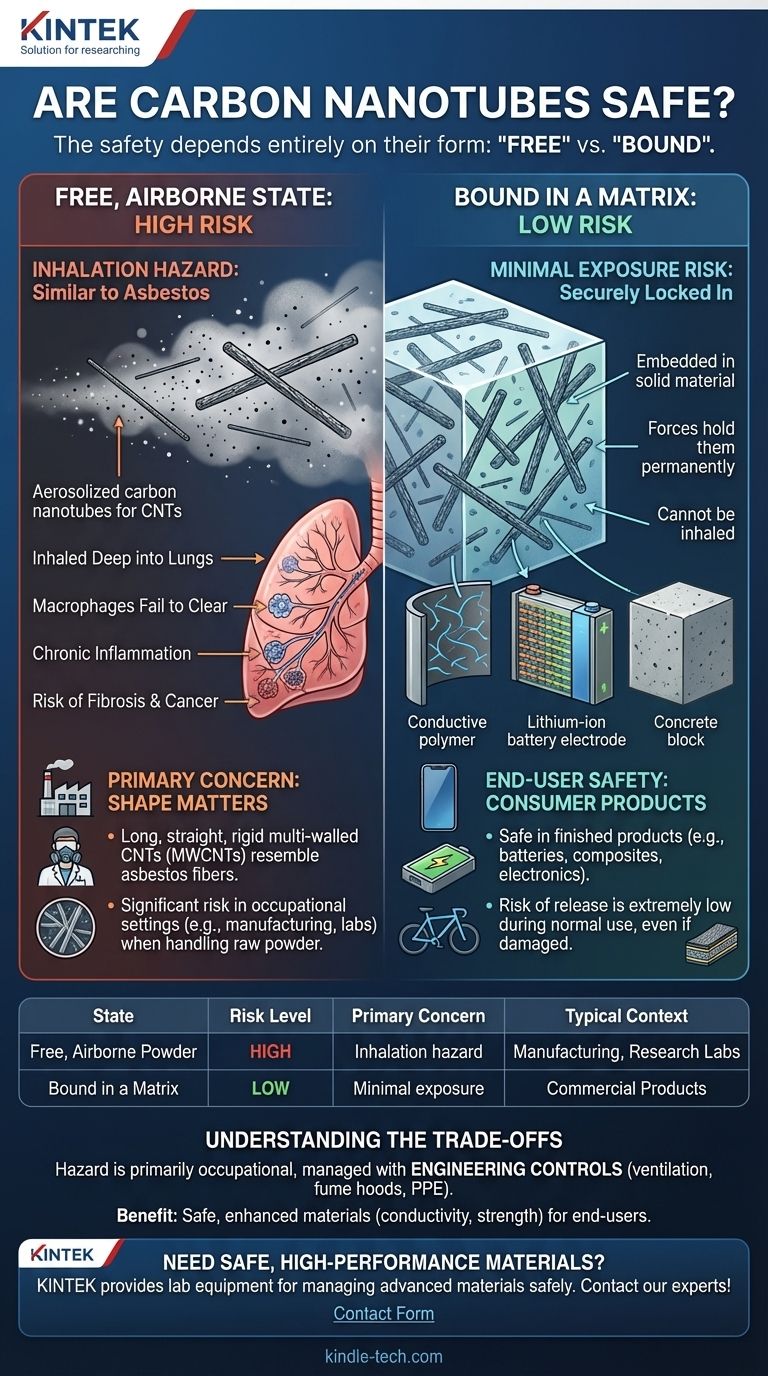
The safety of carbon nanotubes depends entirely on their form. In their raw, airborne powder state, certain types of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) present a significant inhalation hazard similar to asbestos. However, once they are integrated and locked into a solid material or liquid suspension—as they are in virtually all commercial products—the risk of exposure and harm to the end-user is considered extremely low.
The critical distinction for carbon nanotube safety is between "free" and "bound". The primary health risk comes from inhaling free, aerosolized nanotubes during manufacturing. For consumers using finished products, where nanotubes are securely bound within a matrix like a polymer or battery electrode, the material is generally considered safe.

The Core Safety Concern: A Matter of Shape
The apprehension surrounding CNT safety is not arbitrary. It stems from a well-understood principle in toxicology where the physical shape of a particle, not just its chemical composition, can determine its hazard.
The Asbestos Analogy
The primary concern is that some types of CNTs—specifically those that are long, thin, and rigid—are structurally similar to asbestos fibers. This physical resemblance is the foundation of the toxicological risk assessment.
How Inhalation Can Cause Harm
When particles of this shape are inhaled deep into the lungs, the body's immune cells, called macrophages, attempt to engulf and clear them. However, if the fibers are too long for the macrophages to enclose, the process fails. This triggers a state of chronic inflammation, which over long periods can lead to serious lung diseases like fibrosis and cancer.
Not All Nanotubes are Created Equal
It is crucial to understand that "carbon nanotube" is a broad term. The risk profile changes based on their physical characteristics. Long, straight, and rigid multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) are of greater concern than shorter, more flexible, and tangled single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs), as the former more closely resemble asbestos fibers.
Context is Everything: The "Bound vs. Free" Principle
Understanding the state of the CNTs is the key to accurately assessing their risk. The hazard is almost entirely a function of the potential for them to become airborne and inhaled.
Free Nanotubes: The High-Risk Scenario
The significant risk is concentrated in occupational settings where CNTs are handled in their raw, dry powder form. This includes manufacturing facilities and research labs. In this state, the nanotubes can easily become aerosolized, creating a direct inhalation risk for workers if not properly controlled.
Bound in a Matrix: The Low-Risk Scenario
In commercial applications, CNTs are used as additives. They are dispersed and locked within a larger material, or "matrix." This includes their use in lithium-ion batteries, conductive polymers, fiber-reinforced composites, and concrete.
Once embedded, the nanotubes are no longer free to become airborne. The forces holding them within the matrix are far stronger than any forces that might release them during normal product use.
End-of-Life Considerations
Concerns are often raised about what happens when a CNT-containing product is broken, burned, or disposed of. Research indicates that when these composite materials degrade, they tend to release larger fragments of the matrix with the CNTs still embedded, rather than releasing free, individual nanotubes. While this is an area of ongoing study, the risk is considered much lower than handling the raw material.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Mitigation
The use of CNTs presents a classic risk-benefit scenario that is managed through established industrial hygiene and safety protocols.
The Hazard is Primarily Occupational
The potential for harm is not to the public or the consumer, but to the workers who handle the raw nanomaterial. This is a known and manageable industrial hazard.
Safety is Achieved Through Engineering Controls
Manufacturers and researchers manage this risk by implementing strict safety protocols. These include using ventilation systems and fume hoods to capture loose particles, handling CNTs in liquid suspensions (slurries) instead of dry powders, and requiring workers to use personal protective equipment (PPE) like respirators and gloves.
The Benefit is a Safe, Enhanced Final Product
The trade-off is clear: by carefully managing the risks during production, it becomes possible to create advanced materials with enhanced properties (like electrical conductivity or strength) that are safe for the end-user.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your perspective on CNT safety should be dictated by your role and how you interact with the material.
- If you are a consumer: Products containing carbon nanotubes are considered safe for use, as the nanotubes are securely locked within the product's structure and cannot be inhaled.
- If you are a manufacturer or researcher: You must treat raw, powdered CNTs as a significant respiratory hazard and implement strict engineering controls and PPE to prevent any inhalation exposure.
- If you are a product developer: Your goal is to ensure the nanotubes are permanently and homogenously dispersed within your material matrix to eliminate any risk of release during the product's lifecycle.
Ultimately, carbon nanotube safety is a solved problem of process control, where the risk is effectively eliminated by preventing exposure to the raw, unbound material.
Summary Table:
| State of Carbon Nanotubes | Risk Level | Primary Concern | Typical Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free, Airborne Powder | High | Inhalation hazard, similar to asbestos | Manufacturing, research labs |
| Bound in a Matrix (e.g., polymer, battery) | Low | Minimal exposure risk; securely locked in | Commercial products (batteries, composites) |
Need Safe, High-Performance Materials for Your Lab?
Carbon nanotubes offer incredible benefits when handled correctly. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables that help you manage advanced materials like CNTs safely and efficiently. Whether you're developing next-generation batteries or conductive composites, we have the solutions to support your research and production goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's safety and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- KF ISO Stainless Steel Vacuum Flange Blind Plate for High Vacuum Systems
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
People Also Ask
- What are the challenges of large-scale biomass energy use? The Hidden Hurdles to a Green Energy Source
- Why does graphite have a high melting point? The Power of Its Giant Covalent Structure
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What role does a laboratory high-temperature furnace play in PHT? Engineer Nano-Scale Coating Durability
- What role do high-temperature furnaces play in SOFC synthesis? Precision Tools for Electrolyte & Electrode Optimization







