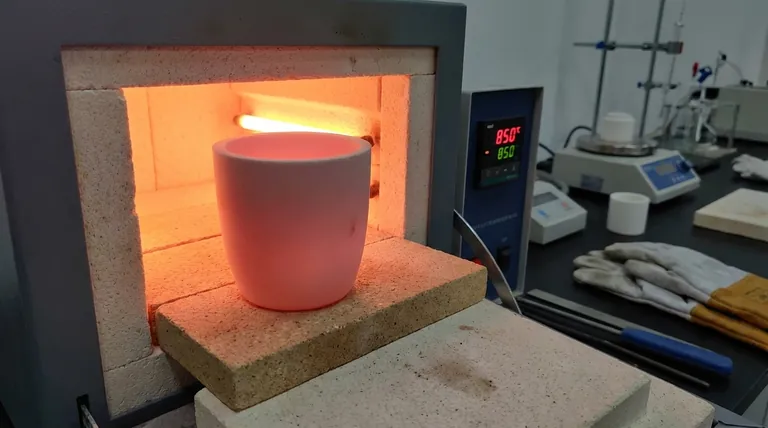
Yes, preheating a crucible is a critical and non-negotiable step for both safety and performance. Failing to do so is one of the most common causes of catastrophic crucible failure. This process is essential for driving out absorbed moisture and preventing thermal shock, which can cause a new or stored crucible to crack or even explode when exposed to the intense, rapid heating of a furnace.
The core purpose of preheating is not simply to warm up the crucible, but to slowly and evenly remove trapped moisture and eliminate internal stresses. This simple procedure is the primary defense against thermal shock, ensuring the crucible remains intact and your melt is successful.

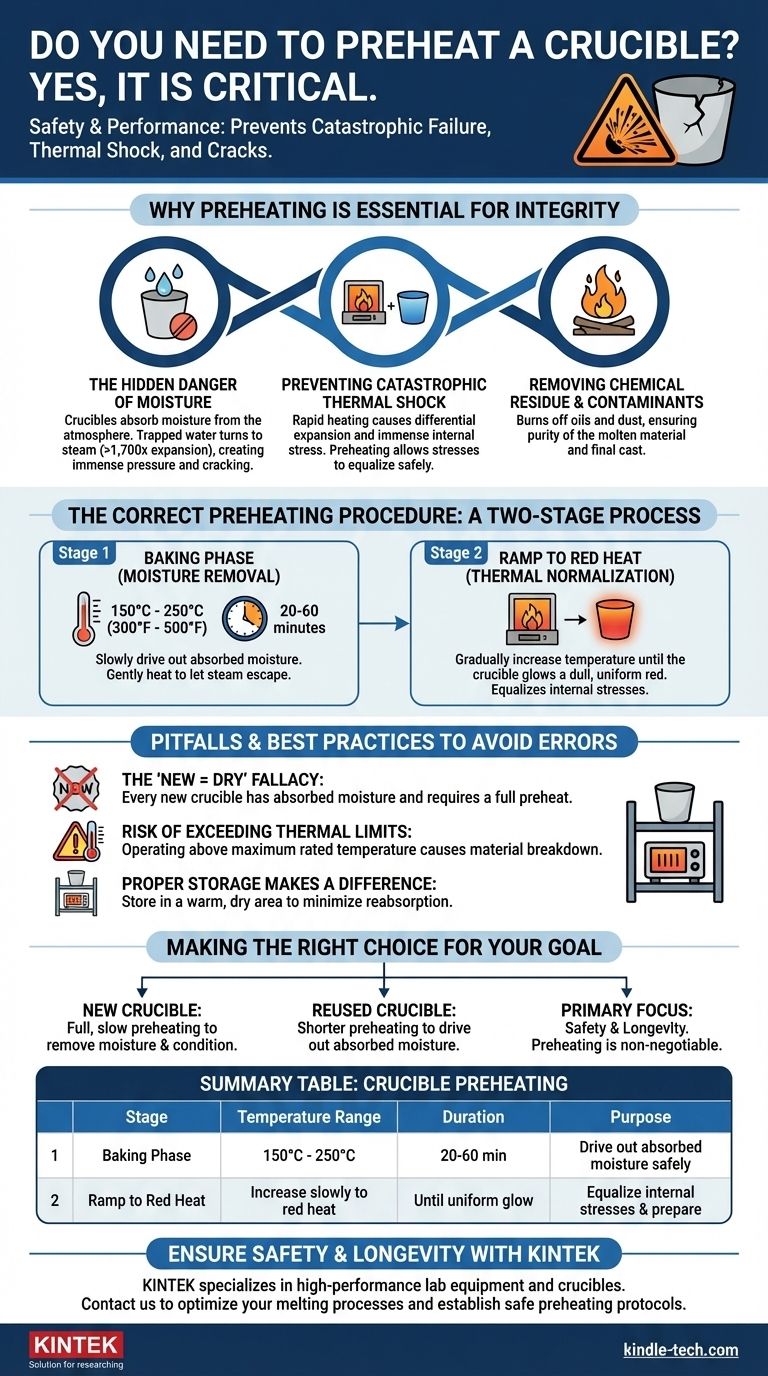
Why Preheating is Essential for Crucible Integrity
A crucible may appear solid and inert, but materials like clay graphite and silicon carbide are porous on a microscopic level. This porosity is the root cause of the problems that preheating solves.
The Hidden Danger of Moisture
Crucibles absorb moisture directly from the atmosphere. Even a brand-new crucible that has been sitting in storage has absorbed water.
When this crucible is heated rapidly, the trapped water turns to steam. This steam expands to over 1,700 times its original volume, creating immense internal pressure that can crack the crucible walls from the inside out.
Preventing Catastrophic Thermal Shock
Thermal shock occurs when different parts of a material expand at different rates due to a rapid temperature change. Placing a cold crucible into a hot furnace creates a massive temperature gradient between its outer and inner surfaces.
This differential expansion creates immense internal stress. Preheating ensures the entire crucible body is brought to a uniform temperature slowly, allowing these stresses to equalize safely and preventing fractures.
Removing Chemical Residue and Contaminants
The preheating process also serves to burn off any oils, dust, or other contaminants from manufacturing, shipping, or handling. This ensures these unwanted substances do not end up in your molten material, which could compromise the purity and quality of your final cast.
The Correct Preheating Procedure
A proper preheat cycle is a slow, methodical process done in stages. Rushing this is as dangerous as skipping it entirely.
Stage 1: The 'Baking' Phase
The initial goal is to gently drive out all absorbed moisture. This should be done at a low temperature, typically between 150°C and 250°C (300°F to 500°F).
Hold the crucible at this temperature for at least 20-60 minutes. For larger crucibles or in humid environments, a longer duration may be necessary. The key is slow, even heat to let the steam escape gently.
Stage 2: The Ramp to Red Heat
After you are confident the moisture is gone, begin to slowly increase the furnace temperature. Continue this gradual ramp-up until the entire crucible glows a dull, uniform red.
This stage ensures the crucible's internal structure has normalized to the heat and is ready for the final temperature increase and the introduction of the metal charge.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Best Practices
Avoiding common misconceptions is crucial for maintaining your equipment and ensuring your safety. A disciplined approach prevents costly and dangerous errors.
The "It's New, So It's Dry" Fallacy
Never assume a new crucible is dry and ready for use. It has been exposed to the atmosphere during shipping and storage, and it has almost certainly absorbed moisture. Every new crucible requires a full preheating cycle.
The Risk of Exceeding Thermal Limits
While preheating is about adding heat, it must be controlled. Every crucible has a maximum rated temperature. Exceeding this limit, even on a properly preheated crucible, will cause the material to break down and lead to a dangerous failure. Always operate within the manufacturer's specified limits.
Proper Storage Makes a Difference
Your work isn't done after the melt. Storing your crucibles correctly minimizes how much moisture they reabsorb. Keep them in a warm, dry area off of cold, damp floors. This makes the next preheating cycle faster and more effective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Adhering to a strict preheating protocol is the mark of a professional. It removes a major variable and protects you, your equipment, and your work.
- If you are using a new crucible: Always perform a full, slow preheating cycle to safely remove absorbed moisture and condition it for its first use.
- If you are reusing a crucible: A shorter preheating cycle is still required to drive out any moisture absorbed from the atmosphere between melts.
- If your primary focus is safety and longevity: Make preheating a non-negotiable, documented step in your standard operating procedure for every single melt.
Proper crucible preparation is the foundation of every safe and successful casting.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Preheating Stage | Temperature Range | Duration | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baking Phase (Moisture Removal) | 150°C - 250°C (300°F - 500°F) | 20-60 minutes | Drive out absorbed moisture safely |
| Ramp to Red Heat (Thermal Normalization) | Increase slowly to red heat | Until uniform glow | Equalize internal stresses and prepare for melting |
Ensure your lab's safety and crucible longevity with KINTEK's expert solutions. Proper crucible handling is non-negotiable for successful melting operations. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including crucibles designed for durability and precise thermal management. Our team can help you select the right crucible and establish safe preheating protocols tailored to your specific laboratory needs. Don't risk equipment failure or compromised results—contact us today to optimize your melting processes and protect your investments.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range of alumina crucibles? Key Factors for Safe High-Temp Use
- What are the benefits of using an alumina crucible with a lid for TiB2 nanopowder heat treatment? Ensure High Purity
- What is the purpose of using an alumina crucible with a lid for g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Nanosheet Production
- What temperature is an Al2O3 crucible? Key Factors for High-Temperature Success Up to 1700°C
- How much heat can a ceramic crucible withstand? A Guide to Material-Specific Temperature Limits



















