The most common materials used for hot forging are metals with good ductility and malleability at elevated temperatures. These primarily include various grades of steel (carbon, alloy, and stainless), aluminum alloys, titanium alloys, and high-performance nickel-based superalloys. The choice depends entirely on the required final properties of the component, such as strength, weight, and resistance to corrosion and heat.
The critical factor for any hot forging material isn't its name, but its ability to undergo plastic deformation without fracturing when heated above its recrystallization temperature. This process allows for significant shaping while simultaneously refining the metal's internal grain structure, which enhances its strength and toughness.

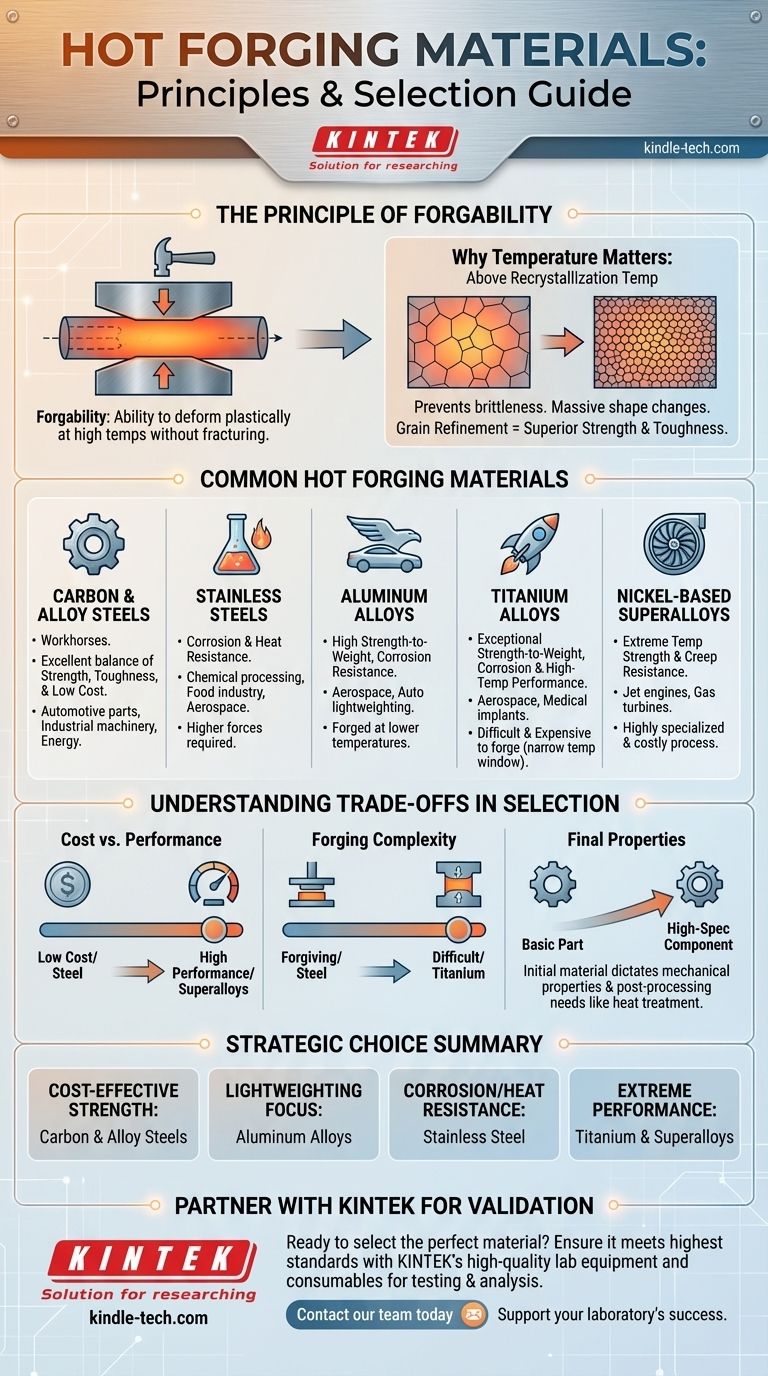
The Principle of "Forgability" at High Temperatures
Hot forging is a process of shaping metal by plastic deformation at a temperature high enough that it doesn't work-harden. The material's suitability for this process is known as its "forgability."
Why Temperature is the Key
A material is hot forged above its recrystallization temperature. This is the critical threshold where new, strain-free grains are formed within the metal's microstructure as it is being deformed.
This process prevents the material from becoming brittle and allows for massive changes in shape that would be impossible with cold forming.
The Microstructural Benefit
Working the metal above this temperature continuously breaks down and reforms the grain structure. This grain refinement is a primary benefit of forging, resulting in a final product with superior mechanical properties, such as high tensile strength and fatigue resistance, compared to casting or machining.
A Breakdown of Common Hot Forging Materials
While many metals can be hot forged, a few categories dominate industrial applications based on their unique properties and cost-effectiveness.
Carbon and Alloy Steels
These are the workhorses of the forging industry. They offer an excellent balance of strength, toughness, and low cost, making them the default choice for countless applications in the automotive, industrial machinery, and energy sectors.
Stainless Steels
Chosen for their corrosion and heat resistance, stainless steels are used for components in chemical processing, food industries, and aerospace. They generally require higher forging forces and more precise temperature control than carbon steels.
Aluminum Alloys
Valued for their high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, aluminum alloys are essential in the aerospace and high-performance automotive industries. They are forged at much lower temperatures than steel.
Titanium Alloys
Titanium offers an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and high-temperature performance. However, it is difficult and expensive to forge due to a very narrow forging temperature window and its tendency to react with oxygen at high temperatures. It is primarily used in aerospace, military, and medical applications.
Nickel-Based Superalloys
These materials are designed for the most demanding environments, offering superior strength and creep resistance at extreme temperatures. They are used in jet engine and gas turbine components. Forging these alloys is a highly specialized and costly process due to their immense strength even when hot.
Understanding the Trade-offs in Material Selection
Choosing a material for hot forging is never about a single property. It is a strategic decision balancing performance requirements, manufacturing complexity, and cost.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between a material's performance characteristics and its cost. Carbon steel is economical and versatile, while titanium and superalloys offer unparalleled performance at a significantly higher price point for both raw material and processing.
Forging Complexity and Control
Different materials behave differently under the forge press. An alloy like titanium requires an extremely narrow and precise temperature range, while some carbon steels are far more forgiving. This complexity directly impacts tooling costs, process control requirements, and rejection rates.
Final Properties and Post-Processing
The initial material selection dictates the final mechanical properties of the part. It also determines the necessary post-forging processes, such as heat treatment, which are required to achieve the desired hardness, strength, and toughness.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Your final choice must be driven by the primary goal for the finished component.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective strength for general use: Carbon and alloy steels are the undisputed standard.
- If your primary focus is lightweighting for automotive or consumer goods: Aluminum alloys provide the best balance of weight, strength, and cost.
- If your primary focus is corrosion and heat resistance: Stainless steel is the most practical choice for a wide range of environments.
- If your primary focus is extreme performance at any cost: Titanium and nickel-based superalloys are necessary for mission-critical aerospace or medical applications.
Ultimately, selecting the right material is a strategic engineering decision that balances the demands of the application with the realities of the manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon & Alloy Steels | High strength, toughness, cost-effective | Automotive parts, industrial machinery |
| Aluminum Alloys | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Aerospace, automotive lightweighting |
| Stainless Steels | Corrosion & heat resistant | Chemical processing, food industry |
| Titanium Alloys | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | Aerospace, medical implants |
| Nickel Superalloys | Extreme temperature strength | Jet engines, gas turbines |
Ready to select the perfect material for your hot forging project? The right choice is critical for achieving the strength, durability, and performance your application demands. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables needed to test and validate forged materials. Our experts can help you ensure your materials meet the highest standards.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success in material testing and analysis.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Bomb Type Probe for Steelmaking Production Process
- Professional Cutting Tools for Carbon Paper Cloth Diaphragm Copper Aluminum Foil and More
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- What is titanium used for in manufacturing? Leveraging High-Performance Properties for Critical Applications
- What are two disadvantages of metal? Understanding Corrosion and Weight Limitations
- How can you improve corrosion resistance? Extend Equipment Life with Proven Strategies
- What products are manufactured with titanium? The Ultimate Guide to High-Performance Materials
- What is titanium disadvantages and advantages? Weighing Performance vs. Cost for Your Project



















