At its core, flux is a chemical cleaning agent that is absolutely critical for successful brazing. It removes the invisible but stubborn oxide layers from the surfaces of the metals being joined, which would otherwise prevent the molten filler metal from forming a strong, continuous bond.
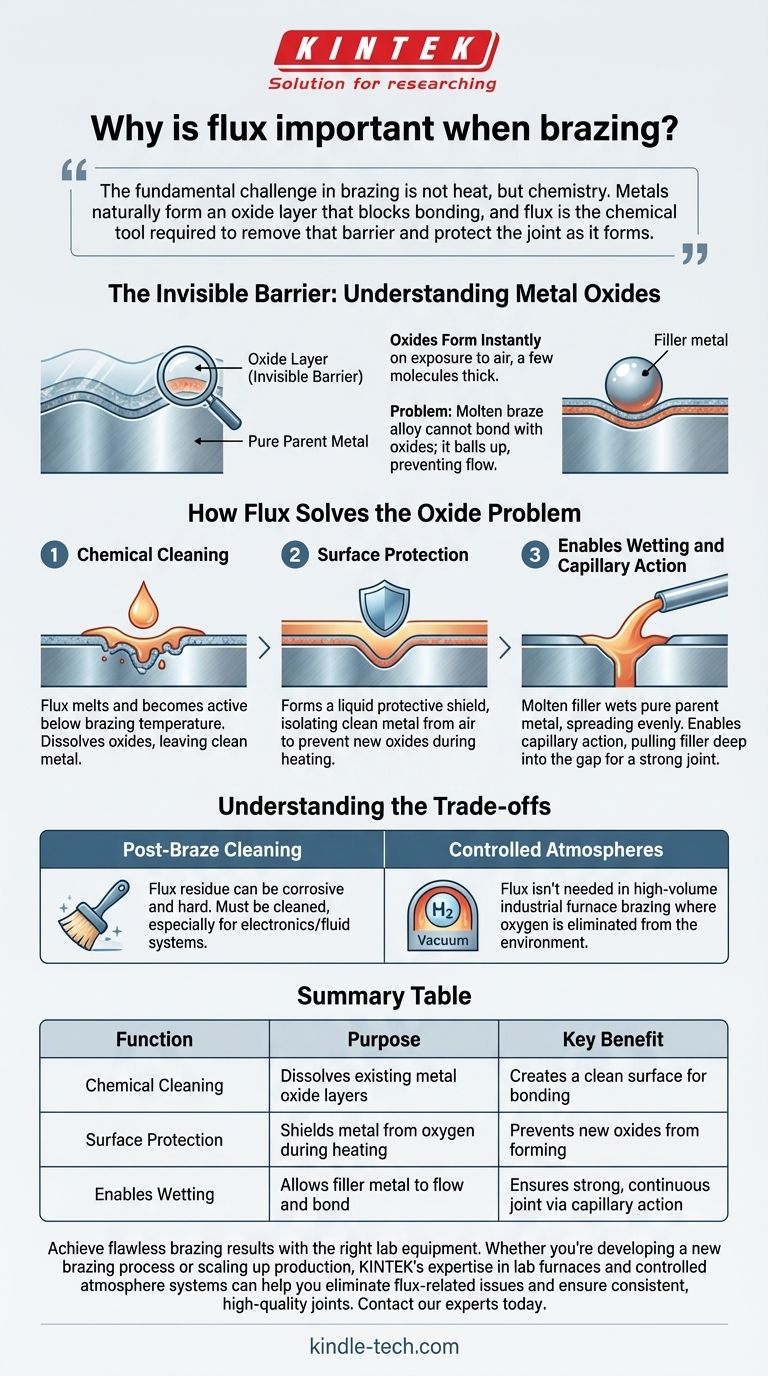
The fundamental challenge in brazing is not heat, but chemistry. Metals naturally form an oxide layer that blocks bonding, and flux is the chemical tool required to remove that barrier and protect the joint as it forms.
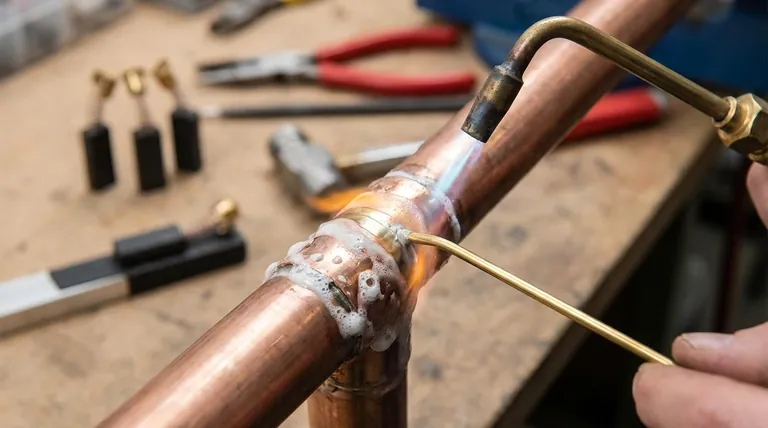

The Invisible Barrier: Understanding Metal Oxides
To grasp the importance of flux, you must first understand the problem it solves. The enemy of a good braze joint is oxidation, a natural chemical reaction.
Why Oxides Form Instantly
Nearly all metals, when exposed to the oxygen in the air, immediately form a thin, transparent, and chemically stable layer of metal oxide on their surface.
This layer is often only a few molecules thick, but it completely covers the pure parent metal underneath.
The Problem with the Oxide Layer
This oxide layer acts as a wall. Molten braze alloy cannot bond with metal oxide; it can only bond with the pure metal beneath it.
Without a way to remove this barrier, the filler metal will simply ball up on the surface, refusing to flow or "wet" the parent metals. This results in a weak, incomplete, or nonexistent joint.
How Flux Solves the Oxide Problem
Flux is a multi-stage solution designed specifically to defeat the oxide problem before and during the heating process. It performs three critical functions in sequence.
Step 1: Chemical Cleaning
Flux is engineered to melt and become active at a temperature below the melting point of the filler alloy.
As it melts, it spreads across the joint area and aggressively dissolves the metal oxides, leaving behind a chemically clean metal surface.
Step 2: Surface Protection
Once the flux has cleaned the surface, its liquid layer forms a protective shield over the parent metals.
This shield isolates the clean metal from the surrounding air, preventing new oxides from forming as the parts are heated to the final brazing temperature.
Step 3: Enabling Wetting and Capillary Action
With the oxide barrier removed and the surface protected, the molten filler metal is now free to make intimate contact with the pure parent metal.
This allows the filler to "wet" the surfaces—spreading thinly and evenly. More importantly, it enables capillary action, the force that pulls the molten filler deep into the tight gap between the two parts, ensuring a full, strong, and void-free joint.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential for most methods, flux is not a perfect solution and introduces its own considerations. Understanding its limitations is key to mastering the brazing process.
The Need for Post-Braze Cleaning
After cooling, the remaining flux residue can be corrosive and is often hard and glass-like.
For many applications, especially in electronics or fluid systems, this residue must be thoroughly cleaned from the assembly to prevent long-term corrosion or contamination.
When Flux Isn't Necessary: Controlled Atmospheres
The function of flux is to remove and prevent oxides. In certain industrial processes, like furnace brazing, this is achieved differently.
By brazing parts inside a furnace filled with a controlled atmosphere (such as hydrogen or a vacuum), oxygen is eliminated from the environment entirely. Since no oxides can form, no flux is needed to remove them.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your brazing method directly dictates the need for flux. The goal is always a clean, oxide-free surface, but how you achieve it can vary.
- If your primary focus is torch, induction, or resistance brazing: Using the correct flux is non-negotiable. It is the only practical way to ensure a chemically clean surface for the filler metal to bond to.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial furnace brazing: The controlled atmosphere of the furnace performs the function of flux, making a separate chemical application unnecessary.
Ultimately, understanding that flux is a tool for chemical cleaning empowers you to create consistently strong and reliable brazed joints.
Summary Table:
| Function | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Cleaning | Dissolves existing metal oxide layers | Creates a clean surface for bonding |
| Surface Protection | Shields metal from oxygen during heating | Prevents new oxides from forming |
| Enables Wetting | Allows filler metal to flow and bond | Ensures strong, continuous joint via capillary action |
Achieve flawless brazing results with the right lab equipment. Whether you're developing a new brazing process or scaling up production, KINTEK's expertise in lab furnaces and controlled atmosphere systems can help you eliminate flux-related issues and ensure consistent, high-quality joints. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your brazing workflow and improve joint reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Conductive Carbon Fiber Brush for Static Removal and Cleaning
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What role does loading equipment play in strain field monitoring verification? Precision Control for Sensor Validation
- What are the basic characteristics requirements in heat treatment? Master Temperature, Time, and Cooling
- What is plasma pyrolysis used for? Transforming Hazardous Waste into Clean Energy
- What are the challenges of welding stainless steel? Overcome Warping, Sensitization, and Contamination
- What are the advantages of using HIP for tungsten-steel joints? Achieve 97%+ Density for Complex FGM Structures
- How many types of hardening techniques are there? A Multi-Layered Security Strategy Explained
- How does a precision heating system influence the coating quality of soft magnetic composite materials? Expert Insights
- What is the future for biomass? A Strategic Shift to High-Value Fuels and Products



















