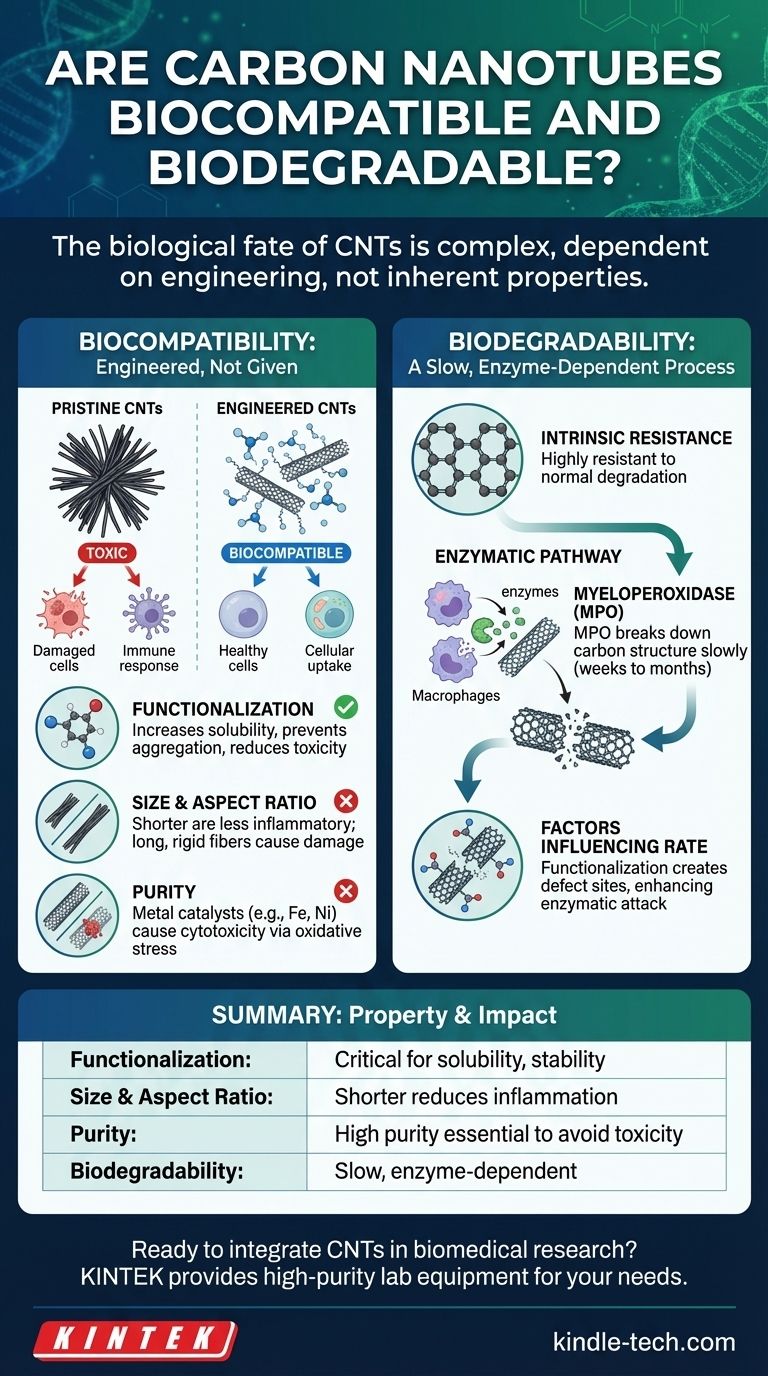
The biological fate of carbon nanotubes is not a simple story. Their biocompatibility and biodegradability are not inherent properties but are critically dependent on their specific physical and chemical characteristics. While pristine, unmodified carbon nanotubes (CNTs) can be cytotoxic, properly engineered and functionalized CNTs can achieve a high degree of biocompatibility for medical use. Their biodegradability, however, is a much slower, more complex process that relies on specific biological mechanisms.
The safety and persistence of carbon nanotubes in biological systems are determined by their functionalization, size, and purity. Unmodified CNTs often pose risks, while properly engineered CNTs can achieve biocompatibility, though their degradation remains a slow, enzyme-dependent process rather than a simple breakdown.

What Determines "Biocompatibility" in Carbon Nanotubes?
Biocompatibility is the ability of a material to perform its desired function without eliciting a harmful or undesirable local or systemic response in the host. For CNTs, this is not a given; it must be engineered.
The Critical Role of Functionalization
Pristine, raw CNTs are hydrophobic (they repel water). This causes them to clump together aggressively in biological fluids like blood, which can lead to blockages and trigger severe immune responses.
Functionalization is the process of attaching other molecules or functional groups to the surface of CNTs. This modification is the single most important factor for biocompatibility, as it increases solubility and stability in the body, preventing aggregation and reducing toxicity.
Size and Aspect Ratio Matter
The physical dimensions of CNTs heavily influence how cells interact with them. Long, rigid, and needle-like CNTs can cause physical damage to cell membranes.
This behavior is sometimes compared to asbestos fibers, where immune cells called macrophages are unable to fully engulf the long fibers. This "frustrated phagocytosis" can lead to chronic inflammation and tissue damage. Shorter, well-dispersed CNTs are generally less inflammatory and can be cleared more easily by the body.
The Problem of Purity
The synthesis of CNTs often requires metal catalysts (e.g., iron, nickel, cobalt). If these metallic impurities are not meticulously removed, they can leach out in the body.
These metal ions are a major source of cytotoxicity, as they can generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) that cause oxidative stress and damage cells. For any biomedical application, using high-purity CNTs is non-negotiable.
The Question of Biodegradability: Do They Break Down?
The strong carbon-carbon bonds that give CNTs their remarkable strength also make them highly resistant to breaking down in the environment or the body.
Intrinsic Resistance to Degradation
Under normal physiological conditions, CNTs are largely biopersistent. They do not simply dissolve or degrade like many biodegradable polymers.
The Enzymatic Pathway
The primary known mechanism for CNT degradation in the body is enzymatic oxidation. Specific enzymes, most notably myeloperoxidase (MPO), can slowly break down the carbon structure.
MPO is found in immune cells like neutrophils and macrophages, which are part of the body's first-line defense against foreign materials. The degradation process is slow and can take weeks to months.
Factors Influencing Degradation Rate
The rate of this enzymatic degradation depends on the CNTs' properties. Functionalization can introduce "defect sites" in the carbon lattice, which act as starting points for enzymatic attack, making the CNTs more susceptible to breakdown.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While their potential is enormous, using CNTs in biological systems involves navigating significant risks that must be managed through careful design.
The Risk of Aggregation and Thrombosis
As mentioned, poor functionalization leads to aggregation. If CNTs clump together in the bloodstream, they can trigger platelet activation and the formation of blood clots (thrombosis), a life-threatening event.
Potential for Chronic Inflammation and Fibrosis
If the body cannot clear or break down CNTs, it may attempt to wall them off. This can lead to a state of chronic inflammation and the formation of fibrotic scar tissue, which can impair organ function over the long term. This is a primary concern for long, pristine CNTs.
The Challenge of Bioaccumulation
Because degradation is slow and clearance can be incomplete, there is a risk that CNTs bioaccumulate in certain organs, particularly the liver and spleen (part of the reticuloendothelial system). The long-term consequences of this accumulation are still an active area of research.
How to Evaluate CNTs for Your Application
Choosing the right type of carbon nanotube is critical and depends entirely on the intended use case.
- If your primary focus is in-vitro diagnostics or cell imaging: Prioritize highly functionalized, short, and well-dispersed CNTs to ensure good solubility, cellular uptake, and low immediate cytotoxicity.
- If your primary focus is drug delivery: Focus on CNTs with surface chemistry that minimizes immune recognition, prevents aggregation in blood, and is engineered to be more susceptible to enzymatic degradation.
- If your primary focus is long-term implants or tissue engineering: The risk of bioaccumulation and chronic inflammation is highest here. You must use the purest, most biodegradable CNTs available and conduct rigorous testing for long-term host response and material breakdown.
Ultimately, treating carbon nanotubes not as a single material but as a tunable platform is the key to safely unlocking their biomedical potential.
Summary Table:
| Property | Impact on Biocompatibility & Biodegradability | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Functionalization | Critical for solubility; prevents aggregation and toxicity. | Attach molecules to surface for stability. |
| Size & Aspect Ratio | Shorter CNTs reduce inflammation; long fibers risk fibrosis. | Optimize length to avoid cellular damage. |
| Purity | Metal impurities (e.g., iron) cause cytotoxicity via ROS. | Use high-purity CNTs for biomedical use. |
| Biodegradability | Slow, enzyme-dependent (e.g., myeloperoxidase) process. | Functionalization can enhance degradation. |
Ready to integrate carbon nanotubes into your biomedical research or product development? KINTEK specializes in providing high-purity lab equipment and consumables tailored to advanced material science and laboratory needs. Our expertise ensures you have the right tools to safely explore CNT applications—from drug delivery to diagnostics. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your innovation with reliable, precision-engineered solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is an RVC glassy carbon sheet? A High-Performance Material for Demanding Applications
- What is the applicable potential range for an RVC glassy carbon sheet? Master Your Electrochemical Analysis
- What is the proper procedure for cleaning a glassy carbon sheet after use? A Definitive Guide to Ensure Reliable Results
- What are the fundamental characteristics of glassy carbon? Discover its Unique Synergy of Properties
- What is the ideal operating environment for a glassy carbon sheet? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity




