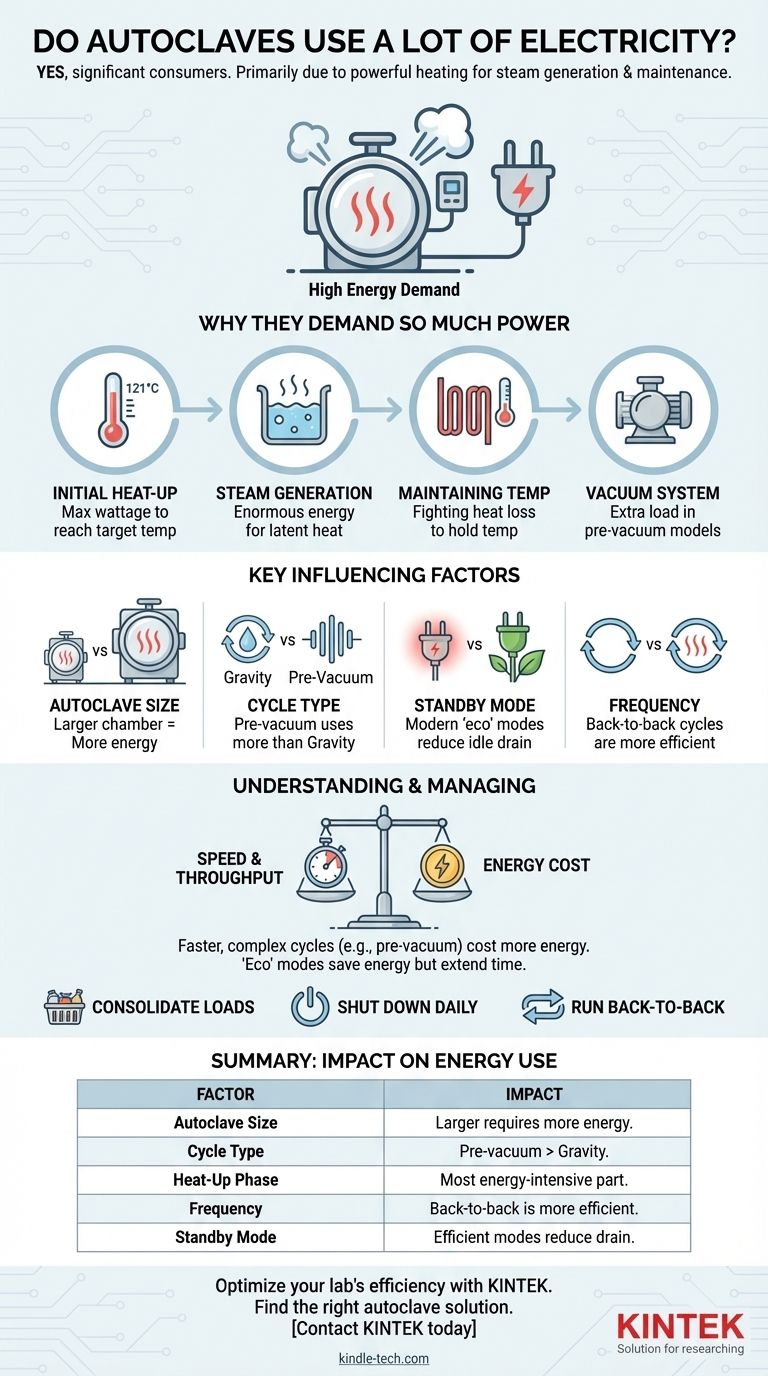
In short, yes, autoclaves are significant consumers of electricity. Their primary function involves using powerful heating elements to boil water into high-pressure steam and maintain precise temperatures, a fundamentally energy-intensive process. The exact consumption, however, varies dramatically based on the autoclave's size, the type of sterilization cycle being run, and its frequency of use.
The question isn't just if an autoclave uses a lot of power, but when and why. The majority of an autoclave's energy consumption is concentrated in the heat-up phase, making operational habits and modern efficiency features the key factors in managing its overall cost.
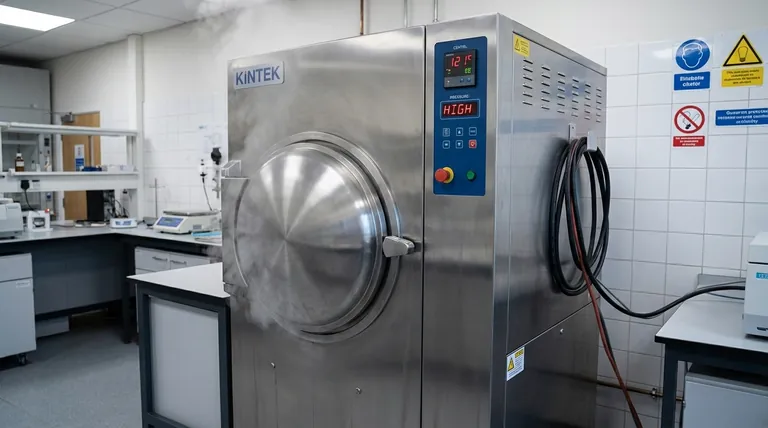

Why Autoclaves Demand So Much Power
An autoclave's high energy draw is a direct result of the physics of sterilization. It must rapidly heat a large mass of steel and water, create steam, and hold it under pressure.
The Initial Heat-Up Phase
This is the single most power-hungry part of any cycle. The internal heating elements draw their maximum wattage to bring the chamber walls and the water reservoir from room temperature up to the target sterilization temperature, typically 121°C (250°F) or 134°C (273°F).
Steam Generation
Turning water into steam requires a tremendous amount of energy, known as the latent heat of vaporization. The autoclave's heaters must supply this energy continuously to create the saturated steam necessary for effective sterilization.
Maintaining Sterilization Temperature
Once at the target temperature, the system must fight against natural heat loss to the surrounding environment. While less intensive than the initial heat-up, the heaters must cycle on and off to maintain the precise temperature and pressure required for the duration of the sterilization phase. The quality of the unit's insulation plays a critical role here.
The Vacuum System
Many modern autoclaves, particularly Class B (pre-vacuum) models, use a vacuum pump. This pump runs before the sterilization phase to remove air from the chamber, ensuring full steam penetration for porous items or complex instruments. This pump adds another electrical load to the cycle.
Key Factors Influencing Consumption
Not all autoclaves or cycles are created equal. Several variables determine the final number on your utility bill.
Autoclave Size and Chamber Volume
This is the most straightforward factor. A larger chamber contains more steel and requires more water and steam to fill, demanding significantly more energy to heat up and pressurize. A small tabletop unit for a dental office may use 2-3 kWh per cycle, while a large hospital unit can use over 50 kWh.
Cycle Type and Duration
A simple gravity displacement cycle, where steam pushes out the cooler air, is generally shorter and more energy-efficient. A pre-vacuum cycle involves multiple vacuum and steam-injection pulses, extending the cycle time and the use of the vacuum pump, thereby increasing energy consumption.
Standby and Idle Modes
An often-overlooked energy drain is the power consumed when the autoclave is idle but turned on. Older models could draw a significant amount of power just to keep the chamber warm and ready for the next cycle. Modern units with advanced, low-power standby modes can reduce this "vampire load" by over 90%.
Frequency of Use
Running back-to-back cycles can be more efficient than running cycles hours apart. The chamber is already hot, so the initial heat-up phase for the subsequent cycle requires far less energy. Conversely, running many small, half-empty loads is much less efficient than running one fully consolidated load.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an autoclave or an operating procedure often involves balancing sterilization efficacy with energy efficiency.
The Cost of Speed and Throughput
Pre-vacuum (Class B) autoclaves use more energy per cycle. However, they are much faster and are the only way to reliably sterilize complex hollow instruments or porous loads like textiles. For a busy clinic, the higher energy cost is a necessary trade-off for higher patient throughput and safety.
The Hidden Cost of Water
Some sterilization systems use a constant flow of water for cooling the vacuum pump or condenser. While not a direct electricity cost, high water consumption is a significant utility and environmental expense that must be considered as part of the total cost of ownership.
"Eco" Modes vs. Standard Cycles
Many modern autoclaves feature "eco" modes. These cycles typically save energy by heating up more slowly or reducing standby power. The trade-off is often a longer total cycle time, which may not be suitable for a high-volume workflow.
How to Manage Your Autoclave's Energy Footprint
You can actively manage the energy consumption of your sterilization process by aligning your equipment and procedures with your specific operational needs.
- If your primary focus is minimizing daily operational costs: Prioritize running fully consolidated loads and train staff to shut down the unit completely at the end of the day rather than leaving it in standby.
- If your primary focus is high throughput in a busy facility: Accept the higher energy use of a pre-vacuum model but optimize its use by scheduling back-to-back cycles to take advantage of the retained chamber heat.
- If your primary focus is selecting a new, efficient unit: Look beyond the purchase price and compare data on energy (kWh) and water consumption per cycle, and specifically request models with intelligent, low-wattage sleep modes.
By understanding how and when an autoclave uses energy, you can transform it from an uncontrollable expense into a manageable operational variable.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Energy Use |
|---|---|
| Autoclave Size | Larger chambers require more energy to heat and pressurize. |
| Cycle Type | Pre-vacuum cycles use more energy than gravity displacement cycles. |
| Heat-Up Phase | The initial heating is the most energy-intensive part of the cycle. |
| Frequency of Use | Back-to-back cycles are more efficient than spaced-out cycles. |
| Standby Mode | Modern units with efficient standby modes reduce idle power drain. |
Optimize your lab's energy efficiency and sterilization workflow with KINTEK.
Autoclaves are essential for laboratory safety, but their energy consumption can significantly impact your operational costs. Whether you need a compact, energy-efficient model for a small clinic or a high-throughput pre-vacuum system for a busy hospital, KINTEK provides reliable lab equipment tailored to your specific needs. Our experts can help you select an autoclave that balances performance with cost-effectiveness, ensuring you get the precise sterilization you need without unnecessary energy waste.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation on finding the right autoclave solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Laboratory High Pressure Steam Sterilizer Vertical Autoclave for Lab Department
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Portable Digital Display Automatic Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave for Sterilization Pressure
- Portable High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- How is an autoclave utilized in antimicrobial experiments? Ensure Precise Nanoparticle Research Integrity
- Why is the prevention of air entrapment critical for the autoclave sterilization process? Ensure 100% Sterility Today
- What role does an autoclave play in remediation experiments? Ensure Precision by Eliminating Biological Noise
- How should solid materials in bags be prepared for decontamination? Master Steam Penetration for Safe Sterilization
- What experimental conditions do stainless steel autoclaves provide for PCT-A leaching? Optimize Phosphate Glass Testing



















