Fundamentally, no, solder cannot be used for brazing. The two processes are distinguished by a specific temperature threshold that dictates the type of filler metal used and the resulting strength of the joint. Using a low-temperature solder alloy in a high-temperature brazing application would simply cause it to melt and fail long before a proper brazed bond could ever be formed.
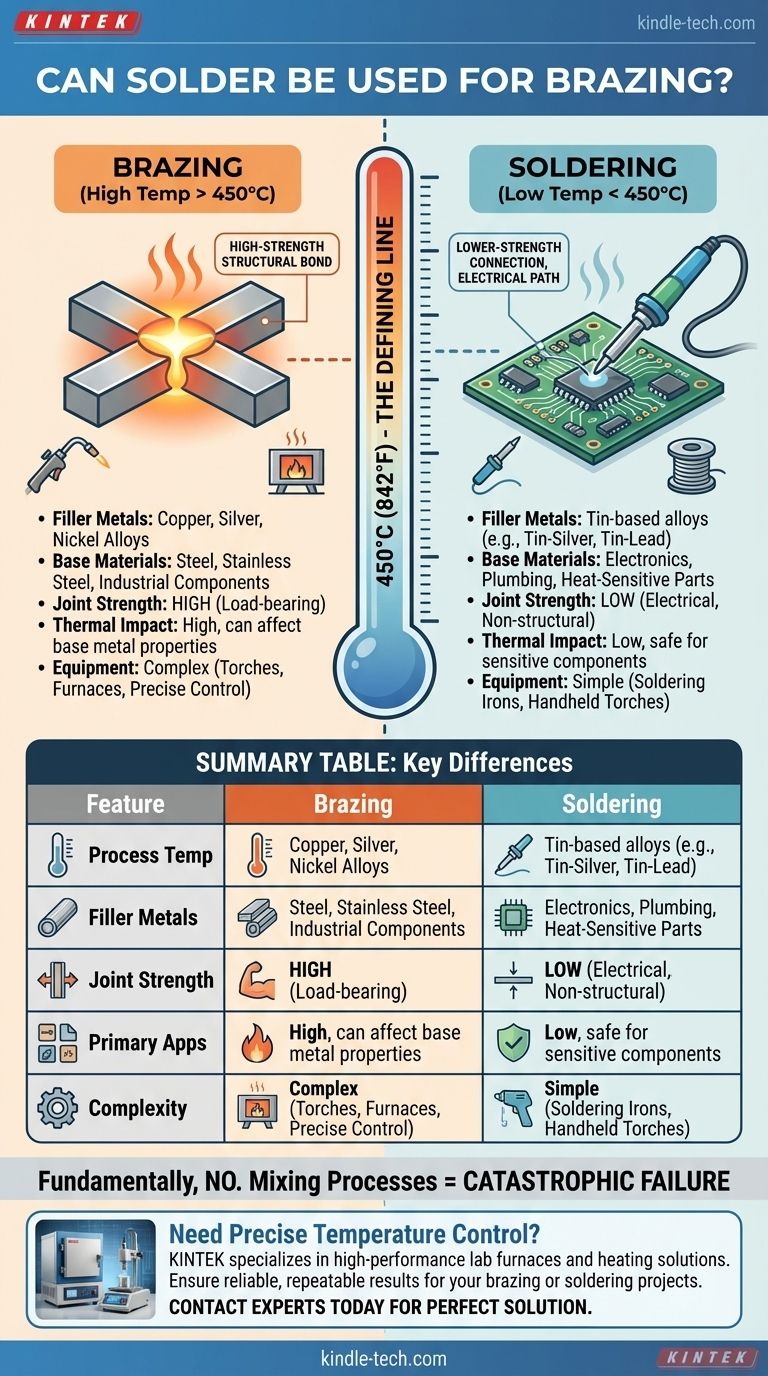
While soldering and brazing appear similar, they are fundamentally different metallurgical processes defined by one critical factor: temperature. Brazing creates a high-strength structural bond above 450°C (842°F), while soldering creates a lower-strength connection well below that threshold. Confusing the two can lead to catastrophic joint failure.

The Defining Line: Temperature and Material Science
To understand why these processes are not interchangeable, we must first establish the clear, industry-standard definition that separates them.
The 450°C (842°F) Rule
The single most important distinction is the melting point of the filler metal.
Brazing is a joining process that uses a filler metal with a melting point above 450°C (842°F), but below the melting point of the base metals being joined.
Soldering uses a filler metal (solder) with a melting point below 450°C (842°F).
How Temperature Dictates Everything
This temperature difference is not arbitrary. It dictates the alloys that can be used as fillers, the equipment required, and most importantly, the mechanical properties of the final joint.
The high temperatures in brazing allow for the use of strong, robust filler alloys like copper, silver, and aluminum-silicon. Soldering, by necessity, uses softer, lower-melting-point alloys based on tin.
What is Brazing? The High-Temperature Bond
Brazing is engineered to create strong, permanent, and often structural joints that can withstand significant stress and high service temperatures.
The Brazing Process
During brazing, the filler metal is heated slightly above its melting point and drawn into the tight-fitting gap between the base materials by capillary action. This phenomenon is often called wetting.
Critically, the base metals themselves do not melt. The bond is formed by the filler metal diffusing into the surface layer of the base materials, creating a powerful metallurgical connection.
Brazing Filler Metals
Brazing alloys are engineered for strength at high temperatures. As the references indicate, common fillers include copper, copper-silver alloys, nickel alloys, and aluminum-silicon alloys.
Compatible Base Materials
Because of its strength, brazing is used to join a vast range of industrial materials, including steel, stainless steel, cast iron, nickel, copper, brass, and even ceramics.
What is Soldering? The Low-Temperature Connection
Soldering is designed for applications where high strength is secondary to other factors, such as electrical conductivity or the need to avoid heat damage to the components.
The Soldering Process
The mechanism of soldering is similar to brazing—a melted filler flows into a joint—but it occurs at a much lower temperature.
The resulting bond is primarily an adhesive one, with very limited diffusion into the base materials. This is why a soldered joint is fundamentally weaker than a brazed one.
Common Solder Alloys
Typical solders are tin-based alloys, often mixed with silver, copper, or historically, lead. These materials are chosen for their low melting points and excellent electrical conductivity.
Typical Applications
Soldering is the standard for assembling electronic circuit boards because the low heat does not destroy sensitive components. It is also widely used in plumbing for joining copper pipes, where the joint needs to be leak-proof but does not face extreme structural loads.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these processes requires acknowledging their inherent compromises.
Joint Strength
Brazing creates joints that are significantly stronger than soldered joints. A properly brazed joint can often be as strong or even stronger than the base metals themselves.
Soldering produces a much weaker joint that is unsuitable for high-stress or structural applications.
Thermal Impact on Materials
The high heat of brazing can affect the base materials. For example, it can anneal or soften hardened steels, a factor that must be considered in the design.
Soldering's low heat input is its primary advantage, making it safe for joining delicate or heat-sensitive components that would be destroyed by brazing temperatures.
Process Complexity
Brazing generally requires more precise heat control and preparation, often involving torches or controlled-atmosphere furnaces to prevent oxidation.
Soldering can typically be done with simpler equipment, such as a soldering iron or a small handheld torch.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The correct process is determined entirely by the demands of the final product.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity and high-temperature performance: Brazing is the only acceptable choice for creating strong, load-bearing joints.
- If your primary focus is joining heat-sensitive electronics or ensuring conductivity: Soldering is the correct method to prevent component damage while creating an electrical path.
- If your primary focus is a simple, leak-proof seal in a low-stress application like plumbing: Soldering is the standard, most accessible, and safest method.
By respecting this fundamental boundary of temperature, you ensure the selection of the correct, reliable, and safe joining method for your project.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Brazing | Soldering |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | Above 450°C (842°F) | Below 450°C (842°F) |
| Filler Metals | Copper, Silver, Nickel alloys | Tin-based alloys (e.g., Tin-Silver, Tin-Lead) |
| Joint Strength | High (structural, load-bearing) | Low (electrical, non-structural) |
| Primary Applications | Steel, stainless steel, industrial components | Electronics, plumbing, heat-sensitive parts |
| Equipment Complexity | Higher (torches, furnaces) | Lower (soldering irons) |
Need the right equipment for your brazing or soldering project? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and heating solutions for precise temperature control. Whether you're joining industrial metals or assembling delicate electronics, our equipment ensures reliable, repeatable results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Rod for High Temperature Applications
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
People Also Ask
- What are 4 disadvantages of brazing? Understanding the Critical Limitations of This Joining Method
- How hot can you heat ceramic? From Pottery to 2700°C with Advanced Materials
- What are the advantages of brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean, and Complex Metal Assemblies
- What are the disadvantages of brazing? Key Challenges in Material Joining
- What are the strengths of brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean, and Precise Metal Joining







