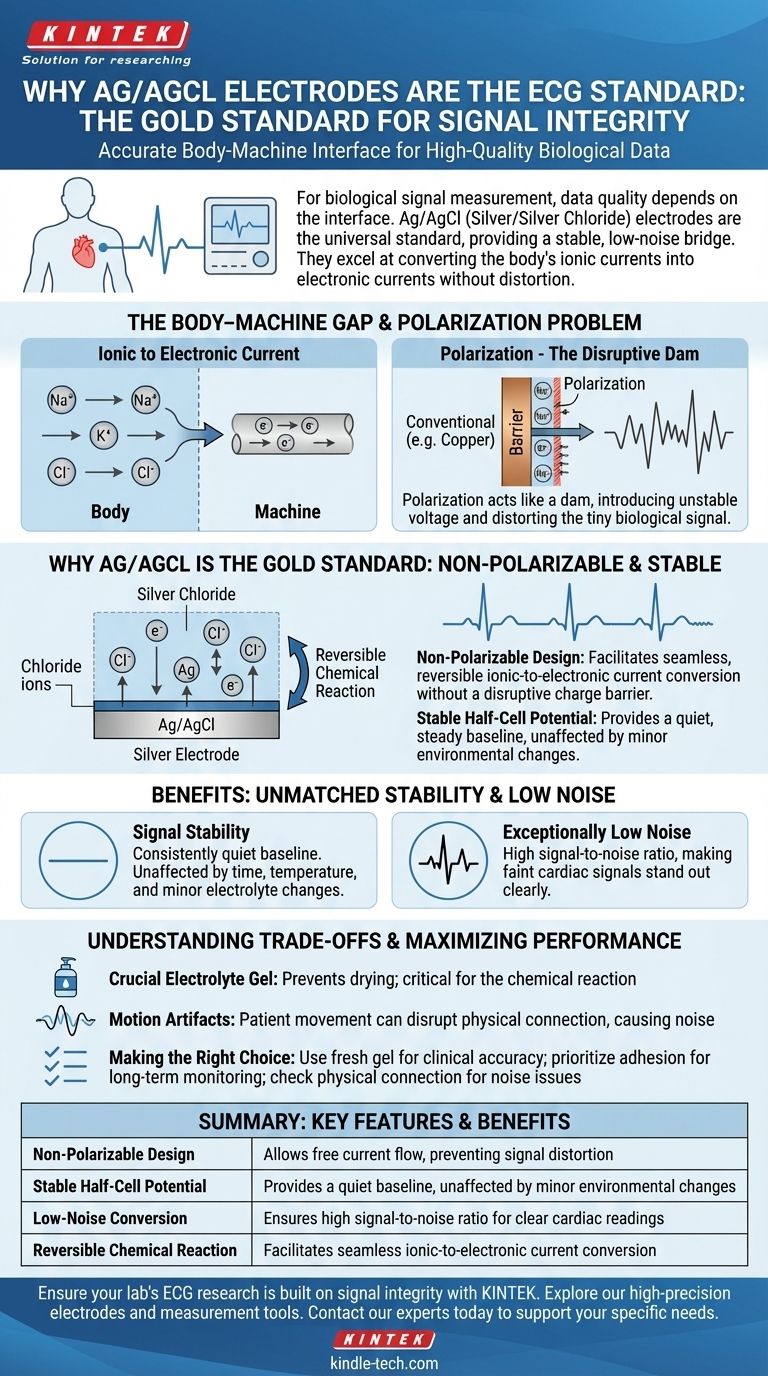
For any biological signal measurement, the quality of the data depends entirely on the quality of the interface between the subject and the machine. Ag/AgCl (Silver/Silver Chloride) electrodes are the universal standard for ECG because they provide an exceptionally stable, low-noise chemical bridge for this interface. They excel at converting the body's ionic currents into the electronic currents a machine can read, without distorting the underlying signal.
The central challenge in ECG is accurately translating the heart's ionic signals into a machine-readable electronic signal. Ag/AgCl electrodes solve this by being "non-polarizable," allowing current to pass with minimal disruption and noise, which ensures the final reading is a true representation of cardiac activity.
The Core Challenge: Bridging the Body-Machine Gap
From Ionic to Electronic Current
The body's electrical system, including the signals from the heart, is conducted by ions (like Na+, K+, Cl-) moving through fluid.
In contrast, the ECG machine and its wires operate on the flow of electrons through metal. An electrode's fundamental job is to manage the conversion between these two different forms of current.
The Problem of "Polarization"
If you were to use a simple metal electrode, like copper, it would react with the chloride ions in the electrolyte gel and skin. This reaction creates a charge barrier at the interface.
This barrier, known as polarization, acts like a dam, impeding the free flow of current and introducing its own unstable voltage. This instability severely distorts the tiny biological signal you are trying to measure.
Why Ag/AgCl is the Gold Standard
The Principle of Non-Polarizability
Ag/AgCl electrodes are clever in their chemical design. They are considered non-polarizable because they don't fight the conversion process; they facilitate it.
The electrode consists of a silver base coated with a layer of silver chloride. Chloride ions from the body can easily react with the silver to form more silver chloride, releasing an electron. This reaction is also perfectly reversible.
This seamless, reversible exchange allows current to flow freely across the interface without creating the disruptive charge barrier seen in other metals.
Unmatched Signal Stability
This chemical elegance results in a highly stable half-cell potential. This means the electrode itself does not introduce its own fluctuating voltage, providing a quiet and steady baseline.
As the references note, this potential is remarkably consistent over time and is not significantly affected by small changes in temperature or electrolyte evaporation.
Exceptionally Low Noise
Signal stability directly leads to a low-noise recording.
Because the chemical reaction at the electrode surface is stable and efficient, there is very little random voltage fluctuation. This creates a high signal-to-noise ratio, making the faint electrical signals from the heart stand out clearly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Crucial Role of Electrolyte Gel
An Ag/AgCl electrode is only as good as its connection to the skin. The chloride-rich electrolyte gel is not optional; it is a critical component that enables the reversible chemical reaction.
If the gel dries out or if skin preparation is poor, the electrode's performance will be compromised, leading to a noisy signal.
Susceptibility to Motion Artifacts
While electrically superior, the physical connection remains a weak point. Patient movement can alter the physical distance and pressure at the skin-electrode junction.
This movement creates large, low-frequency noise known as motion artifact, which can easily overwhelm the ECG signal. This is a mechanical problem, not a chemical failure of the electrode itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure a high-quality ECG reading, you must consider both the electrode and its application.
- If your primary focus is clinical accuracy: Always use high-quality, single-use Ag/AgCl electrodes with fresh, moist gel. Proper skin preparation is non-negotiable to minimize baseline wander and noise.
- If your primary focus is long-term monitoring: Prioritize electrodes designed for stable, long-duration adhesion and gels that resist drying out to maintain a consistent, reliable signal over many hours or days.
- If you are troubleshooting a noisy signal: First, check the physical interface. The most common culprits are patient movement, poor adhesion, or expired electrolyte gel—not the inherent chemistry of the electrode.
Ultimately, the universal reliance on Ag/AgCl reflects a deep understanding of electrochemistry, ensuring that the vital story told by the heart is heard with absolute clarity.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit in ECG |
|---|---|
| Non-Polarizable Design | Allows free current flow, preventing signal distortion |
| Stable Half-Cell Potential | Provides a quiet baseline, unaffected by minor environmental changes |
| Low-Noise Conversion | Ensures high signal-to-noise ratio for clear cardiac readings |
| Reversible Chemical Reaction | Facilitates seamless ionic-to-electronic current conversion |
Ensure your lab's ECG and electrophysiology research is built on a foundation of signal integrity. KINTEK specializes in high-precision lab equipment and consumables, including reliable electrodes and measurement tools designed for accurate biological signal acquisition. Whether you're conducting clinical studies or developing new monitoring technologies, our solutions help you capture clean, trustworthy data. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
People Also Ask
- Why is the calomel electrode used as a secondary reference electrode? A Practical Guide to Stable Measurements
- What are the general precautions for using a reference electrode? Ensure Stable Potentials for Accurate Data
- What is the reference electrode for mercury mercurous sulfate? A Guide to Chloride-Free Electrochemistry
- Why is a Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) used as a reference electrode in microbial fuel cell research?
- Why and how should the electrodes of an electrolytic cell be calibrated? Ensure Reliable Results


















