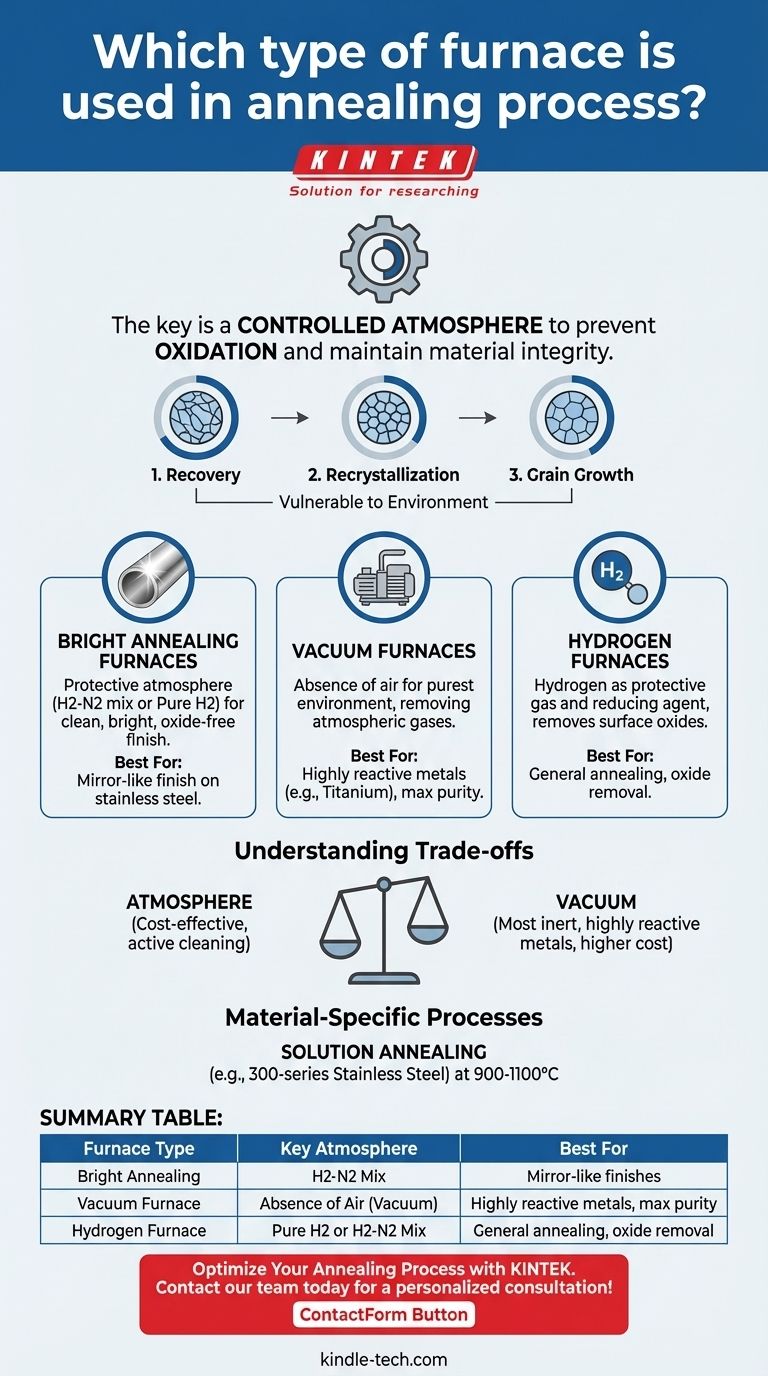
The short answer is that various furnaces are used for annealing, but they are all defined by one critical feature: the ability to maintain a controlled atmosphere. The most common types include bright annealing furnaces, vacuum furnaces, and hydrogen furnaces, each chosen based on the specific material being treated and the desired surface finish.
The defining characteristic of an annealing furnace is not its heating method, but its capacity to create a protective environment. This controlled atmosphere is essential to prevent oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions at high temperatures, ensuring the metal's properties are altered as intended without surface damage.

Why a Controlled Atmosphere is Non-Negotiable
Annealing involves heating a material to a specific temperature to alter its microstructure, making it softer and more ductile. This process makes the metal extremely vulnerable to its surrounding environment.
The Primary Goal: Preventing Oxidation
At elevated temperatures, metals react readily with oxygen in the air. This reaction, known as oxidation, forms a layer of scale on the metal's surface.
A controlled atmosphere, which is either inert (like argon) or a vacuum, displaces the oxygen and prevents this from occurring.
The Three Stages of Vulnerability
The annealing process unfolds in three key stages, during which the material's structure is actively changing and susceptible to damage.
- Recovery: The furnace heats the material to relieve internal stresses locked in from previous processing.
- Recrystallization: The material is heated above its recrystallization temperature, causing new, strain-free grains to form.
- Grain Growth: As the material is carefully cooled, these new grains grow, resulting in a softer, more pliable structure.
Throughout these stages, an uncontrolled atmosphere would compromise the integrity of the material's surface.
Common Furnaces and Their Atmospheres
The type of furnace is named after the method it uses to create this protective environment.
Bright Annealing Furnaces
These furnaces are specifically designed to produce a clean, bright, oxide-free surface. They achieve this by using a protective atmosphere.
This atmosphere is typically a hydrogen-nitrogen mixture or pure hydrogen, which envelops the part during the heating and cooling cycles.
Vacuum Furnaces
A vacuum furnace provides the purest environment by simply removing the air. By pumping out the atmospheric gases, there is nothing left to react with the metal.
This method is widely used across industries for processing ceramics, high-purity metals, and materials that are exceptionally reactive.
Hydrogen Furnaces
As a specific type of controlled-atmosphere furnace, a hydrogen furnace uses hydrogen or a hydrogen-nitrogen mix as its protective gas.
Hydrogen is not just protective; it is a reducing agent. This means it can actively remove any light surface oxides that may have been present on the material before treatment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right furnace involves balancing the desired outcome with operational complexity and cost. A furnace suitable for one metal may be unnecessary or even detrimental for another.
Atmosphere vs. Vacuum
A vacuum provides the most inert environment possible, making it ideal for highly reactive metals like titanium. However, vacuum furnaces can have longer cycle times and higher equipment costs.
Gaseous atmospheres, like hydrogen, can be more cost-effective and offer the added benefit of actively cleaning the part's surface. The primary risk is ensuring the purity of the gas supply.
Material-Specific Processes
Certain alloys require specialized annealing cycles. For example, 300-series austenitic stainless steels undergo solution annealing.
This process uses temperatures between 900°C and 1100°C to dissolve unwanted carbide precipitates back into the metal's structure, followed by rapid cooling to lock them in place. This enhances corrosion resistance and requires precise temperature and atmospheric control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection depends entirely on the material you are processing and your end goal.
- If your primary focus is a mirror-like finish on stainless steel: A bright annealing furnace using a hydrogen-based atmosphere is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals or achieving maximum purity: A vacuum furnace offers the ultimate protection against atmospheric contamination.
- If your primary focus is general stress relief of common steels where surface finish is less critical: A simpler furnace with an endothermic gas atmosphere may be sufficient.
Ultimately, the right annealing furnace is the one that provides the precise atmospheric control your material requires to achieve its desired properties.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Key Atmosphere | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Bright Annealing | Hydrogen-Nitrogen Mix | Mirror-like finishes on stainless steel |
| Vacuum Furnace | Absence of Air (Vacuum) | Highly reactive metals (e.g., titanium), maximum purity |
| Hydrogen Furnace | Pure Hydrogen or H2-N2 Mix | General annealing with surface oxide removal |
Optimize Your Annealing Process with KINTEK
Choosing the right furnace is critical to achieving the desired material properties and surface finish. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, including a range of annealing furnaces designed for precise atmospheric control.
Our experts can help you select the ideal solution—whether you need a bright annealing furnace for a flawless finish, a vacuum furnace for reactive metals, or a hydrogen furnace for efficient oxide removal.
Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a reaction system with gas protection required for Fe3O4 co-precipitation? Ensure Pure Magnetite Synthesis
- How does argon remove oxygen? By Physically Displacing It to Create an Inert Shield
- Why use a precision atmospheric control furnace for annealing HEAs? Unlock Pure Material Stability Data
- How does an atmospheric furnace work? A Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Heating
- What gases are used in brazing? A Guide to Choosing the Right Atmosphere for Strong Joints
- What is the technical significance of controlling the high-purity argon (Ar) flow rate? Optimize W-SiC Heat Treatment
- What is the atmosphere of the annealing furnace? A Guide to Protective Gas Selection
- What is protective atmosphere heat treatment? Prevent Oxidation and Decarburization for Superior Metal Parts



















