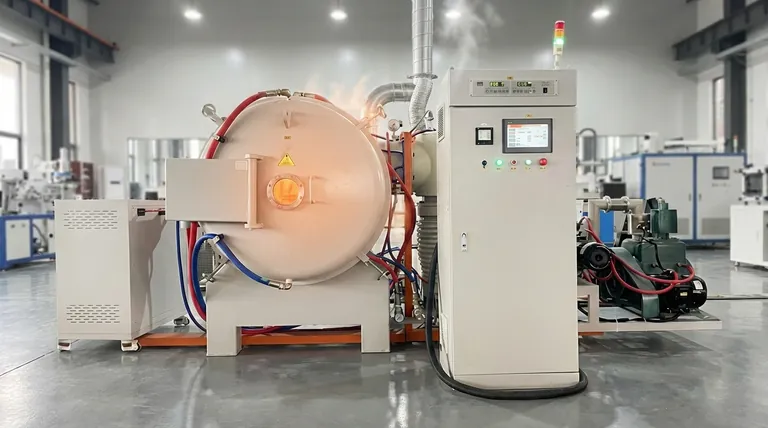

The Three Modes of Heat Transfer Explained
To understand why only radiation works in a vacuum, you must first understand the fundamental mechanism of all three heat transfer modes. Each relies on a different physical principle.
Conduction: Heat Through Direct Contact
Conduction is the transfer of thermal energy between particles that are in direct contact with one another. Think of it as a chain reaction where vibrating atoms bump into their neighbors, passing energy down the line.
A solid metal spoon heating up in a cup of hot coffee is a classic example of conduction. Because a vacuum is, by definition, a space devoid of matter, there are no particles to touch and transfer this vibrational energy.
Convection: Heat Through Fluid Movement
Convection is the transfer of heat through the bulk movement of fluids (liquids or gases). When a portion of a fluid is heated, it becomes less dense and rises, while the cooler, denser fluid sinks to take its place, creating a circulating current.
This is the principle that drives weather patterns and makes a radiator heat a room. Convection is impossible in a vacuum because there is no fluid medium to create these convection currents.
Radiation: Heat Through Electromagnetic Waves
Thermal radiation is fundamentally different. Every object with a temperature above absolute zero (-273.15°C) emits energy as electromagnetic waves, primarily in the infrared spectrum.
These waves are pure energy. They do not need any medium to propagate and can travel at the speed of light through empty space. When these waves strike another object, they transfer their energy, causing the object to heat up.
The Practical Implications of Heat in a Vacuum
Understanding this principle is not just academic; it has critical applications in engineering and everyday life. The behavior of heat in a vacuum creates unique challenges and opportunities.
A Perfect Example: The Thermos Flask
A thermos (or vacuum flask) is engineered specifically to defeat all three modes of heat transfer.
The vacuum created between the inner and outer walls is the key feature. It effectively stops heat transfer by both conduction and convection because there is no medium to carry the energy across the gap. The shiny, reflective surfaces then minimize heat transfer by radiation.
The Challenge of Spacecraft Design
In the vacuum of space, managing temperature is a primary concern. With no air for conduction or convection, radiation is the only way for a spacecraft to shed the intense heat it builds up from its electronics and from solar exposure.
Engineers design large panels called radiators, often with special coatings, to efficiently radiate this excess heat away into space as infrared waves. Conversely, they use multi-layer insulation (MLI)—thin, reflective sheets—to block incoming solar radiation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to thermal management depends entirely on the environment and your objective.
- If your primary focus is insulation in a normal environment: You must account for all three modes, but a vacuum remains the most effective theoretical barrier against conduction and convection.
- If your primary focus is thermal control in a vacuum: Radiation is your only tool; managing surface properties (emissivity and reflectivity) is the most critical factor for either retaining or shedding heat.
- If your primary focus is fundamental understanding: Remember that all heat transfer is simply energy in motion, but only radiation can move that energy without the help of matter.
By understanding that radiation is energy in wave form, you can master thermal control in any environment, from your morning coffee to the vacuum of deep space.
Summary Table:
| Heat Transfer Method | How It Works | Works in a Vacuum? |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Energy transfer through direct contact of particles. | ❌ No |
| Convection | Energy transfer through the movement of fluids (liquids/gases). | ❌ No |
| Radiation | Energy transfer via electromagnetic waves (e.g., infrared). | ✅ Yes |
Need precise thermal control for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment designed to master heat transfer challenges, whether you're working in controlled environments or specialized conditions. From vacuum furnaces to thermal analysis tools, our solutions ensure accuracy and efficiency. Contact our experts today to optimize your thermal management!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the plasma arc technology? A Guide to Advanced Material Processing
- Which type of metals can be melted using tilting furnace? Your Guide to Ferrous, Non-Ferrous & Precious Metals
- What is a sintering process? A Guide to Fusing Powders into High-Performance Parts
- Does hardening steel change dimensions? Mastering the Forces of Thermal and Metallurgical Change
- What is the vacuum pyrolysis method? Maximize Liquid Yield with Precise Process Control
- What is the main advantage of vacuum evaporation over atmospheric evaporation? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Purity Processing
- What is the strength of brazing aluminum? Achieve Robust, Leak-Tight Assemblies
- What are the applications of vacuum brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean Joints for Critical Components



















