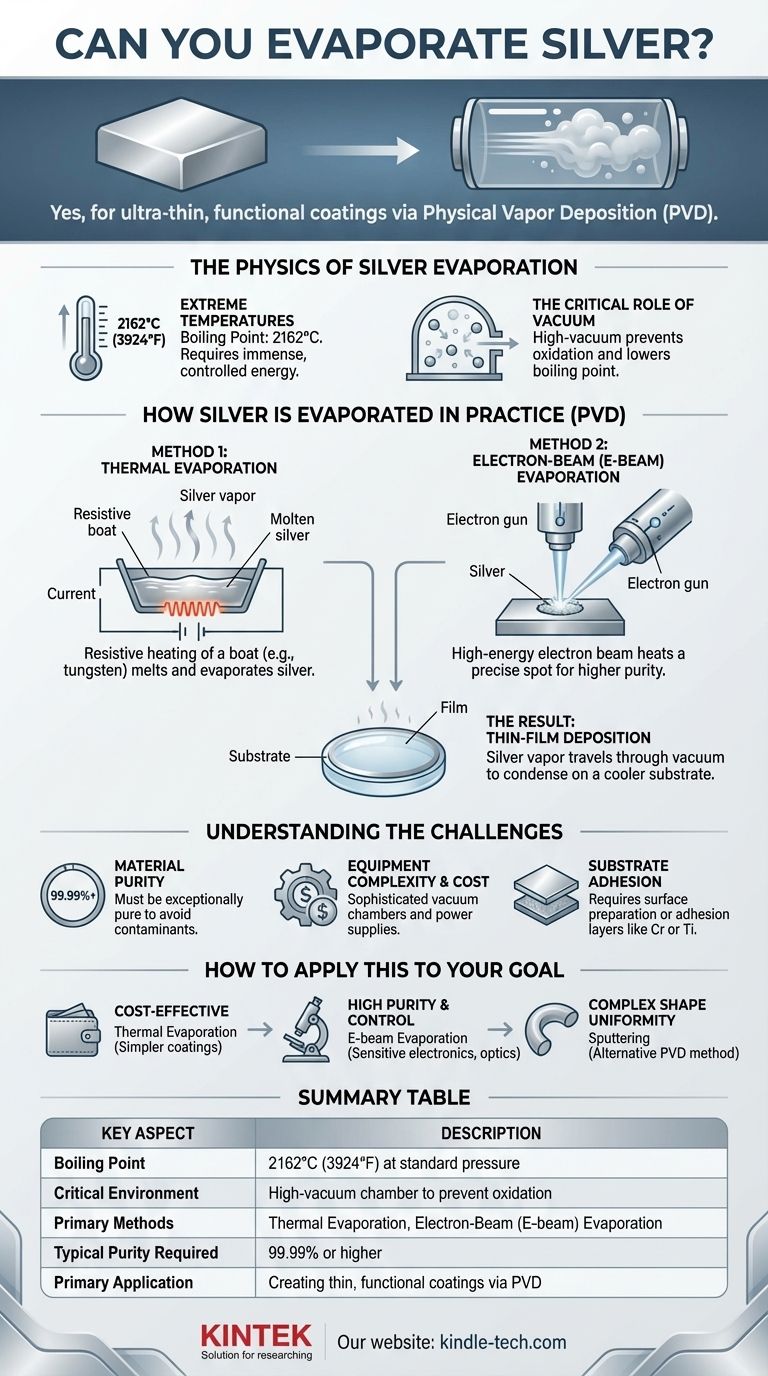
Yes, silver can be evaporated, but not in the way you might evaporate water on a stove. The process requires extreme temperatures and highly specialized equipment to turn solid silver into a vapor for industrial and scientific applications. This is done to create ultra-thin, functional coatings on surfaces like glass, plastics, or semiconductors.
The core challenge isn't just if silver can be evaporated, but how to do so without it instantly reacting with the air. The solution lies in combining immense heat with a high-vacuum environment, a process central to modern manufacturing.
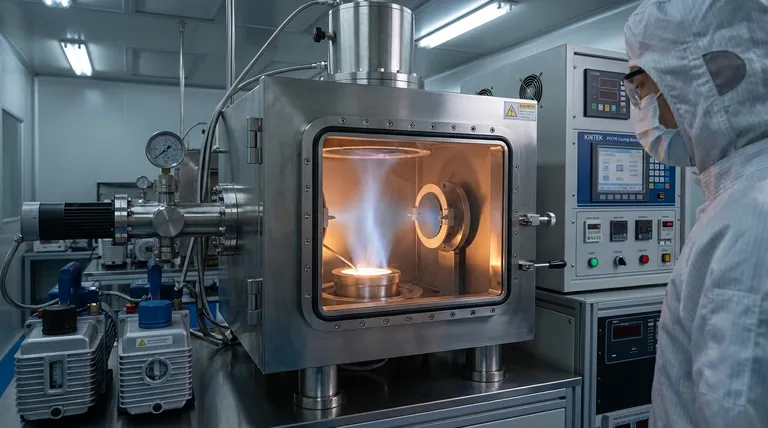

The Physics of Silver Evaporation
To understand how to turn a solid metal into a gas, we need to look at the specific conditions required to overcome its strong metallic bonds.
Extreme Temperatures Required
Silver has a very high boiling point, measured at 2162°C (3924°F) at standard atmospheric pressure.
Reaching this temperature requires a significant and highly controlled energy source, far beyond the capability of conventional ovens or torches.
The Critical Role of Vacuum
Attempting to boil silver in open air would be ineffective. The hot silver vapor would immediately react with oxygen and other atmospheric gases, forming silver oxide and other contaminants.
To prevent this, the entire process is conducted inside a high-vacuum chamber. A vacuum lowers the boiling point of the silver and, more importantly, removes air molecules that would otherwise contaminate the process and block the vapor from its target.
How Silver is Evaporated in Practice
In manufacturing and research, evaporating silver is a key step in a process called Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). The goal is to create a thin, uniform film of silver on a target object, or substrate.
Method 1: Thermal Evaporation
This is the most direct method. A small amount of pure silver is placed in a small container, often called a "boat," made of a material with a much higher melting point, like tungsten or molybdenum.
A very high electrical current is passed through this boat. The boat's electrical resistance causes it to heat up intensely, which in turn heats the silver past its boiling point, causing it to evaporate.
Method 2: Electron-Beam (E-beam) Evaporation
For higher purity and more precise control, e-beam evaporation is used. Inside the vacuum chamber, a high-energy beam of electrons is magnetically guided and aimed at the source silver.
The immense kinetic energy of the electrons is converted to thermal energy upon impact, heating a very localized spot on the silver to the point of evaporation.
The Result: Thin-Film Deposition
Regardless of the heating method, the silver atoms travel in a straight line through the vacuum chamber once they become a vapor.
They eventually strike the cooler substrate (like a lens, silicon wafer, or medical instrument) and condense back into a solid, forming a highly uniform, ultra-thin film.
Understanding the Challenges
While powerful, the process of evaporating silver is complex and requires careful management of several factors to achieve a successful outcome.
Material Purity is Essential
The starting silver material must be exceptionally pure (typically 99.99% or higher). Any impurities in the source material will also be evaporated and deposited, potentially compromising the final film's electrical or optical properties.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
Vacuum chambers, high-current power supplies, and electron beam guns are sophisticated and expensive pieces of industrial equipment. They require skilled operators and careful maintenance to function correctly.
Substrate Adhesion
Simply depositing silver vapor is not enough; the resulting film must stick firmly to the substrate. This often requires carefully cleaning the substrate surface or depositing a thin "adhesion layer" of another material, like chromium or titanium, before the silver.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The right method for evaporating silver depends entirely on the required quality and characteristics of the final thin film.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for simpler coatings: Thermal evaporation is often a more accessible and economical choice for applications where ultimate purity is not the top priority.
- If your primary focus is high purity and precise control: E-beam evaporation offers superior control over the deposition rate and results in a purer film, making it the standard for sensitive electronics and high-performance optics.
- If your primary focus is coating a complex shape uniformly: You may need to explore an alternative PVD method called sputtering, which offers better coverage over non-flat surfaces.
By precisely controlling heat and vacuum, we can transform a solid piece of metal into a high-performance surface one atom at a time.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 2162°C (3924°F) at standard pressure |
| Critical Environment | High-vacuum chamber to prevent oxidation |
| Primary Methods | Thermal Evaporation, Electron-Beam (E-beam) Evaporation |
| Typical Purity Required | 99.99% or higher |
| Primary Application | Creating thin, functional coatings via Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
Ready to achieve flawless thin-film coatings?
Whether you are developing advanced optics, sensitive electronics, or durable medical devices, the right evaporation method is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-purity lab equipment and consumables essential for precise thermal and e-beam evaporation processes.
Let our experts help you select the ideal solution for your specific substrate and performance requirements.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how we can support your PVD coating projects with reliable equipment and expert guidance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
People Also Ask
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods


















