Design Principle of Lithium Battery Reference Electrode
Key Design Principles
The design principles of reference electrodes for lithium batteries are paramount to ensuring accurate and reliable measurements. These principles encompass three primary attributes: potential stability, electrochemical inertness, and compatibility with electrolyte solutions.
-
Potential Stability: A stable potential is crucial for the accuracy of electrochemical measurements. Fluctuations in potential can lead to erroneous data, compromising the integrity of battery performance evaluations.
-
Electrochemical Inertness: The material used must not participate in the electrochemical reactions occurring within the battery. This inertness ensures that the reference electrode does not interfere with the battery's performance, providing a true and consistent reference point.
-
Compatibility with Electrolyte: The reference electrode must be chemically compatible with the electrolyte solution used in the battery. This compatibility prevents any unwanted reactions that could alter the electrolyte's composition or the electrode's performance.
Common materials used in reference electrodes for lithium batteries include lithium/lithium ion and LiFePO4. These materials are chosen for their ability to meet the stringent requirements of potential stability, electrochemical inertness, and compatibility with various electrolyte solutions.
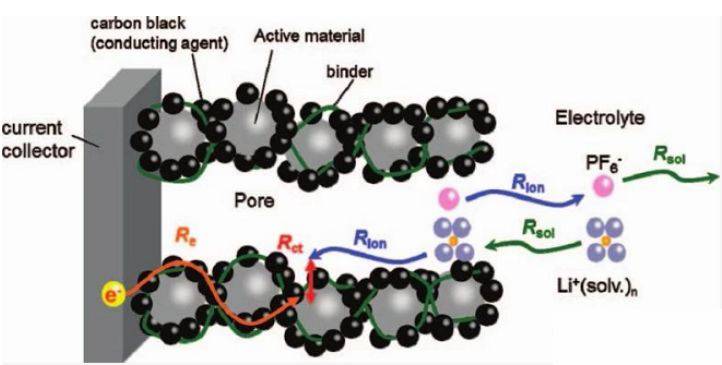
Material Considerations
When designing a reference electrode for lithium batteries, the choice of material is paramount. The material must exhibit robust electrochemical properties and exceptional stability to guarantee precise battery test results. This involves selecting materials that not only maintain a stable potential over extended periods but also demonstrate electrochemical inertness, meaning they do not react with the electrolyte or other battery components.
Key Properties of Ideal Materials
- Potential Stability: The material should maintain a consistent potential over time and under varying conditions, ensuring reliable test outcomes.
- Electrochemical Inertness: The material must not participate in unwanted side reactions with the electrolyte or other battery components, preserving the integrity of the test environment.
- Compatibility with Electrolyte: The material should be chemically compatible with the electrolyte, preventing any degradation or contamination that could skew test results.
Common Materials and Their Suitability
| Material | Potential Stability | Electrochemical Inertness | Compatibility with Electrolyte |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium/Lithium Ion | High | High | High |
| LiFePO4 | Moderate | High | High |
| Calomel | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Silver | Silver Chloride | High | High |
| Mercury | Mercuric Oxide | High | Moderate |
Each of these materials has its own set of advantages and limitations, making them suitable for different types of battery tests. For instance, while lithium/lithium ion and LiFePO4 are highly stable and inert, they may not be ideal for all electrolyte types. Conversely, calomel and silver | silver chloride electrodes offer excellent potential stability but may have limitations in compatibility.
In summary, the selection of material for a reference electrode is a critical decision that directly impacts the accuracy and reliability of lithium battery tests. By carefully considering the electrochemical properties and stability of the material, researchers can ensure that their tests yield precise and meaningful results.
Common Types of Lithium Battery Reference Electrode
Various Electrode Types
In the realm of lithium battery research and testing, a variety of reference electrode types are employed, each tailored to specific applications and tests. The most common types include calomel, silver | silver chloride, mercury | mercuric oxide, lithium/lithium ion, and LiFePO4 electrodes. These electrodes are chosen based on their unique electrochemical properties and the requirements of the tests they are intended to support.
| Electrode Type | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Calomel | Provides stable potential and is suitable for low-temperature applications. |
| Silver | Silver Chloride |
| Mercury | Mercuric Oxide |
| Lithium/Lithium Ion | Widely used due to its compatibility with lithium-based batteries. |
| LiFePO4 | Offers excellent cycling stability and is favored in long-term tests. |
Each of these electrode types has its own set of advantages, making them suitable for different aspects of battery testing and research. The choice of electrode type is critical for ensuring accurate and reliable results in evaluating the performance of lithium batteries.
Selection Criteria
The selection of reference electrode types is a pivotal decision in the evaluation and research of lithium battery performance. The choice of electrode directly impacts the accuracy and reliability of the data obtained from electrochemical tests such as cyclic voltammetry and constant current charge/discharge cycles. Each type of reference electrode, including calomel, silver | silver chloride, mercury | mercuric oxide, lithium/lithium ion, and LiFePO4 electrodes, possesses unique electrochemical properties and advantages that make them suitable for specific testing scenarios.
For instance, lithium/lithium ion electrodes are highly stable and inert, making them ideal for long-term studies where potential stability is critical. Conversely, LiFePO4 electrodes offer excellent compatibility with various electrolytes, ensuring accurate measurements across different battery chemistries. The selection process must therefore consider not only the inherent properties of the electrode material but also its compatibility with the electrolyte and the specific testing conditions.
Moreover, the selection criteria extend beyond just material properties to include factors such as ease of fabrication, cost-effectiveness, and operational durability. This holistic approach ensures that the chosen reference electrode not only meets the immediate testing requirements but also supports broader research objectives and potential future advancements in battery technology.
Application of Reference Electrode for Lithium Battery
Electrochemical Testing
Reference electrodes play a pivotal role in various electrochemical tests, such as cyclic voltammetry and constant current charge/discharge cycles. These tests are essential for measuring potential differences and evaluating the performance of lithium batteries. By providing a stable reference point, these electrodes allow researchers to accurately gauge the electrochemical behavior of battery materials.

In cyclic voltammetry, the reference electrode helps in tracing the current-voltage curves, which are crucial for understanding the redox reactions within the battery. This technique is particularly useful for identifying the capacity, efficiency, and stability of the battery under different conditions. Similarly, in constant current charge/discharge tests, the reference electrode ensures that the potential measurements are consistent and reliable, thereby providing insights into the battery's operational characteristics and lifespan.
Moreover, the choice of reference electrode material is critical in these tests. Materials like lithium/lithium ion and LiFePO4, known for their potential stability and electrochemical inertness, are commonly used. These materials not only ensure accurate measurements but also maintain compatibility with the electrolyte, thereby reducing interferences and enhancing the reliability of the test results.
In summary, reference electrodes are indispensable in electrochemical testing, offering a stable and reliable reference point for measuring potential differences and evaluating the performance of lithium batteries. Their correct selection and use are vital for obtaining precise and meaningful test results.
Material Research
In the realm of lithium battery material research, reference electrodes play a pivotal role in assessing the electrochemical performance and stability of various materials. These electrodes are indispensable tools for evaluating how different materials interact with the electrolyte and how they contribute to the overall battery performance.
One of the primary applications of reference electrodes in material research is to monitor the potential changes of battery materials under different operational conditions. This is crucial for understanding the behavior of materials during charging and discharging cycles, as well as under varying environmental conditions. For instance, the potential stability of lithium-ion intercalation materials, such as LiFePO4, can be precisely measured using reference electrodes, providing insights into their long-term stability and performance.
Moreover, reference electrodes are used to evaluate the electrochemical kinetics of battery materials. By analyzing the current-potential relationships, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the rate capabilities and limitations of different materials. This information is vital for optimizing material selection and for developing new materials with enhanced electrochemical properties.
In summary, reference electrodes are essential tools in material research for lithium batteries, enabling precise evaluations of electrochemical performance and stability. Their use allows for a comprehensive understanding of material behavior, which is critical for the development of advanced battery technologies.
Future Development Direction
Material Innovations
Future advancements in the field of reference electrodes for lithium batteries are poised to introduce materials that offer enhanced stability and activity. These innovations are not merely incremental improvements but represent a paradigm shift in how reference electrodes are conceived and utilized.
Key Areas of Innovation
-
Enhanced Stability: Researchers are exploring novel materials that can maintain their structural integrity and electrochemical properties over extended periods, even under harsh operational conditions. This includes the development of materials that resist degradation due to electrolyte interactions and temperature fluctuations.
-
Increased Activity: The focus is on creating materials that are more responsive to changes in battery conditions, providing more accurate and timely data for battery performance evaluation. This involves the synthesis of materials with higher electrochemical activity and better compatibility with various battery chemistries.
-
Multifunctional Materials: Future reference electrodes may incorporate multifunctional materials that serve dual roles, such as acting as both a reference electrode and a component of the battery's active material. This could lead to more compact and efficient battery designs.
Potential Material Candidates
| Material Type | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Graphene-based | High conductivity, excellent stability, and flexibility in design |
| Nanocomposites | Enhanced electrochemical properties and mechanical robustness |
| Solid-state | Improved safety and stability, especially in high-temperature environments |
| Organic Materials | Biodegradable and sustainable options, reducing environmental impact |
These material innovations aim to address the current limitations of reference electrodes, thereby improving the accuracy and reliability of lithium battery performance evaluations. By leveraging these advancements, the industry can push the boundaries of what is possible in battery technology, paving the way for more efficient and sustainable energy solutions.
Performance Improvements
Improving the cycling stability and expanding the operating voltage range of reference electrodes remain pivotal for enhancing the overall performance of lithium batteries. These enhancements are not merely incremental adjustments but represent critical advancements that can significantly impact the accuracy and reliability of battery testing.
Cycling stability refers to the electrode's ability to maintain consistent electrochemical behavior over repeated charge and discharge cycles. A reference electrode with superior cycling stability ensures that the potential measurements remain accurate, thereby providing reliable data for battery performance evaluation. This is particularly crucial in long-term testing scenarios where the battery undergoes numerous cycles.
Expanding the operating voltage range, on the other hand, allows the reference electrode to function effectively across a broader spectrum of battery chemistries and operating conditions. This capability is essential for testing advanced battery technologies that operate at higher or lower voltages than traditional systems. By broadening the voltage range, reference electrodes can support the development of next-generation batteries, including those designed for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems.
To achieve these improvements, researchers are exploring innovative materials and advanced fabrication techniques. For instance, the use of nanostructured materials and composites can enhance the electrode's durability and electrochemical stability. Additionally, optimizing the electrode's interface with the electrolyte can mitigate issues such as degradation and contamination, further extending its operational lifespan and voltage range.
In summary, the ongoing focus on enhancing cycling stability and operating voltage range is driving significant advancements in reference electrode technology. These improvements are essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of battery performance evaluations, thereby supporting the development of more efficient and durable lithium batteries.
Process Development
The advancement of reference electrode preparation processes is pivotal for the future of lithium battery research and development. These processes must be both flexible and controllable to accommodate the diverse demands of various battery applications. Flexibility ensures that the processes can be adapted to different materials and configurations, while controllability guarantees reproducibility and accuracy in the fabrication of reference electrodes.
To achieve these goals, several key strategies are being explored:
-
Automation and Precision Engineering: Incorporating advanced automation techniques and precision engineering can significantly enhance the controllability of the fabrication process. This includes the use of robotics for material handling and precise placement of components.
-
Material Compatibility: Developing processes that are compatible with a wide range of materials is essential. This involves optimizing the chemical and physical interactions between the electrode material and the processing environment to prevent degradation or contamination.
-
Scalability: Ensuring that the processes can be scaled up from laboratory-scale experiments to industrial production is crucial. This requires the development of robust techniques that maintain performance and consistency across different scales.
-
Environmental Considerations: The processes must also consider environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and atmospheric conditions to ensure the stability and reliability of the reference electrodes.
By focusing on these areas, researchers can develop more sophisticated and reliable reference electrode preparation processes, paving the way for future innovations in lithium battery technology.
Conclusion
Significance of Reference Electrodes
The design and application of reference electrodes hold a pivotal role in the realm of battery performance evaluation and material research. These specialized components, known for their stable and known electrode potentials, serve as indispensable tools in the accurate measurement and analysis of electrochemical processes.
Reference electrodes are integral to the functioning of electrochemical cells, where they act as half-cells, enabling the precise determination of the potential of the other half-cell. This capability is crucial for various electrochemical measurements, including cyclic voltammetry and constant current charge/discharge tests, which are essential for evaluating battery performance.
Moreover, reference electrodes are not confined to laboratory settings. They are also pivotal in the development of electrochemical devices such as differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) and electrochemical biosensors. These devices rely on the stable and consistent potential provided by reference electrodes to function accurately and reliably.
The classification of reference electrodes is diverse, encompassing aqueous, calomel, non-aqueous, and custom-constructed types. Each category offers unique advantages and is suited to specific applications, ensuring that researchers have the appropriate tools for their needs.
In summary, the significance of reference electrodes extends beyond mere measurement tools; they are foundational elements in the advancement of battery technology and electrochemical research. Their ability to maintain a constant potential, even under minimal current flow, ensures the reliability and accuracy of experimental results, making them indispensable in the quest for improved battery performance and material stability.
Future Innovations
The future of reference electrodes in lithium batteries lies in continuous innovation and improvement, which will significantly enhance the accuracy and reliability of battery performance evaluation. This advancement is not just about refining existing materials but also about exploring new, more stable and active materials that can withstand the rigors of extended testing and varied operational conditions.
One promising direction is the development of materials that offer superior electrochemical inertness and potential stability, ensuring that the reference electrode remains unaffected by the aggressive environments within the battery. For instance, novel compounds such as graphene-based composites and solid-state electrolytes are being investigated for their potential to provide enhanced stability and accuracy.
Moreover, advancements in the preparation processes of reference electrodes are crucial. The development of more flexible and controllable fabrication techniques will allow for the creation of electrodes with tailored properties, optimized for specific battery testing requirements. This could involve the use of advanced manufacturing methods such as 3D printing and nanotechnology, which can produce electrodes with precise microstructures and superior performance characteristics.
In addition to material and process innovations, there is also a growing focus on improving the cycling stability and operating voltage range of reference electrodes. This involves not only enhancing the durability of the electrode materials but also optimizing their interaction with the electrolyte to maintain consistent performance over multiple charge-discharge cycles.
| Innovation Area | Key Focus |
|---|---|
| Material Innovations | Exploration of new, stable, and active materials; graphene-based composites |
| Process Development | Advanced manufacturing techniques; 3D printing; nanotechnology |
| Performance Improvements | Enhancing cycling stability and operating voltage range; optimizing material-electrolyte interactions |
These innovations are essential for pushing the boundaries of what is possible in battery performance evaluation, ultimately leading to more efficient and reliable lithium batteries.
Related Products
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Flat Corrosion Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
Related Articles
- How to Make Your Own Ag/AgCl Reference Electrode for Electrochemical Experiments
- Comprehensive Guide to Reference Electrodes: Types, Applications, and Selection Criteria
- A Comprehensive Guide to Reference Electrodes
- A Beginner's Guide to Understanding Reference Electrodes in Electrochemistry
- Electrochemical Electrodes in Chemical Analysis


















