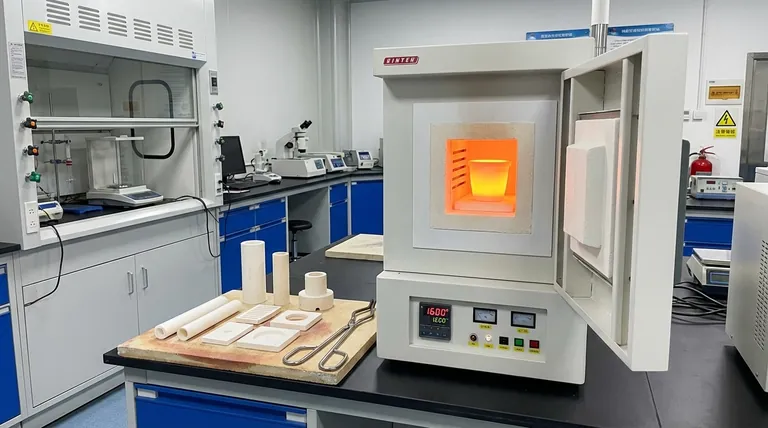
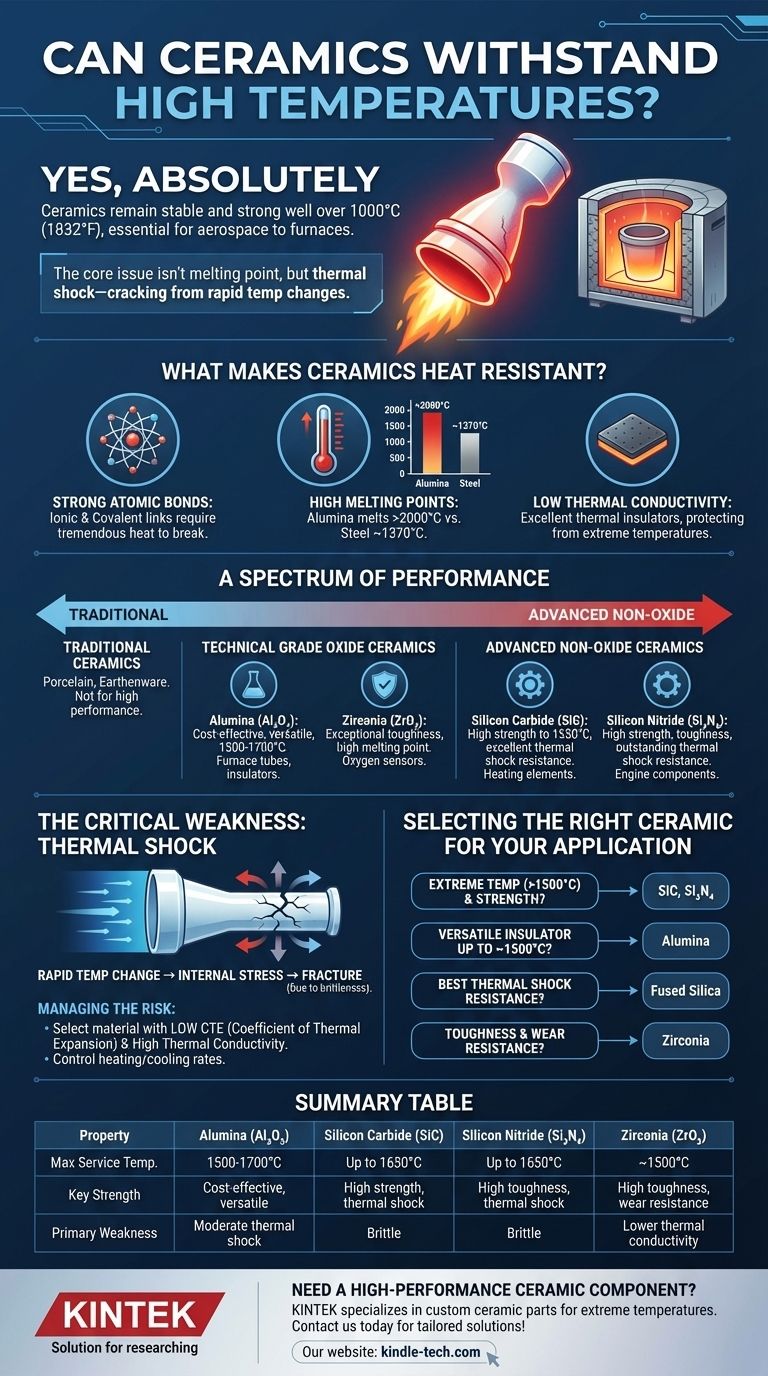
Yes, absolutely. The ability to withstand extremely high temperatures is a defining characteristic of ceramic materials. While metals often weaken and melt, many ceramics remain stable and strong at temperatures well over 1000°C (1832°F), making them essential for applications ranging from aerospace to industrial furnaces. However, not all ceramics are created equal, and their performance depends entirely on their specific chemical composition and structure.
The core issue isn't simply a ceramic's melting point, which is almost always exceptionally high. The true challenge lies in managing its inherent brittleness and susceptibility to thermal shock—the tendency to crack when subjected to rapid temperature changes.

What Makes Ceramics Heat Resistant?
The remarkable thermal stability of ceramics is not an accident; it is a direct result of their fundamental atomic structure. Understanding this is key to appreciating both their strengths and weaknesses.
The Power of Atomic Bonds
Unlike metals, which are held together by a flexible sea of shared electrons, atoms in most advanced ceramics are linked by incredibly strong ionic and covalent bonds. These bonds require a tremendous amount of thermal energy (heat) to vibrate and ultimately break, which is why ceramics have such high melting and boiling points.
High Melting Points are the Norm
The strength of these atomic bonds directly translates to very high melting temperatures. For example, Alumina (Al₂O₃), a common technical ceramic, melts at over 2000°C (3632°F), while metals like aluminum and steel melt at approximately 660°C and 1370°C, respectively.
Low Thermal Conductivity
Many ceramics are also excellent thermal insulators. They resist the transfer of heat, a property that is just as important as not melting. This is why they are used as refractory linings in kilns and as heat shield tiles on spacecraft—they protect what's underneath from extreme temperatures.
A Spectrum of Performance: Not All Ceramics Are Equal
The term "ceramic" covers a vast range of materials, from common pottery to engineered components for jet engines. Their performance in high-temperature environments varies significantly.
Traditional Ceramics
Materials like porcelain and earthenware are fired at high temperatures, but their composition includes fluxes and impurities that lower their maximum service temperature. They are useful for many things but are not considered high-performance in this context.
Technical Grade Oxide Ceramics
These are the workhorses of high-temperature applications.
- Alumina (Aluminum Oxide): Widely used due to its excellent balance of high strength, hardness, and a continuous service temperature of around 1500-1700°C. It's a cost-effective choice for furnace tubes, insulators, and wear components.
- Zirconia (Zirconium Dioxide): Known for its exceptional toughness (for a ceramic) and an even higher melting point than Alumina. Stabilized Zirconia is often used for oxygen sensors and solid oxide fuel cells.
Advanced Non-Oxide Ceramics
These materials offer the highest performance at extreme temperatures, often in highly demanding chemical or mechanical environments.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): Maintains its strength at temperatures up to 1650°C (3000°F) and has excellent thermal shock resistance. It's used for heating elements, rocket nozzles, and components in semiconductor manufacturing.
- Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄): Possesses an extraordinary combination of high strength, toughness, and outstanding thermal shock resistance. This makes it a primary candidate for components in advanced automotive and gas turbine engines.
Understanding the Critical Weakness: Thermal Shock
A high melting point is useless if the material shatters the moment it heats up or cools down too quickly. This failure mode, known as thermal shock, is the primary engineering challenge when working with ceramics.
The Physics of a Crack
When a ceramic is heated or cooled rapidly, different parts of the material expand or contract at different rates. This creates internal stress. Because ceramics are brittle, they cannot bend or deform to relieve this stress like a metal can. Instead, the stress builds until the material fractures.
The Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE)
The single most important property for predicting thermal shock resistance is the Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE). This value measures how much a material expands per degree of temperature increase. A ceramic with a low CTE will expand and contract less, generate lower internal stresses, and thus have better resistance to thermal shock.
Managing the Risk
Engineers manage thermal shock in two ways. First, by selecting a material with a low CTE and high thermal conductivity (like Silicon Nitride). Second, by carefully controlling the heating and cooling rates of the ceramic component to keep temperature gradients and internal stresses to a minimum.
Selecting the Right Ceramic for Your Application
Choosing the correct material requires balancing thermal performance against mechanical requirements and cost.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature resistance (>1500°C) with high strength: Choose a non-oxide ceramic like Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄).
- If your primary focus is a versatile, cost-effective insulator for use up to ~1500°C: Alumina (Al₂O₃) is the industry standard and an excellent choice.
- If your primary focus is the absolute best resistance to thermal shock: Fused Silica is unmatched due to its near-zero CTE, though it has lower strength than other ceramics.
- If your primary focus is toughness and wear resistance at high temperatures: Zirconia (ZrO₂) is a leading candidate.
Understanding the interplay between a ceramic's atomic structure, its thermal properties, and its mechanical brittleness is the key to successfully deploying these materials in the most demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Property | Alumina (Al₂O₃) | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) | Zirconia (ZrO₂) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Service Temp. | 1500-1700°C | Up to 1650°C | Up to 1650°C | ~1500°C |
| Key Strength | Cost-effective, versatile | High strength, thermal shock resistance | High toughness, thermal shock resistance | High toughness, wear resistance |
| Primary Weakness | Moderate thermal shock resistance | Brittle | Brittle | Lower thermal conductivity |
Need a high-performance ceramic component for your lab or industrial process? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables, including custom ceramic parts designed for extreme temperatures and harsh environments. Our experts can help you select the right material—from durable Alumina furnace tubes to ultra-resistant Silicon Carbide elements—to ensure reliability, efficiency, and safety in your application. Contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements and get a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How to cool a muffle furnace? Ensure Safety and Maximize Equipment Lifespan
- Why do we use a muffle furnace? For Pure, Precise, and Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What are 2 advantages of dry ashing? Achieve High-Throughput Sample Analysis with Safety
- What is the principle of muffle furnace in laboratory? Master Precise High-Temp Heating
- What are the uses of muffle furnace in pharmaceutical industry? Essential for Drug Purity & Safety



















