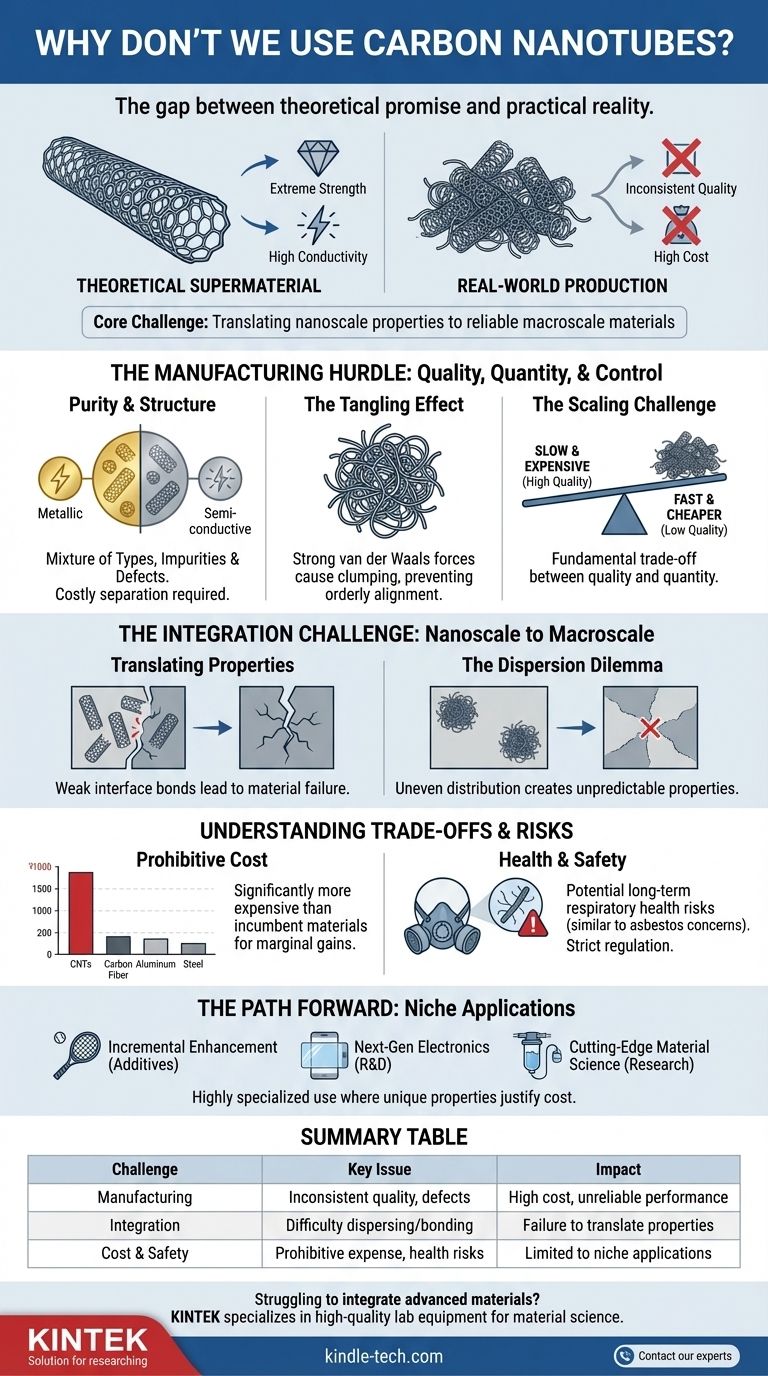
In short, we don't use carbon nanotubes widely because we cannot yet produce them with consistent quality, at a low enough cost, or on a large enough scale. While a single, perfect carbon nanotube (CNT) is a theoretical "supermaterial," the process of manufacturing trillions of them and assembling them into a usable, real-world product negates most of their miraculous properties.
The core challenge is one of translation. The extraordinary strength and conductivity of carbon nanotubes exist at the nanoscale, but we have not yet mastered the engineering required to translate those properties into macroscale materials that are both reliable and economical.

The Manufacturing Hurdle: Quality, Quantity, and Control
The promise of any material is irrelevant if you cannot make it reliably and affordably. For CNTs, the production process itself is the primary bottleneck, creating a cascade of problems that limit their application.
The Purity and Structure Problem
Most large-scale synthesis methods, like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), create a mixture of different types of CNTs. Some are metallic (conductive) while others are semiconducting. For any advanced electronic application, this mixture is unusable without a costly and complex separation process.
Furthermore, these methods often leave behind residual metal catalysts and introduce structural defects (like holes or unwanted atoms) into the nanotube walls. These impurities and defects dramatically weaken the material, undermining its primary benefit.
The Tangling Effect
Due to their extreme length-to-diameter ratio and powerful intermolecular van der Waals forces, CNTs have a powerful tendency to clump and tangle together, like microscopic spaghetti.
This tangling prevents the nanotubes from aligning in an orderly way. For a material to achieve maximum strength or conductivity, its constituent fibers must be aligned parallel to the direction of stress or current flow. Clumped, disordered CNTs cannot provide this.
The Scaling Challenge
The methods that produce the highest-quality, most pristine CNTs (such as arc discharge or laser ablation) are incredibly slow and expensive, making them unsuitable for mass production.
While methods like CVD can produce CNTs in larger quantities, they typically sacrifice quality, resulting in the purity and defect issues mentioned earlier. There is a fundamental trade-off between quality and quantity that has not yet been solved.
The Integration Challenge: From Nanoscale to Macroscale
Even if perfect CNTs could be produced cheaply, a second major hurdle exists: incorporating them effectively into other materials, such as polymers, metals, or ceramics.
Translating Properties is Not Simple
Adding CNTs to a plastic resin doesn't automatically create a super-strong composite. The strength of the final material depends entirely on the interface—the bond between the nanotube surface and the surrounding matrix material.
If this bond is weak, the nanotubes simply act as slippery defects within the material. Under stress, the matrix will break away from the CNTs, and the composite will fail long before the nanotubes themselves are challenged.
The Dispersion Dilemma
To be effective, CNTs must be distributed evenly throughout the host material. Because of their tendency to tangle, achieving good dispersion is extremely difficult.
Poor dispersion results in a material with clumps of CNTs in some areas and none in others. This creates weak points and makes the material's properties unpredictable and unreliable, rendering it useless for critical applications like aerospace or structural components.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Beyond the technical hurdles, practical and economic factors create significant barriers to widespread adoption.
The Prohibitive Cost
High-purity, well-structured carbon nanotubes remain exceptionally expensive compared to incumbent materials. For most applications, traditional materials like carbon fiber, aluminum, or steel are much cheaper and "good enough."
The marginal performance gain offered by today's CNT composites rarely justifies the massive increase in cost and manufacturing complexity.
Potential Health and Safety Concerns
The physical form of CNTs—long, thin, and highly durable fibers—has drawn comparisons to asbestos. There are legitimate concerns that inhaling airborne nanotubes could pose a long-term respiratory health risk.
This has led to strict handling protocols and regulatory uncertainty, adding cost and complexity to their use in industrial environments and discouraging investment.
The Path Forward: Where CNTs Are Making an Impact
Despite these challenges, it is more accurate to say that CNTs are used in a highly specialized manner rather than not at all. They have found success in niche applications where their unique properties justify the cost and complexity.
- If your primary focus is incremental enhancement: CNTs are used in small quantities as additives to polymers to improve electrostatic discharge (ESD) properties, thermal conductivity, and toughness in high-end sporting goods, aerospace components, and electronics.
- If your primary focus is next-generation electronics: CNTs are critical in research and development for transparent conductive films, advanced battery electrodes, and highly sensitive chemical sensors where their unique electrical properties are paramount.
- If your primary focus is cutting-edge material science: They are being explored for advanced water filtration membranes, drug delivery systems, and next-generation composites, though these are largely in the research or early commercialization phase.
Carbon nanotubes have transitioned from a hyped "miracle material" to a sophisticated, high-value additive whose full potential is still locked behind fundamental manufacturing and engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Key Issue | Impact on Use |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Inconsistent quality, mixture of metallic/semiconducting types, defects | High cost, unreliable performance for most applications |
| Integration | Difficulty dispersing and bonding with other materials | Failure to translate nanoscale properties to macroscale products |
| Cost & Safety | Prohibitive expense compared to traditional materials; potential health risks | Limited to niche applications where unique properties justify the cost |
Struggling to integrate advanced materials like carbon nanotubes into your research or product development? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables that support cutting-edge material science. Our expertise can help you navigate the complexities of nanomaterial handling and processing. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs and help you overcome material science challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What are the primary advantages of the CVD method for growing diamonds? Engineering High-Purity Gems and Components
- How does a microwave plasma reactor facilitate the synthesis of diamond? Master MPCVD with Precision Technology
- What are the advantages of microwave plasma? Faster, Purer Processing for Demanding Applications
- How does MPCVD work? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Quality Film Deposition
- How difficult is it to grow a diamond? The Immense Challenge of Atomic-Level Precision



















