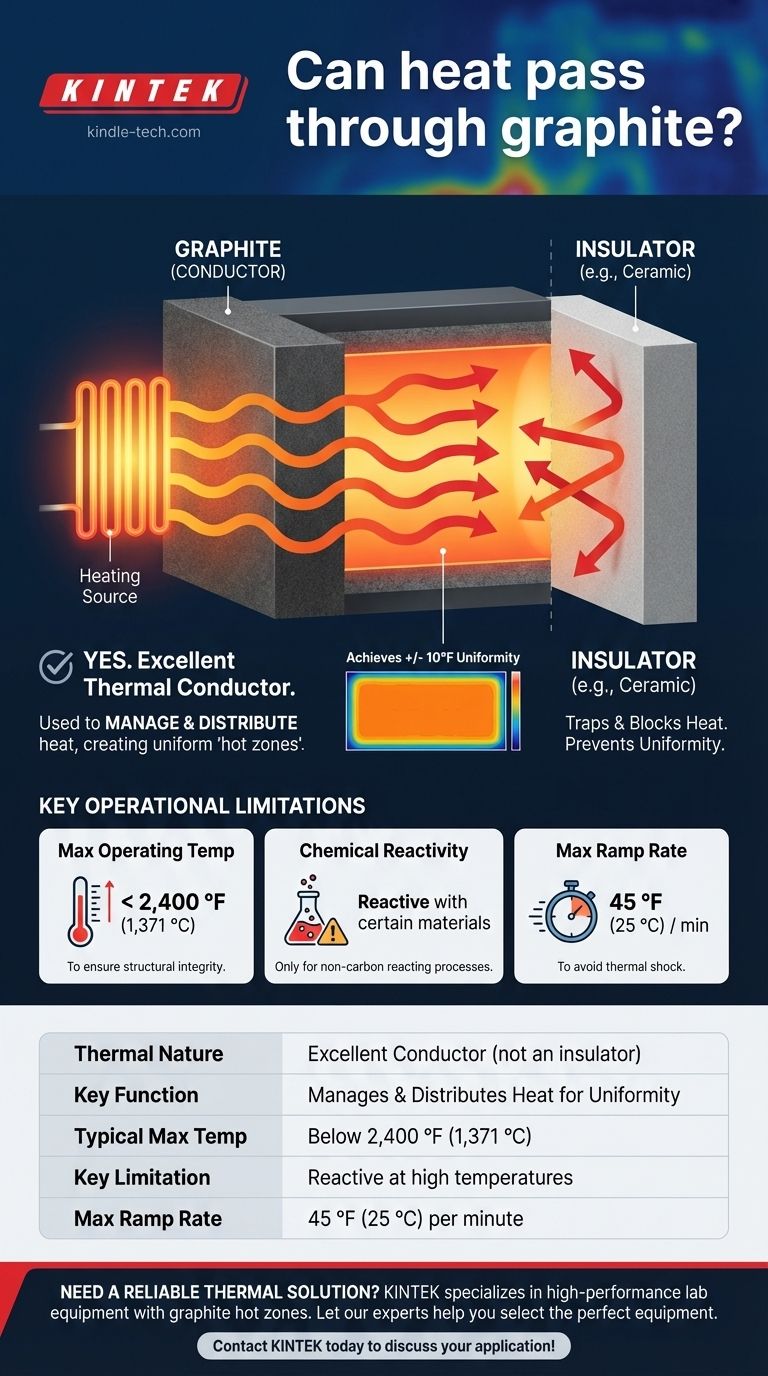
Yes, heat passes through graphite remarkably well. In fact, graphite is an excellent thermal conductor, not an insulator. Its ability to efficiently transfer heat is precisely why it is used to construct core components, known as "hot zones," in high-temperature furnaces.
The critical insight is that graphite is not used to block heat but to manage and distribute it. Its high thermal conductivity allows it to create the stable, uniform temperature environments required for industrial processes.

Understanding Graphite's Role in Heat Transfer
To grasp why graphite is so valuable, it's essential to distinguish between a thermal conductor and a thermal insulator.
A Conductor, Not an Insulator
An insulator traps heat and prevents it from moving. Think of the ceramic fiber lining the walls of a furnace, which keeps the heat contained inside.
A conductor allows heat to move through it easily. Graphite excels at this, transferring thermal energy efficiently from one area to another.
The Function of a "Hot Zone"
The term "hot zone" refers to the internal area of a furnace where the work is actually heated. These components must withstand extreme temperatures while ensuring the heat is applied evenly.
Because graphite conducts heat so well, it can absorb energy from heating elements and distribute it evenly throughout the chamber, minimizing hot spots.
Achieving Temperature Uniformity
The reference to achieving a temperature uniformity of +/- 10 °F is a direct result of graphite's conductive properties.
If the material were an insulator, some parts of the furnace would get much hotter than others. Graphite's ability to transfer heat helps average out these differences, creating a consistent and predictable environment.
Key Operational Limitations
While powerful, graphite is not a universal solution. Its use is governed by specific physical and chemical constraints.
Maximum Operating Temperature
Graphite components have an upper limit. As noted, they are best suited for temperatures below 2,400 °F (1,371 °C) in certain environments to ensure structural integrity and a long service life.
Chemical Reactivity
The most significant limitation is graphite's reactivity. It is pure carbon and can react with certain materials at high temperatures.
Therefore, it is only suitable for processes where the material being heated does not react with carbon.
Thermal Ramp Rates
Heating a system too quickly can induce thermal shock and stress. Graphite hot zones have a recommended maximum ramp rate of 45 °F (25 °C) per minute to ensure components heat up evenly and without damage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right material depends entirely on how you need to control heat in your application.
- If your primary focus is creating a uniform, high-temperature environment: Graphite is an exceptional choice for internal furnace structures, fixtures, and heating elements.
- If your primary focus is containing heat and preventing its escape: Graphite is the wrong choice; you should use a ceramic or refractory fiber insulator instead.
Ultimately, understanding graphite as an effective thermal conductor is the key to leveraging its properties for demanding high-temperature applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value / Description |
|---|---|
| Thermal Nature | Excellent Conductor (not an insulator) |
| Key Function | Manages and distributes heat for uniformity |
| Typical Max Operating Temp | Below 2,400 °F (1,371 °C) |
| Key Limitation | Reactive with certain materials at high temperatures |
| Max Recommended Ramp Rate | 45 °F (25 °C) per minute |
Need a reliable thermal solution for your high-temperature processes?
Graphite's exceptional thermal conductivity is key to achieving temperature uniformity and efficiency in demanding applications. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including furnaces with graphite hot zones, tailored to your specific laboratory needs.
Let our experts help you select the perfect equipment to enhance your process reliability and results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is graphite good in high temperature? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential
- What is the graphite furnace used for? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C in a Controlled Environment
- What is the thermal limit of graphite? Unlock Extreme Heat Performance in Your Lab
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab
- Is a graphite melting point high or low? Discover Its Extreme Thermal Resilience



















