At its core, ceramics are sintered to transform a compacted powder into a dense, strong, and stable solid object. This high-temperature process works by causing the individual ceramic particles to bond and fuse together, eliminating the empty spaces between them and fundamentally changing the material's properties. Without sintering, a formed ceramic object would simply be a fragile collection of powder with no practical strength or function.
The purpose of sintering is not merely to harden a ceramic shape. It is a critical engineering step to control the material's internal microstructure, which directly dictates its final density, strength, thermal stability, and overall performance.
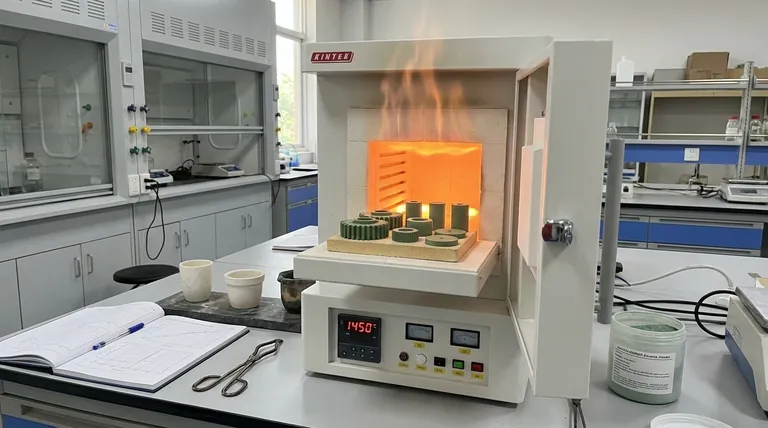

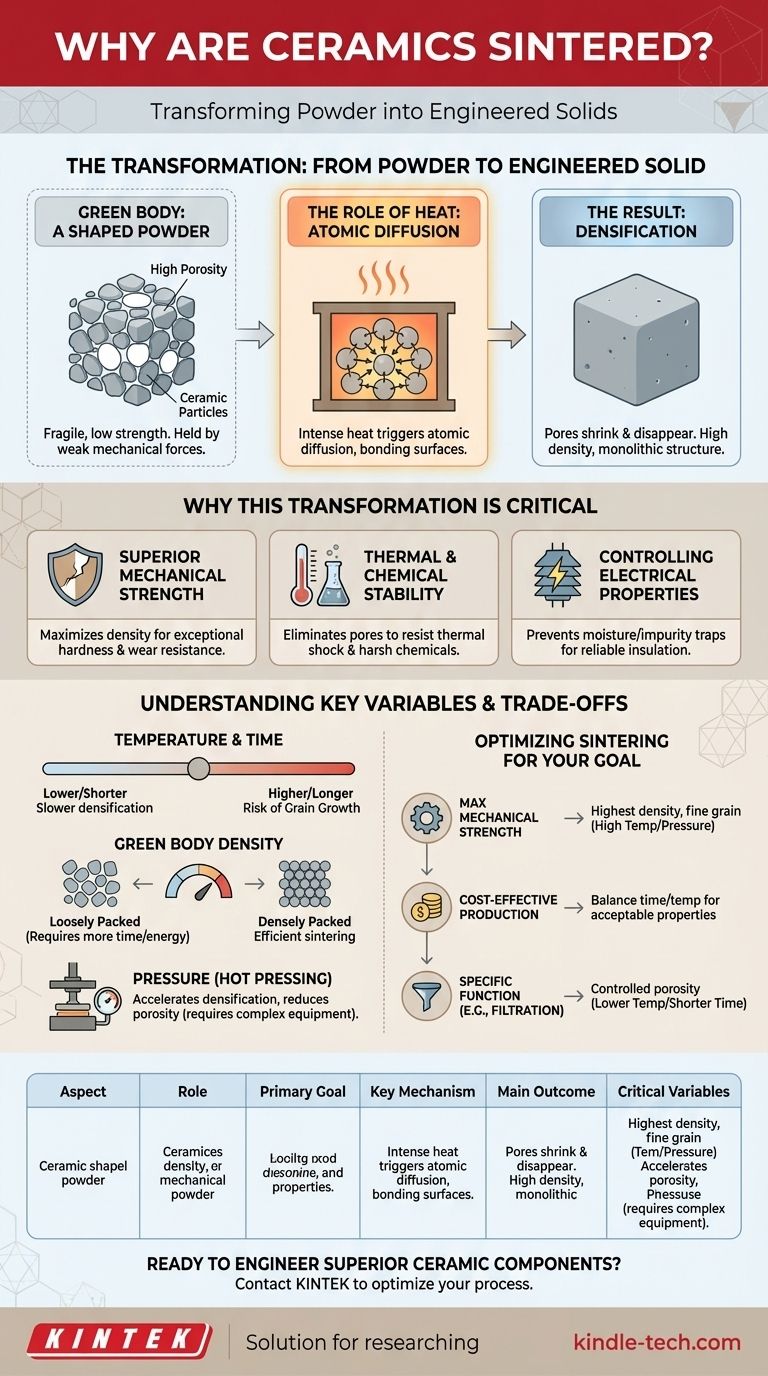
The Transformation: From Powder to Engineered Solid
Sintering is the pivotal step that gives advanced ceramics their remarkable characteristics. It's a process of controlled atomic-level change.
The "Green Body": A Shaped Powder
Before sintering, ceramic powder is compressed into the desired shape. This initial, fragile object is known as a green body or a green compact.
While it has a defined shape, the green body has very low strength and high porosity (the volume of empty space between particles). It is held together only by weak mechanical forces.
The Role of Heat: Driving Atomic Diffusion
The green body is then placed in a furnace and heated to a high temperature, typically below the material's actual melting point.
This intense heat provides the thermal energy needed to trigger atomic diffusion. Atoms on the surfaces of adjacent particles migrate across the boundaries, filling the pores and forming strong chemical bonds between the particles.
The Result: Densification
As the particles fuse, the pores shrink and are eliminated. This process, called densification, causes the entire ceramic part to shrink while its density dramatically increases. The result is a monolithic, polycrystalline material with a stable shape and a uniform internal structure.
Why This Transformation Is Critical
Controlling the densification process allows engineers to precisely tailor the final properties of the ceramic part for its intended application.
Achieving Superior Mechanical Strength
The primary goal of sintering is often to maximize density. A dense, low-porosity ceramic has exceptional hardness and mechanical strength, making it resistant to wear, fracture, and deformation. This is essential for applications like industrial cutting tools and wear-resistant components.
Ensuring Thermal and Chemical Stability
Pores within a ceramic can act as initiation points for cracks, especially under thermal stress. By eliminating this porosity, sintering creates a material that is much more stable at high temperatures and resistant to thermal shock. A dense structure is also less permeable to chemicals, improving its durability in harsh environments like refractory linings.
Controlling Electrical Properties
For applications like electrical insulators, a dense microstructure is critical. Porosity can trap moisture and impurities, degrading the material's ability to resist the flow of electricity. Sintering ensures the high density required for reliable insulation performance.
Understanding the Key Variables and Trade-offs
The final properties of a sintered ceramic are not guaranteed; they are the result of carefully controlling several process variables.
Temperature and Time: A Balancing Act
Higher sintering temperatures and longer durations generally lead to greater densification. However, there is a trade-off. Excessive heat or time can cause grain growth, where smaller crystal grains merge into larger ones, which can sometimes reduce the material's toughness.
The Impact of the Green Body
The process starts before the furnace. A green body that is more densely packed to begin with will sinter more efficiently, requiring less time and energy to achieve full density. The initial particle size also plays a crucial role.
The Role of Pressure
To accelerate densification or achieve it at lower temperatures, pressure can be applied during the heating cycle. This technique, known as hot pressing, helps force particles together, reducing sintering time and final porosity. However, it requires more complex and expensive equipment.
Optimizing Sintering for Your Goal
The ideal sintering strategy depends entirely on the desired outcome for the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum mechanical strength: You must aim for the highest possible density with a controlled, fine-grained microstructure, often requiring high temperatures or pressure-assisted techniques.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production: You must balance sintering time and temperature to achieve acceptable properties without incurring excessive energy costs or requiring complex equipment.
- If your primary focus is a specific function like filtration: You can intentionally use lower temperatures or shorter times to create a strong, bonded structure that retains a controlled level of porosity.
Mastering the principles of sintering is what allows us to engineer ceramic materials with precision for the world's most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Role in Sintering |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Transform compacted powder (green body) into a dense, strong solid. |
| Key Mechanism | Atomic diffusion bonds particles together at high temperatures. |
| Main Outcome | Increased density, strength, thermal stability, and controlled properties. |
| Critical Variables | Temperature, time, initial particle size, and applied pressure. |
Ready to engineer superior ceramic components?
The precise control of sintering parameters is critical to achieving the density, strength, and performance your application demands. At KINTEK, we specialize in the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to perfect your sintering process, from research and development to production.
Our expertise supports laboratories in developing high-performance ceramics for cutting tools, wear-resistant parts, electrical insulators, and more. Let us help you optimize your results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific sintering challenges and discover the right solutions for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the roles of laboratory drying ovens and muffle furnaces in biomass analysis? Precision Thermal Treatment
- Is the sintering process hazardous? Identifying Key Risks and Safety Protocols
- How does a high-temperature muffle furnace work? Achieve Contaminant-Free, Uniform Heating
- How is heat transferred in a furnace? Master Radiation, Convection & Conduction
- What is the burnout cycle on a furnace? Stop This Destructive Overheating Pattern Now



















