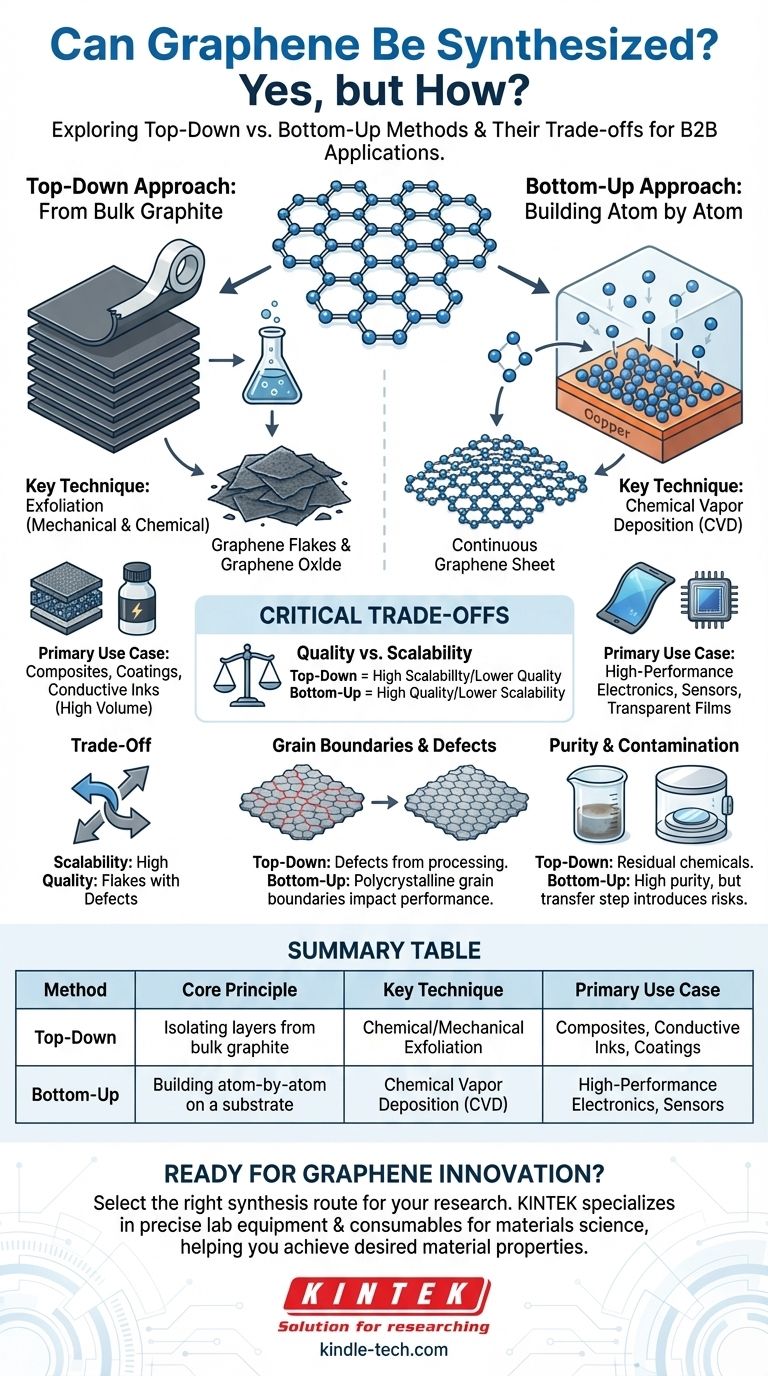
Yes, graphene can be synthesized using a range of sophisticated methods. These techniques are broadly categorized into two fundamental approaches: "top-down," which involves isolating graphene from a bulk source like graphite, and "bottom-up," which involves constructing the graphene sheet atom by atom on a substrate.
The central challenge in graphene synthesis is not if it can be made, but how it is made. The choice of method dictates a critical trade-off between producing large quantities of graphene flakes versus creating high-quality, continuous sheets for advanced applications.

The "Top-Down" Approach: Starting from Graphite
This family of methods begins with a bulk carbon source, typically graphite, and works to separate it into individual, one-atom-thick layers of graphene.
The Core Principle
Think of graphite as a dense stack of paper. Top-down methods are designed to peel off a single sheet from that stack without tearing it.
Key Method: Exfoliation
The most common approach is exfoliation. This can be done mechanically, famously using adhesive tape to peel away layers, which produces extremely high-quality but tiny flakes.
More scalable methods involve chemical oxidation, where graphite is treated with strong acids. This process forces the layers apart, but it also introduces defects that can impact the material's pristine properties.
Primary Use Case
Top-down methods are ideal for producing large volumes of graphene flakes or graphene oxide. These materials are often used as additives in composites, conductive inks, and coatings.
The "Bottom-Up" Approach: Building Atom by Atom
In contrast to breaking down graphite, bottom-up methods construct graphene from the ground up by assembling individual carbon atoms into the desired hexagonal lattice.
The Core Principle
This approach is like building a perfect mosaic, tile by tile. Carbon-containing precursor molecules are deposited onto a substrate where they self-assemble into a continuous sheet of graphene.
The Dominant Method: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is the most prominent bottom-up technique. It involves flowing a carbon-containing gas over a heated metallic substrate, often copper.
The high temperature causes the gas to decompose, depositing carbon atoms onto the metal surface. These atoms then arrange themselves into the characteristic graphene lattice, forming a large, continuous film.
Primary Use Case
CVD is the leading method for creating the large-grain, single-crystalline graphene sheets required for high-performance electronics, transparent conductive films, and advanced sensors.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
The choice between a top-down and bottom-up method is dictated entirely by the end application, as each comes with significant compromises.
Quality vs. Scalability
Top-down chemical methods are highly scalable for producing tons of material, but the resulting graphene often contains defects from the harsh chemical processing. Bottom-up CVD produces much higher-quality material but is a more complex and expensive process.
The Impact of Grain Boundaries
For electronics, performance is everything. CVD can produce large, single-crystal sheets, but it often creates polycrystalline graphene—a patchwork of smaller graphene crystals.
The seams between these crystals, known as grain boundaries, disrupt the flow of electrons and weaken the material, negatively impacting both its electrical and mechanical properties.
Purity and Contamination
Chemical exfoliation can leave behind residual chemicals and oxygen groups, altering the graphene's properties. CVD, while capable of producing very pure graphene, requires extremely controlled conditions and a subsequent step to transfer the graphene from its growth substrate to a target substrate, which can introduce new contaminants or tears.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Application
To select the appropriate synthesis route, you must first define your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics or sensors: You require large-area, high-quality sheets, making bottom-up methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition the necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is bulk materials like composites, coatings, or conductive inks: You need large quantities at a lower cost, so top-down chemical exfoliation methods are the more practical and economical path.
Understanding these fundamental synthesis routes is the first step in harnessing graphene's potential for a specific technological goal.
Summary Table:
| Method | Core Principle | Key Technique | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top-Down | Isolating layers from bulk graphite | Chemical/Mechanical Exfoliation | Composites, Conductive Inks, Coatings |
| Bottom-Up | Building atom-by-atom on a substrate | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | High-Performance Electronics, Sensors |
Ready to integrate graphene into your research or product development?
The choice of synthesis method is critical to your project's success. Whether you need high-purity sheets for advanced electronics or cost-effective flakes for composite materials, having the right lab equipment is paramount.
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables you need for materials science innovation. Our expertise can help you select the ideal tools for your graphene synthesis and characterization workflow, ensuring you achieve the desired material properties.
Let's discuss your specific application requirements. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- CVD Diamond Wire Drawing Die Blanks for Precision Applications
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Achieve Precision Coating for Complex Geometries
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance



















