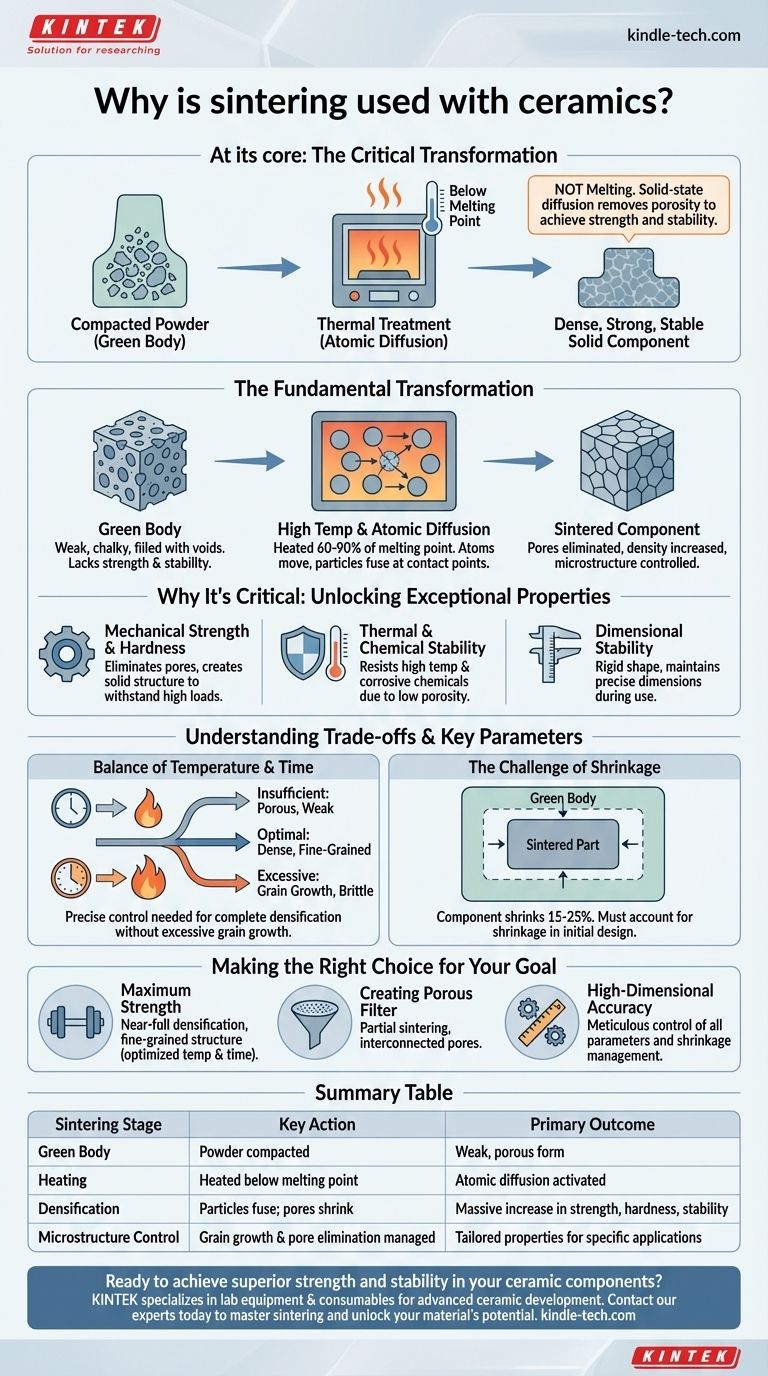
At its core, sintering is the critical process used to transform a compacted, fragile ceramic powder into a dense, strong, and stable solid component. This thermal treatment, conducted below the material's melting point, uses atomic diffusion to fuse individual particles together, eliminating the spaces between them and creating a unified, robust structure with specific, engineered properties.
Sintering solves the fundamental challenge of ceramic manufacturing: how to create a strong, solid object from a loose powder without melting it. It is not a melting process, but a solid-state diffusion process that systematically removes porosity to achieve strength and stability.
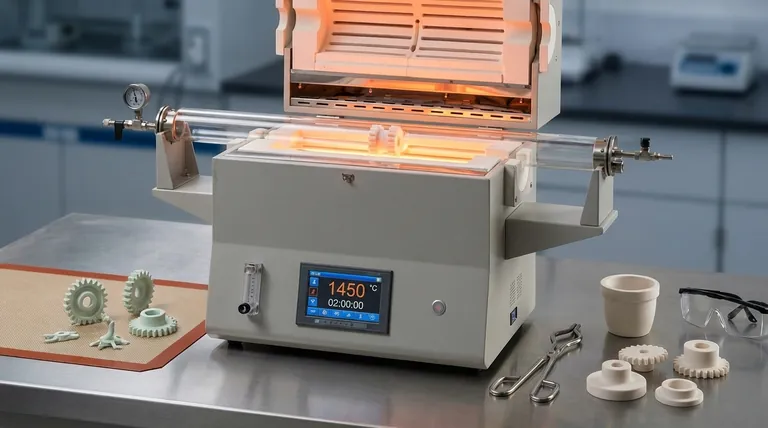

The Fundamental Transformation: From Powder to Solid
To understand why sintering is indispensable, you must first visualize the material's journey from a loose collection of particles to a finished, high-performance ceramic.
The "Green Body" Starting Point
The process begins by compacting ceramic powder into a desired shape. This initial form, known as a "green body," is weak, chalky, and filled with tiny voids or pores between the particles.
While it has the right shape, a green body lacks the mechanical strength, density, and thermal stability required for nearly any practical application.
The Role of High Temperature
The green body is then heated in a furnace to a high temperature, typically between 60% and 90% of the ceramic's absolute melting point.
This heat acts as a catalyst. It gives the atoms within the ceramic particles enough energy to move, but not enough to cause a phase change into a liquid.
The Driving Force: Atomic Diffusion
With this elevated thermal energy, atoms begin to move from areas of high concentration (the bulk of a particle) to areas of low concentration (the contact points and necks between particles). This process is called atomic diffusion.
This mass transfer effectively "welds" the particles together at their points of contact. These contact points grow, pulling the particle centers closer together.
The Result: Densification and Microstructure Control
As the particles fuse and draw closer, the pores between them shrink and are eventually eliminated. This process, called densification, dramatically increases the material's density.
The final arrangement of the fused grains and any remaining pores is the material's microstructure. Sintering allows engineers to precisely control this microstructure, which in turn dictates the final properties of the ceramic.
Why This Transformation Is Critical
The change from a porous green body to a dense, sintered part is what unlocks the exceptional properties that ceramics are known for.
Achieving Mechanical Strength and Hardness
The primary benefit of sintering is a massive increase in mechanical strength and hardness. Pores are natural stress concentrators and weak points where cracks can easily form and propagate.
By eliminating these pores, sintering creates a solid, continuous structure that can withstand much higher mechanical loads.
Gaining Thermal and Chemical Stability
A dense, sintered ceramic is also far more stable when exposed to high temperatures or corrosive chemicals. The unified, low-porosity structure minimizes the surface area available for chemical attack and improves thermal conductivity.
Securing Dimensional Stability
The sintering process creates a rigid, stable shape that will not deform under its own weight or minor loads. This ensures the component maintains its precise dimensions during use.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Parameters
Sintering is a process of careful control. The final outcome is highly sensitive to several key variables, and balancing them is essential.
The Balance of Temperature and Time
Controlling the sintering temperature and duration is critical. Insufficient heat or time results in incomplete densification, leaving behind a porous and weak part.
Conversely, excessive heat or time can lead to grain growth, where smaller grains merge into larger ones. While this increases density, overly large grains can make the ceramic brittle and prone to fracture.
The Challenge of Shrinkage
As densification removes the voids between particles, the entire component shrinks. This shrinkage can be significant, often ranging from 15% to 25% in linear dimensions.
Engineers must precisely calculate and account for this shrinkage during the initial design and mold-making stage to achieve the final desired dimensions. Uncontrolled shrinkage leads to warped or out-of-spec parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Controlling the sintering process allows you to tailor the ceramic's final properties for a specific application.
- If your primary focus is maximum mechanical strength: You will aim for near-full densification with a controlled, fine-grained microstructure by optimizing temperature and time.
- If your primary focus is creating a porous filter: You will use partial or incomplete sintering to create a strong body with a network of interconnected pores.
- If your primary focus is high-dimensional accuracy: You must meticulously control the raw powder characteristics, green body compaction pressure, and the entire heating and cooling cycle to manage shrinkage predictably.
Ultimately, sintering is the essential engineering step that unlocks the inherent potential of ceramic materials, transforming them from simple powder into highly functional, resilient components.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Stage | Key Action | Primary Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Green Body | Powder is compacted into shape. | Weak, porous form with the desired geometry. |
| Heating | Heated below melting point. | Atomic diffusion is activated. |
| Densification | Particles fuse; pores shrink. | Massive increase in strength, hardness, and stability. |
| Microstructure Control | Grain growth and pore elimination are managed. | Tailored properties for specific applications (e.g., dense vs. porous). |
Ready to achieve superior strength and stability in your ceramic components?
The precise control of the sintering process is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced ceramic development and production, helping you optimize every parameter for your specific goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you master sintering and unlock the full potential of your ceramic materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How is temperature controlled in a furnace? Mastering Precise Thermal Management
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?



















