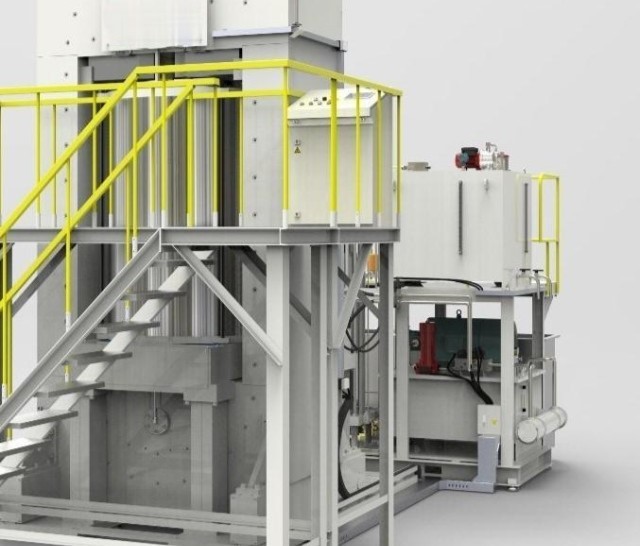
Introduction: Explanation of Isostatic Pressing
Isostatic pressing is a process used in the production of high-performance materials and components. It involves applying uniform pressure on all sides of a material or part, resulting in a more uniform density and improved mechanical properties. There are two types of isostatic pressing techniques: cold isostatic pressing (CIP) and hot isostatic pressing (HIP). CIP is conducted at room temperature and is suitable for materials that can withstand high pressure but cannot be exposed to high temperatures. HIP, on the other hand, is conducted at high temperatures and high pressures and is used for materials that require both high pressure and high-temperature treatment.
Table of Contents
Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP): Advantages & Applications
Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) is a process of compacting powdered materials into a solid homogeneous mass before machining or sintering. CIP involves the use of a pressurized fluid to apply uniform pressure to a sample inside a pressure vessel at room temperature. This process offers several advantages over other methods, making it a popular choice in many industries.
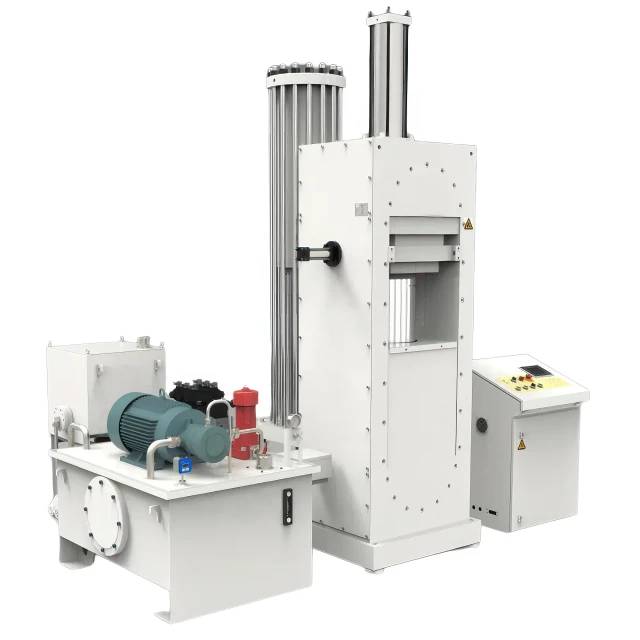

Advantages of Cold Isostatic Pressing
Uniform Density
CIP ensures that materials have a uniform density, which means that there will be uniform shrinkage when the material is going through other processes such as sintering. The uniform density can be attributed to the fact that the pressure used in CIP reaches every part of the material with equal magnitude.
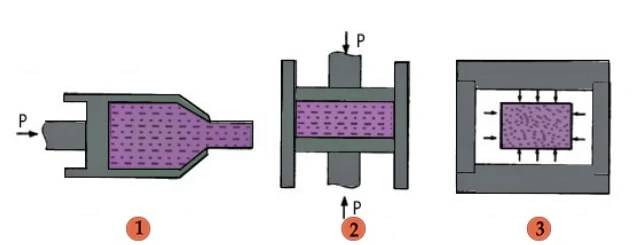
Uniform Strength
Since the pressure used to compact the materials is equal in all directions, the material has uniform strength. Materials with uniform strength are usually more efficient than those without uniform strength.
Versatility
CIP can be used to produce difficult shapes which can not be produced by other methods. In addition, it can be used to produce large-sized materials. The only limitation to the size of materials produced by this method is the size of the pressure vessel.
Corrosion Resistance
Cold isostatic pressing improves the corrosion resistance of a material. Thus materials that undergo this process have a longer lifespan than most other materials.
Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of cold isostatic pressed materials are improved. Some of the properties improved include ductility and strength.
Applications of CIP
Powder Metallurgy
CIP is used in powder metallurgy for the compacting step that comes just before the sintering step. In powder metallurgy, CIP is often used to produce complex shapes and dimensions.
Refractory Metals
CIP is used to produce refractory metals such as tungsten, molybdenum, and tantalum. Tungsten, for example, is used to manufacture wires for filaments in the lamp industry.
Sputtering Targets
CIP can press indium tin oxide (ITO) powder into large ceramic preforms, which are then sintered under certain conditions. This method can theoretically produce ceramic targets with a density of 95%.

Automobiles
CIP is used in manufacturing automobile components such as bearings and oil pump gears.
In conclusion, Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) is a versatile and efficient method that offers several advantages in terms of cost, complexity, and material compatibility. Its uniformity in density and strength, versatility, corrosion resistance, and improved mechanical properties make it a popular choice in many industries. CIP has a wide range of applications including powder metallurgy, refractory metals, sputtering targets, and automobile components.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP): Advantages & Applications
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is a material processing technique that involves compressing materials using high temperatures and isostatic pressure. The HIP method is often preferred over the Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP) method due to its ability to produce stronger and more uniform materials. This section will discuss the advantages and applications of HIP.

Advantages of Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
One of the significant advantages of HIP is that it can create materials with extremely high densities and uniform microstructures. The combination of heat and pressure allows for greater control over the final product. Additionally, HIP can produce complex shapes and geometries that are difficult or impossible to achieve with other methods.
HIP is also used in the aerospace and medical industries to create high-strength components that can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. HIP is often used to create turbine blades and other critical components for aircraft engines.
Applications of Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
HIP is applied in a wide range of fields including;
- Pressure sintering of powder
- Diffusion bonding of different types of materials
- Removal of residual pores in sintered items
- Removal of inner defects of castings
- Rejuvenation of parts damaged by fatigue or creep
- High-pressure impregnated carbonization method
HIP is also used to produce superalloy components for the aerospace industry. It is used for the densification of WC cutting tools and PM tool steels. HIP is also used to close internal porosity and improve properties in superalloy and Ti alloy castings for the aerospace industry.

HIP Treatment
Materials need various treatments depending on the situation. The most typical methods include 'Capsule Method' and 'Capsule Free Method'.
'Capsule Method' is to carry out HIP after enclosing powder or a body molded from powder in a gas-tight capsule and evacuating the capsule.
Conclusion
In conclusion, HIP is an excellent method for producing high-strength, uniform materials. It has advantages over other methods, including the ability to create complex shapes and geometries and produce materials with extremely high densities and uniform microstructures. HIP is widely applied in various fields, including powder metallurgy, aerospace, and medical industries.
Comparison: Cold Isostatic Pressing vs. Hot Isostatic Pressing
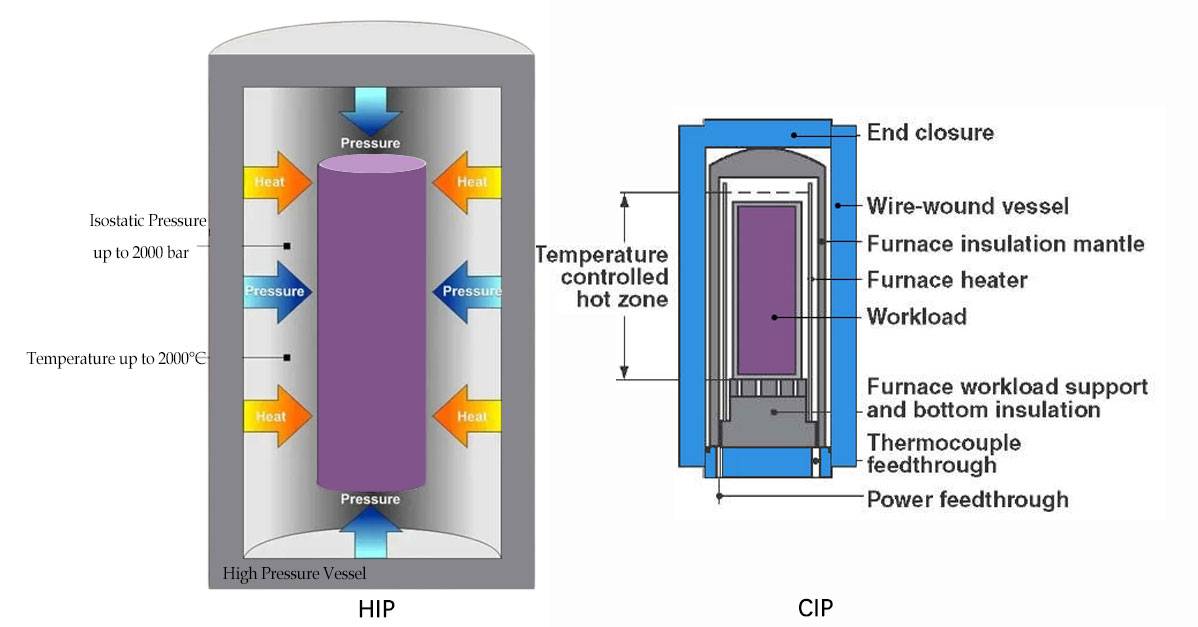
Comparison
The primary difference between the two methods is the temperature at which the pressure is applied. CIP is generally preferred for the production of ceramics and metallic powders, while HIP is preferred for the production of high-performance components. Both CIP and HIP have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two methods depends on the specific application and material requirements.
CIP provides increased and more uniform density at a given compaction pressure and relative freedom from compact defects when applied to brittle or fine powders. It can be used to compact more complex shapes than possible with uniaxial pressing. CIP is suitable for temperature sensitive materials such as ceramics, metal powders, etc.
HIP offers improved mechanical properties such as impact resistance, ductility, and fatigue strength as a result of internal porosity elimination. It achieves a fine grain structure that achieves part uniformity. HIP can produce homogeneous microstructures, and enables diffusion bonding of similar and dissimilar materials, either in powder or solid form. Components can be designed and fabricated with a reduction, or complete elimination, in the number of welds and related inspections.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both CIP and HIP have their advantages and disadvantages. The decision to use CIP or HIP should be based on the desired properties of the final product, as well as the cost and time constraints of the manufacturing process. Ultimately, the choice between CIP and HIP depends on the specific application and material requirements.
Which is Better?: Factors to Consider
When it comes to choosing between cold isostatic pressing (CIP) and hot isostatic pressing (HIP), a number of factors should be considered. Here are some important factors to keep in mind when making this decision:
Material Type
One of the most important factors to consider is the type of material being shaped. CIP is preferred for materials that are sensitive to heat or have low melting points, while HIP is better suited for materials that require high temperatures to achieve proper compaction. For instance, CIP is commonly used for ceramics, composites, and polymers, while HIP is a popular choice for metals and alloys.

Required Properties
The choice between CIP and HIP also depends on the desired properties of the final product. HIP is known for producing parts with higher density and strength, making it ideal for high-performance applications. However, the high temperatures involved in HIP can also cause thermal degradation or oxidation of some materials. CIP, on the other hand, can produce parts with lower densities, but it is less likely to cause thermal damage to the material.
Cost
Finally, cost is always a consideration when choosing between CIP and HIP. CIP is generally less expensive than HIP due to lower operating temperatures and simpler equipment requirements. However, the cost of CIP can increase when materials with high powder costs or complex shapes are involved.
In conclusion, the choice between CIP and HIP depends on a number of factors, including material type, required properties, production volume, component complexity, and cost. Careful consideration of these factors is important to ensure that the right method is chosen to achieve the desired outcomes.
Conclusion: Summary of Key Points
In conclusion, both cold isostatic pressing (CIP) and hot isostatic pressing (HIP) offer unique advantages and applications in the field of material science and engineering. CIP is ideal for producing high-density components with complex shapes, while HIP is best for creating homogeneous structures with improved mechanical properties. Choosing between CIP and HIP depends on several factors, including the material properties, component design, and production requirements. Ultimately, the decision should be based on a careful evaluation of the benefits and limitations of each process.
Related Products
- Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP for Small Workpiece Production 400Mpa
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Vacuum Cold Mounting Machine for Sample Preparation
Related Articles
- How Isostatic Presses Help Eliminate Defects in Materials
- Zirconia Ceramic Rod Production Processes: Isostatic Pressing vs. Dry Pressing
- Isostatic Pressing Technology: Principles, Classification, and Applications
- Understanding the Isostatic Pressing Process and its Types
- Understanding Isostatic Pressing: Process, Benefits, Limitations, and Applications















