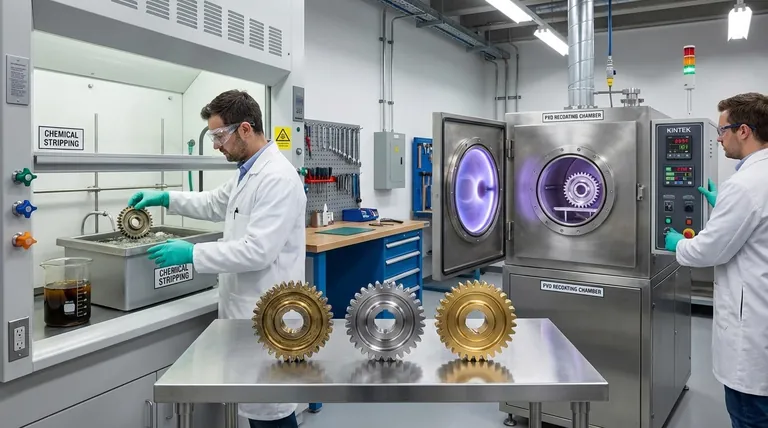
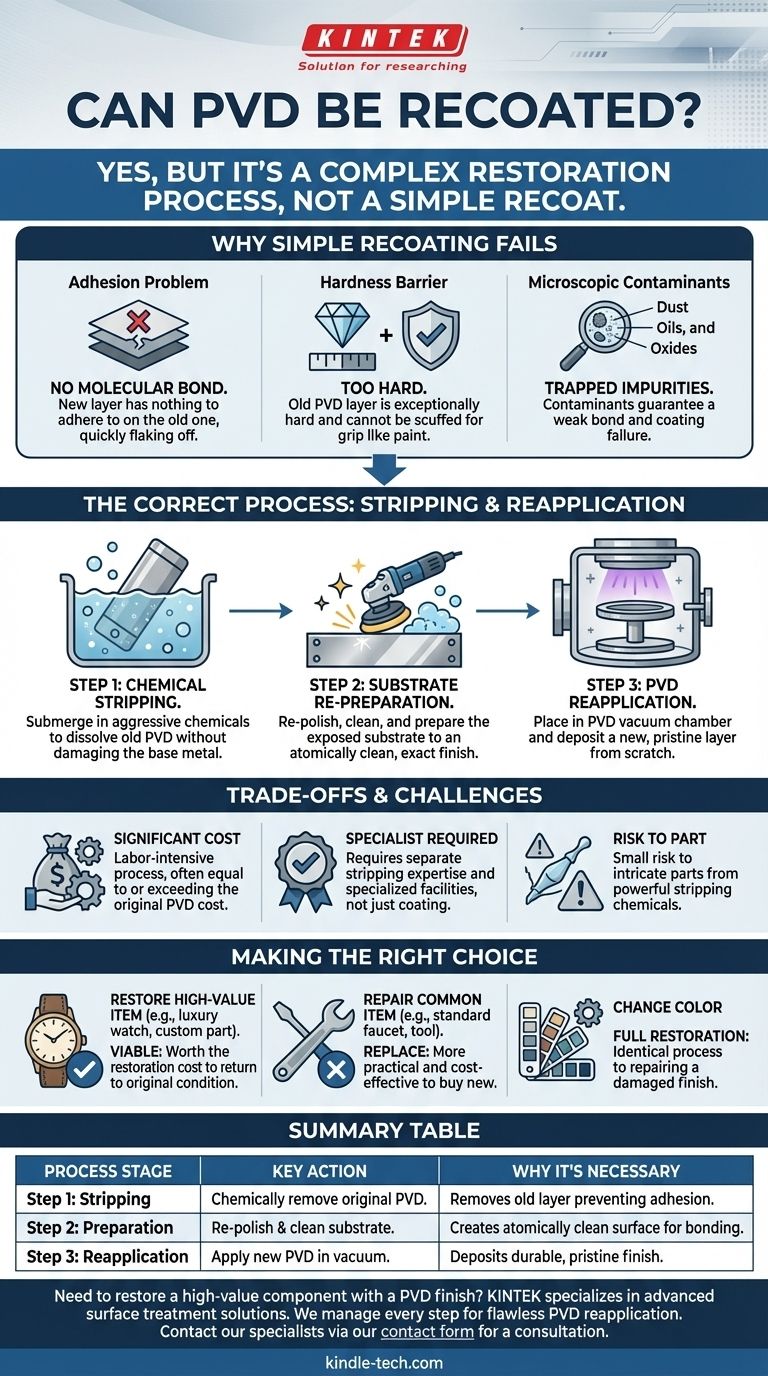
Yes, it is possible to recoat a PVD-finished item, but it is not a simple process. A new PVD coating cannot be applied directly on top of an old one. The original PVD layer must be completely and chemically stripped off before the item can be prepared and placed back into a PVD chamber for a new coating to be applied.
The critical point to understand is that "recoating" PVD is not like applying a second coat of paint. It is a full restoration process that involves chemically removing the original hard coating down to the bare substrate, re-polishing the base material, and then applying a brand-new PVD coating from scratch.

Why You Can't Simply Coat Over Old PVD
Applying a new PVD layer over an existing one is destined to fail. The process requires an atomically clean surface to create the molecular bond that gives the coating its signature durability.
The Problem of Adhesion
Physical Vapor Deposition works by bonding a thin film of material to a substrate at the atomic level inside a vacuum. An existing PVD layer, even if worn or scratched, prevents this essential bond from forming. The new layer would have nothing to adhere to and would quickly flake off.
The Hardness Barrier
As a coating, PVD is exceptionally hard—in some cases approaching the hardness of diamond. This incredible durability means you cannot simply sand or "scuff up" the surface to create a texture for a new coat to grip, as you might with paint. The old layer is a chemically inert and physically robust barrier.
Microscopic Contaminants
Any surface exposed to the environment, even one that looks clean, is covered in microscopic oils, oxides, and other contaminants. If you were to apply a new PVD coat over the old one, these contaminants would be trapped between the layers, guaranteeing a weak bond and a failed coating.
The Correct Process: Stripping and Reapplication
The professional method for recoating a PVD item is a multi-stage industrial process that essentially re-manufactures the surface finish.
Step 1: Complete Chemical Stripping
The first and most critical step is to submerge the item in a specialized, aggressive chemical bath designed to dissolve the original PVD coating. This process removes the thin film without damaging the base metal (the substrate) underneath.
Step 2: Substrate Re-Preparation
Once the PVD layer is gone, the exposed substrate must be prepared all over again. This almost always involves re-polishing and cleaning the surface to the exact finish required before any PVD application can occur. Any deep scratches that were in the base metal will need to be polished out at this stage.
Step 3: PVD Reapplication
With the part stripped, polished, and perfectly clean, it can finally be placed back into a PVD vacuum chamber. The standard PVD process is then run, depositing a new, pristine layer onto the prepared surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While technically possible, pursuing PVD recoating comes with practical considerations that you must weigh.
Significant Cost
The process of stripping, re-polishing, and recoating is labor-intensive and requires specialized facilities. Consequently, the cost can often be equal to, or even greater than, the cost of the original PVD application.
Finding a Specialist
Not all companies that apply PVD coatings also offer stripping services. It is a separate chemical process that requires different equipment, expertise, and safety protocols. You will need to find a specialist shop that handles the entire restoration workflow.
Risk to the Original Part
While generally safe for the substrate, the powerful chemicals used for stripping can pose a risk to delicate or intricately detailed items if not handled with expert care. There is always a small, but non-zero, risk of affecting the underlying material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to recoat a PVD item comes down to the value of the object and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is restoring a high-value or sentimental item (like a luxury watch or custom part): The stripping and recoating process is a viable, albeit expensive, method to bring it back to its original condition.
- If your primary focus is repairing a common, mass-produced item (like a standard faucet or tool): It is nearly always more practical and cost-effective to replace the item entirely.
- If your primary focus is changing the color of an item: You must be prepared for the full cost of a restoration, as the process is identical to repairing a damaged finish.
Understanding that PVD recoating is a full surface restoration empowers you to make the most practical and informed decision for your component.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Action | Why It's Necessary |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1: Stripping | Chemically remove the original PVD coating. | The old, hard layer prevents proper adhesion of a new coat. |
| Step 2: Preparation | Re-polish and clean the exposed substrate. | Creates an atomically clean surface for a strong molecular bond. |
| Step 3: Reapplication | Apply a new PVD coating in a vacuum chamber. | Deposits a new, durable, and pristine finish on the prepared surface. |
Need to restore a high-value component with a PVD finish?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab equipment and consumables, including advanced surface treatment solutions. Our expertise ensures your valuable parts are restored with the highest quality standards. The recoating process is complex, but we manage every step—from safe chemical stripping to flawless PVD reapplication—to bring your item back to its original glory.
Contact our specialists today via our contact form to discuss your project and receive a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is the advantage by using hot press forming? Achieve Stronger, More Complex Parts
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of hot stamping? Unlock Ultra-High Strength for Automotive Parts
- What is vacuum lamination? Achieve a Flawless, Durable Finish on Complex Shapes
- What is hot press lamination? The Ultimate Guide to Strong, Durable Material Bonding
- What is hot press forging? Creating Complex, High-Strength Metal Components



















