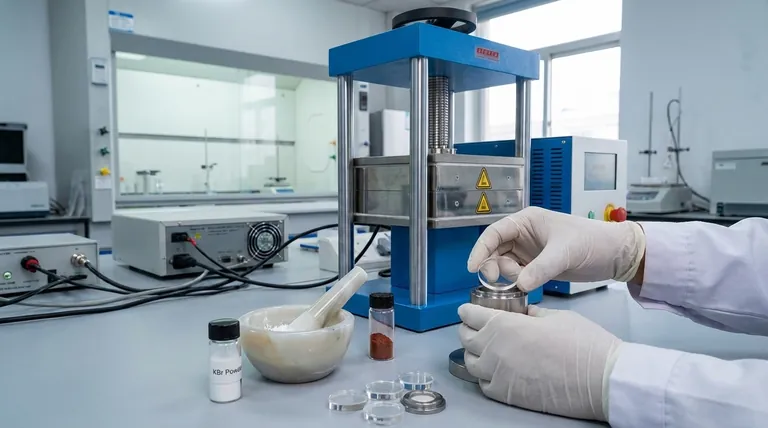
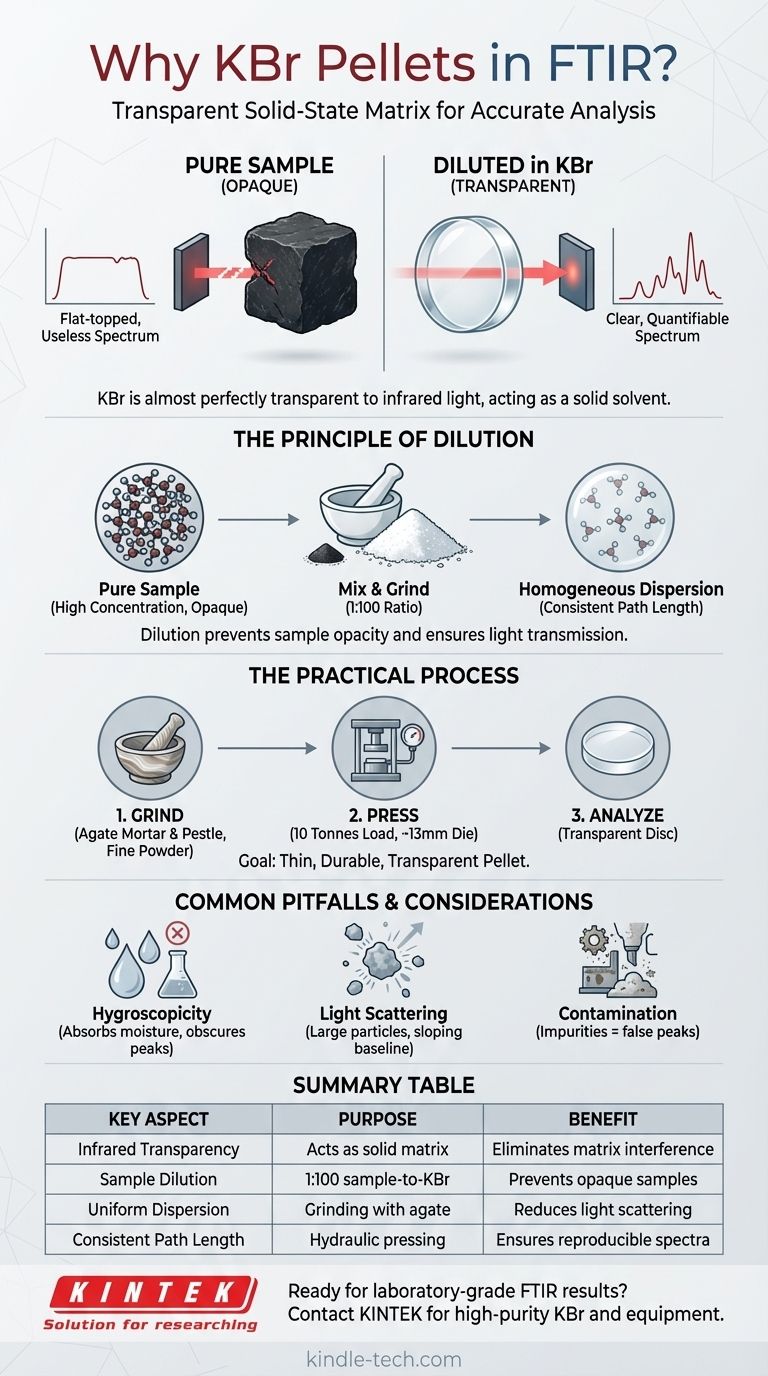
In FTIR spectroscopy, Potassium Bromide (KBr) pellets are used because KBr is almost perfectly transparent to infrared light. This property allows it to act as a solid-state "solvent" or matrix. By thoroughly mixing a small amount of a solid sample with KBr powder and pressing it into a thin disc, the sample can be analyzed without the matrix itself absorbing the light and interfering with the measurement.
The core purpose of a KBr pellet is not just to hold the sample, but to uniformly disperse it in an infrared-transparent medium. This dilution prevents the solid sample from being too concentrated, ensuring the infrared beam can pass through to produce a clear, quantifiable spectrum.

The Principle of Dilution in Solid-State Analysis
Analyzing a solid sample directly is often impossible because most organic and inorganic solids are too concentrated in their pure form. They are effectively opaque to infrared light, absorbing or scattering the entire beam and yielding no useful data. The KBr pellet method solves this fundamental problem.
Why Dilute a Solid Sample?
A pure, powdered sample often has such a high concentration of molecules that it will completely absorb the infrared radiation at its characteristic frequencies. This results in "flat-topped" peaks in the spectrum, where no light passes through at all, making quantitative analysis impossible and qualitative identification difficult.
Creating a "Solid Solution"
The KBr matrix serves to separate the sample particles from one another. By grinding a small amount of sample (typically 1 part) with a much larger amount of KBr (about 100 parts), you create a homogeneous mixture where individual sample molecules are isolated within the transparent KBr.
Ensuring a Consistent Path Length
Pressing this mixture into a pellet of uniform thickness ensures that the infrared beam travels through a consistent amount of sample. This is critical for obtaining a reproducible and high-quality spectrum, similar to how a cuvette of a specific width is used for liquid samples.
The Practical Process of Pellet Preparation
Creating a high-quality KBr pellet is a straightforward but precise technique. The goal is to produce a thin, durable, and transparent disc.
The Standard Ratio
The typical ratio is approximately 1 part sample to 100 parts KBr by weight. For a standard 13 mm (or ½ inch) diameter pellet, this usually translates to a few milligrams of sample mixed with 200-250 mg of high-purity KBr powder.
Grinding for Uniformity
The sample and KBr are combined and ground together into a very fine, homogenous powder. An agate pestle and mortar is preferred because its hard, non-porous surface minimizes contamination and produces the finest particles. This step is critical to reduce light scattering.
Applying High Pressure
The powder mixture is placed into a pellet die and compressed using a hydraulic press. A load of around 10 tonnes is typically applied, which fuses the KBr powder into a solid, glass-like, and transparent disc ready for analysis.
Common Pitfalls and Key Considerations
While effective, the KBr pellet technique has potential issues that can compromise the quality of your results. Awareness of these is key to successful analysis.
The Challenge of Hygroscopicity
The most significant drawback is that KBr is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the atmosphere. This absorbed water has strong absorption bands in the infrared spectrum, which can obscure important peaks from your sample. In humid environments, preparation in a glovebox may be necessary.
Avoiding Light Scattering
If the sample is not ground finely enough, the larger particles will scatter the infrared light rather than absorb it. This leads to a common problem known as a sloping baseline, which reduces the quality of the spectrum and makes interpretation more difficult.
The Risk of Contamination
The KBr used must be of high-purity, FTIR-grade. Any impurities in the KBr or contamination from a dirty pestle and mortar will appear in your spectrum. Always ensure your equipment is impeccably clean before use.
Achieving a High-Quality Spectrum
Your preparation technique should be guided by your analytical goal. A spectrum for simple identification has different requirements than one for precise quantitative measurement.
- If your primary focus is qualitative identification: Ensure the pellet is visually transparent and free of cracks to get a clean spectrum with a flat baseline for library matching.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis: Pay strict attention to weighing the exact sample-to-KBr ratio and achieving a consistent pellet thickness for repeatable results.
- If your sample is sensitive or you're in a humid environment: Work as quickly as possible or use a controlled environment like a glovebox or a vacuum die to minimize water absorption.
Mastering the KBr pellet technique transforms a seemingly simple powder into a window for precise molecular analysis.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Infrared Transparency | Acts as a solid matrix | Eliminates matrix interference |
| Sample Dilution | 1:100 sample-to-KBr ratio | Prevents opaque, concentrated samples |
| Uniform Dispersion | Grinding with agate mortar | Reduces light scattering |
| Consistent Path Length | Hydraulic pressing at ~10 tonnes | Ensures reproducible spectra |
Ready to achieve laboratory-grade FTIR results with precision? KINTEK specializes in high-purity FTIR-grade KBr powders, agate mortars and pestles, and hydraulic pellet presses designed specifically for reliable sample preparation. Our products ensure minimal contamination, consistent pellet formation, and accurate spectral data—perfect for both qualitative identification and quantitative analysis.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your FTIR needs and let our experts help you optimize your solid sample analysis workflow. #ContactForm
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- kbr pellet press 2t
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Pellet Press Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- How accurate is the XRF measurement? Unlock the True Potential of Your Material Analysis
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press assist in sample preparation for verifying MEP theories in hydrogen diffusion?
- How does pressure control of a laboratory hydraulic press affect W-Ti alloys? Optimize Grain Structure & Density
- Why is hydraulic oil bad for the environment? The Hidden Dangers of Petroleum-Based Fluids
- How does a pellet press work? From Raw Material to Dense, Uniform Pellets
- What are the hazards of a hydraulic press? Understanding Crushing, Injection, and Fire Risks
- How do you make XRF pellets? A 4-Step Guide to Flawless Sample Preparation
- What is machine pressed laminate? The Standard Manufacturing Process Explained



















