Yes, graphite can hold an electrical charge, but the way it does so is what makes it a cornerstone of modern energy storage. While any isolated electrical conductor can hold a static charge, graphite’s unique layered structure allows it to store charge in a far more practical and powerful way by physically hosting ions, which is the fundamental principle behind the lithium-ion battery.
Graphite's true value isn't just in holding a simple static charge like a metal ball, but in its ability to both conduct electricity and safely store ions within its structure. This dual capability makes it the dominant anode material for rechargeable batteries.

Graphite's Electrical Properties: More Than a Conductor
To understand how graphite holds a charge, we must first look at its fundamental electrical nature. It’s not a simple wire or a perfect insulator; its properties are more nuanced.
An Excellent Conductor
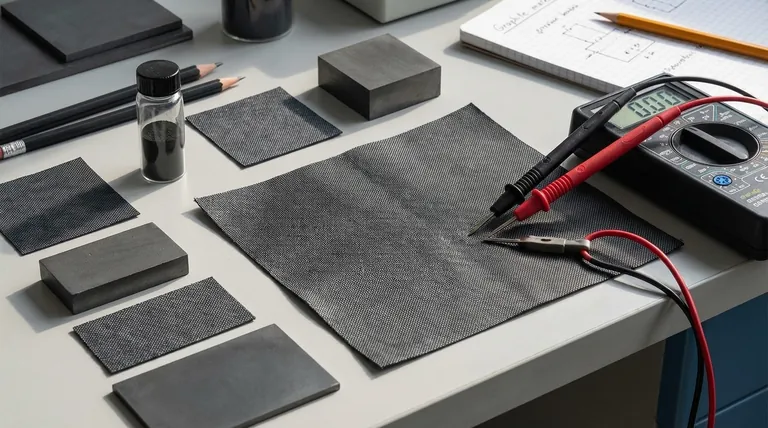
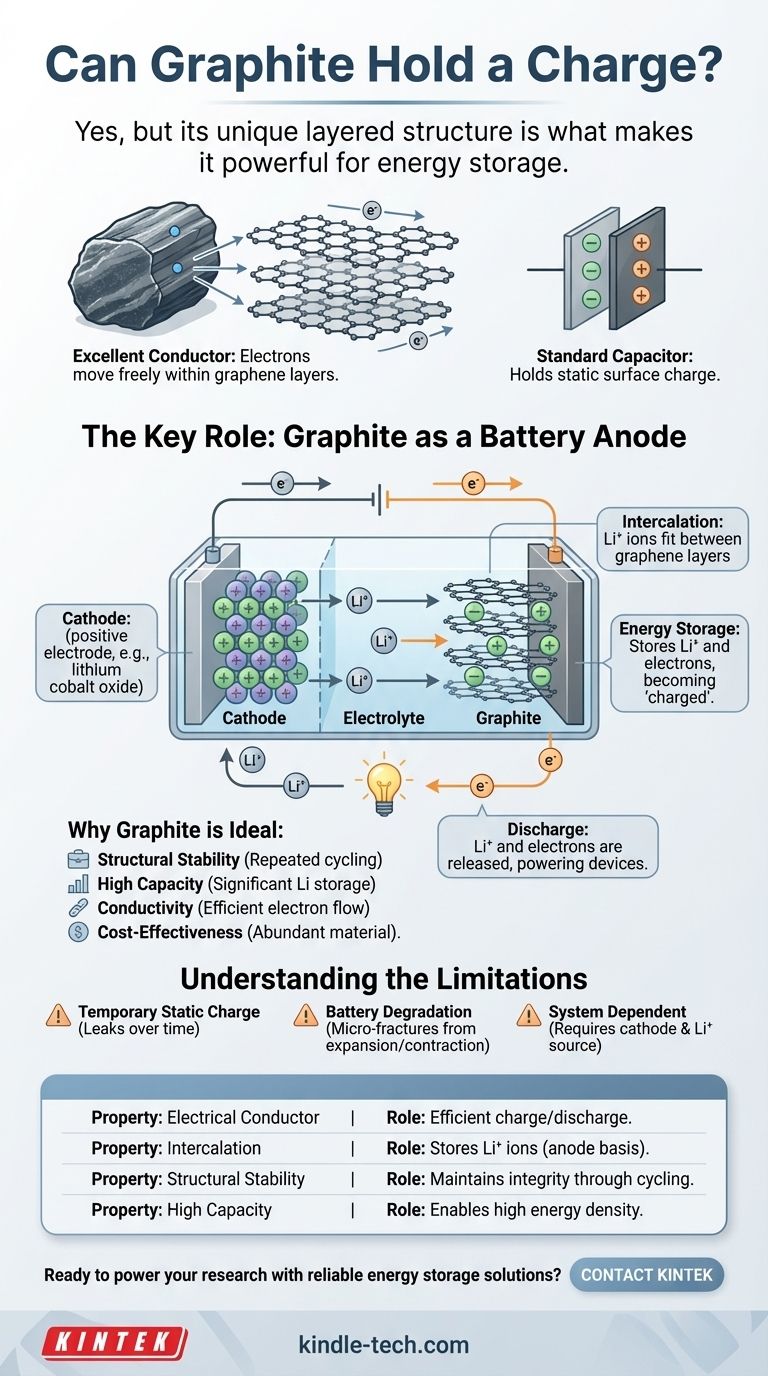
Graphite is an excellent electrical conductor. Its structure consists of stacked layers of carbon atoms (graphene sheets). Within these layers, electrons can move freely, allowing electricity to pass through it with ease.
This conductivity is the essential prerequisite for any charge-storing application. A material cannot effectively accumulate or release charge if it cannot first allow that charge to move.
A Standard Capacitor
In the simplest physical sense, an isolated piece of graphite can hold a static electrical charge on its surface, just like any other conductive material. If you transfer electrons to it (giving it a negative charge) or remove them (giving it a positive charge), that imbalance will remain as long as it is electrically isolated.
This is the basic principle of a capacitor, where conductive plates store energy in an electric field. Forms of graphite with extremely high surface areas, like activated carbon, are used to build supercapacitors that can store a significant amount of this surface charge.
The Key Role: Graphite as a Battery Anode
The most important way graphite "holds a charge" is electrochemically, specifically as the anode (negative electrode) in virtually all modern lithium-ion batteries.
The Principle of Intercalation
The secret lies in a process called intercalation. The space between graphite's graphene layers is perfectly sized to accept and hold lithium ions.
During charging, lithium ions (Li⁺) are forced to travel from the cathode, through the electrolyte, and physically wedge themselves between the graphite layers. For every lithium ion stored, an electron is stored in the graphite's conductive structure to maintain charge neutrality.
How It "Holds" and "Releases" a Charge
This stored combination of lithium ions and electrons represents the battery's stored energy, or its "charge." The graphite anode is literally full of lithium.
When you use the battery, the process reverses. The lithium ions leave the graphite structure and travel back to the cathode, releasing their corresponding electrons, which flow through the external circuit to power your device.
Why Graphite is Ideal for This
Graphite is used for this purpose because it has a unique combination of properties:
- Structural Stability: It can absorb and release lithium ions repeatedly without its structure crumbling.
- High Capacity: It can hold a significant amount of lithium (one lithium atom for every six carbon atoms).
- Conductivity: Its natural electrical conductivity allows electrons to move in and out efficiently.
- Cost-Effectiveness: It is abundant and relatively inexpensive to process.
Understanding the Limitations
While incredibly effective, graphite's ability to hold a charge is not without its constraints. Understanding these is key to grasping the full picture.
Static Charge is Temporary
As a simple capacitor holding a static charge, graphite is no different from other conductors. The charge will eventually leak away into the air or any object it touches. It is not a permanent storage method.
Battery Degradation
The physical process of intercalation and de-intercalation causes the graphite to expand and contract slightly with each charge cycle. Over hundreds or thousands of cycles, this stress can cause micro-fractures, slowly reducing the battery's ability to hold a full charge.
Not a Standalone System
In a battery, graphite does not hold a charge in a vacuum. Its capacity is entirely dependent on having a system with a cathode (like lithium cobalt oxide) and a sea of lithium ions to draw from. By itself, it is just a stable, conductive material.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your understanding of how graphite "holds a charge" depends entirely on your context and application.
- If your primary focus is basic physics: Think of it as a standard electrical conductor that can store static charge on its surface, with its potential maximized in high-surface-area forms for supercapacitors.
- If your primary focus is energy storage: Recognize that its most vital role is acting as a stable, high-capacity "hotel" for lithium ions, forming the anode of nearly every lithium-ion battery.
Ultimately, graphite's layered structure allows it to transcend the simple role of a conductor and become an active participant in electrochemical energy storage.
Summary Table:
| Property | Role in Charge Storage |
|---|---|
| Electrical Conductor | Allows electrons to move freely, enabling efficient charge/discharge. |
| Intercalation | Stores lithium ions between its graphene layers, the basis for battery anodes. |
| Structural Stability | Maintains integrity through repeated charging cycles (expansion/contraction). |
| High Capacity | Can hold a significant amount of lithium, enabling high energy density. |
Ready to power your research with reliable energy storage solutions?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables. Whether you are developing next-generation batteries or require precise materials for your energy research, our expertise and products are designed to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your projects with the right tools and materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type
- What can carbon nanotubes be used for? Unlock Superior Performance in Batteries & Materials
- What are the material properties of carbon paper? Unlocking High Conductivity & Porosity for Your Lab
- What is the ideal operating environment for a glassy carbon sheet? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity



















