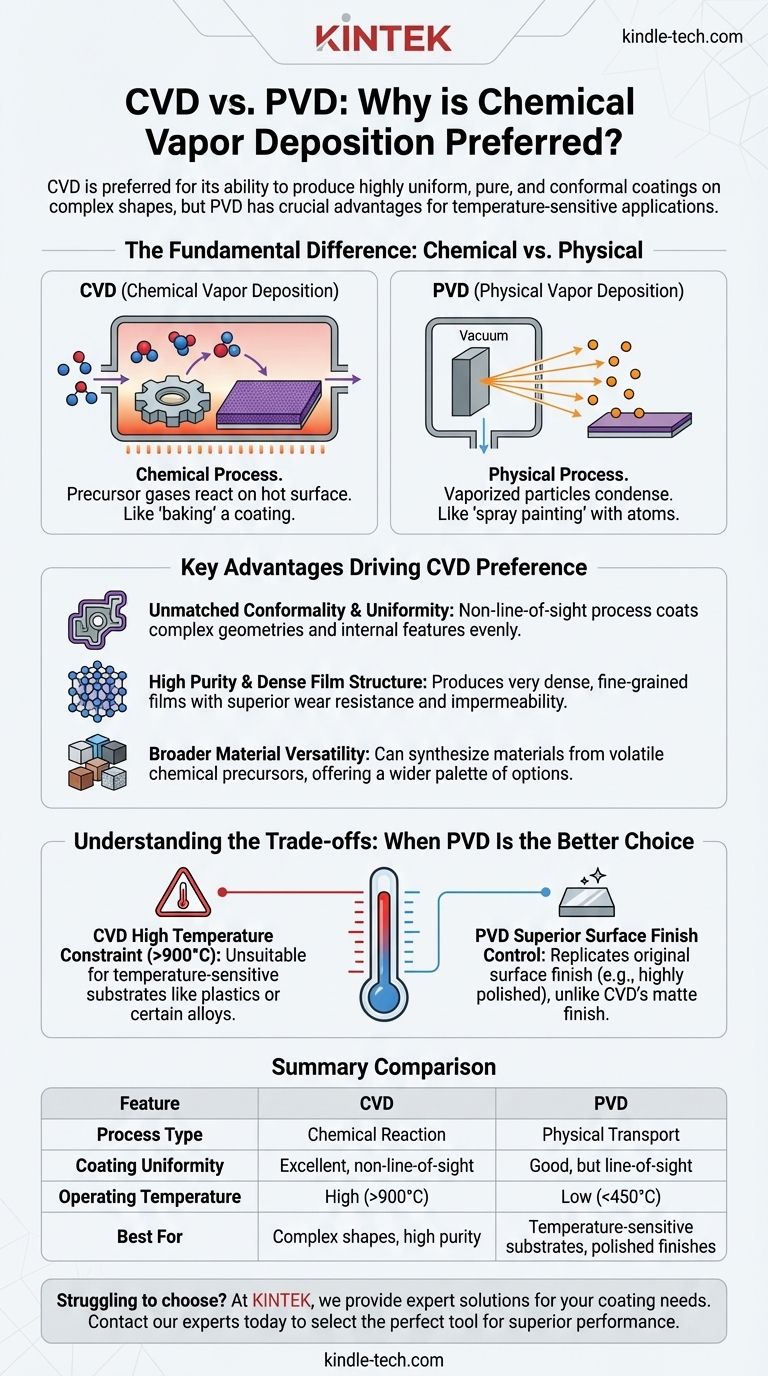
In many industrial contexts, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is preferred over Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) for its unique ability to produce highly uniform, pure, and conformal coatings on complex shapes. Unlike line-of-sight PVD processes, CVD uses a chemical reaction from precursor gases that can penetrate and evenly coat intricate surfaces, deep holes, and internal features, often at a lower operational cost for high-volume production.
The choice between CVD and PVD is not a matter of universal superiority, but a critical engineering decision. The core trade-off is between CVD's exceptional coverage and film quality versus PVD's crucial low-temperature processing and surface replication.
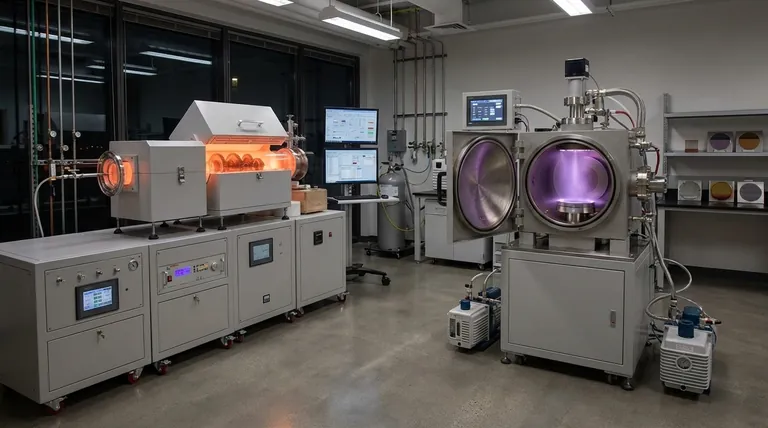

The Fundamental Difference: Chemical Reaction vs. Physical Transport
To understand why one is chosen over the other, you must first grasp their fundamentally different mechanisms.
What is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)?
CVD is a chemical process. Precursor gases are introduced into a reaction chamber where the substrate is heated to a high temperature.
These gases decompose and react on the hot surface, forming a new solid material as a thin film. Think of it as "baking" a coating onto a surface; the ingredients (gases) transform chemically to create the final layer.
What is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)?
PVD is a physical process. It takes place in a vacuum, where a solid source material (a "target") is bombarded with energy, causing atoms or molecules to be ejected.
These vaporized particles then travel in a straight line and condense on the substrate, physically building up the coating layer by layer. This is more analogous to "spray painting" with atoms; there is no chemical change in the coating material itself.
Key Advantages Driving CVD Preference
The chemical nature of CVD gives it several distinct advantages that make it the preferred method for specific, demanding applications.
Unmatched Conformality and Uniformity
Because CVD relies on a gas that fills the entire chamber, it is not a line-of-sight process. The reactive gas can flow into and coat complex geometries, sharp corners, and internal channels with exceptional uniformity.
PVD, being a line-of-sight physical process, struggles to coat areas that are not directly exposed to the source target, resulting in thinner or non-existent coatings in "shadowed" regions.
High Purity and Dense Film Structure
The CVD process can produce films of extremely high purity. The resulting coatings are often very dense, fine-grained, and harder than materials produced by other methods.
This results in excellent performance characteristics, including superior wear resistance and impermeability.
Broader Material Versatility
CVD can be used with a wide range of elements and compounds, including those that are very difficult to evaporate for use in a PVD process.
If a material can be synthesized from a volatile chemical precursor, it can likely be deposited via CVD, opening up a wider palette of material options for engineers.
Cost-Effectiveness and High Deposition Rates
For many applications, CVD systems can be more cost-effective and offer higher deposition rates than PVD, making them well-suited for large-scale manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs: When PVD Is the Better Choice
Asserting a universal preference for CVD would be a mistake. Its primary drawback—heat—makes PVD the superior and sometimes only choice in many common scenarios.
The Critical Constraint of Temperature
The single greatest limitation of CVD is its high processing temperature, which can reach 900°C or higher. This extreme heat makes it completely unsuitable for temperature-sensitive substrates.
Materials like plastics, aluminum alloys, or any pre-hardened steel that would be softened by the heat cannot be coated with CVD. Here, PVD's much lower operating temperatures (often below 450°C) make it the clear and necessary choice.
Superior Surface Finish Control
PVD coatings physically replicate the substrate's original surface finish. If you coat a highly polished part with PVD, you will get a highly polished coating.
CVD coatings, by contrast, typically result in a matte or slightly rough finish due to their crystal growth mechanism. Achieving a polished look requires post-coating processing, adding time and cost.
Operational Safety and Simplicity
Many of the precursor gases used in CVD are toxic, flammable, or corrosive, creating significant challenges for material handling, storage, and safety compliance.
PVD processes generally use solid, inert targets, making the operation significantly safer and procedurally simpler.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be driven by your substrate material and your primary performance goal.
- If your primary focus is coating complex geometries or achieving the highest purity: CVD is the clear choice due to its non-line-of-sight nature and chemical reaction process.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive materials like plastics or certain alloys: PVD is your only viable option because its low-temperature process will not damage the substrate.
- If your primary focus is preserving a highly polished surface finish: PVD is superior as it directly replicates the substrate's original finish without requiring additional polishing.
- If your primary focus is operator safety and process simplicity: PVD presents fewer hazards and is generally a more straightforward process to manage than CVD.
Ultimately, understanding the core mechanism—chemical reaction versus physical transport—is the key to selecting the right tool for your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Chemical Reaction | Physical Transport |
| Coating Uniformity | Excellent, non-line-of-sight | Good, but line-of-sight |
| Operating Temperature | High (often >900°C) | Low (often <450°C) |
| Best For | Complex shapes, high purity | Temperature-sensitive substrates, polished finishes |
| Primary Limitation | High temperature damages some materials | Struggles with deep holes and internal features |
Struggling to choose the right coating technology for your lab's specific materials and geometries?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing expert solutions for your laboratory equipment needs, including advanced coating systems. Whether your project requires the high-temperature, conformal capabilities of CVD or the low-temperature precision of PVD, our team can help you select the perfect tool to ensure superior performance and efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment can enhance your research and production outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- Why is PECVD better than CVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the precursor gas in PECVD? The Key to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between thermal CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- What is the difference between CVD and PVD process? A Guide to Choosing the Right Coating Method
- What are the examples of CVD method? Discover the Versatile Applications of Chemical Vapor Deposition



















