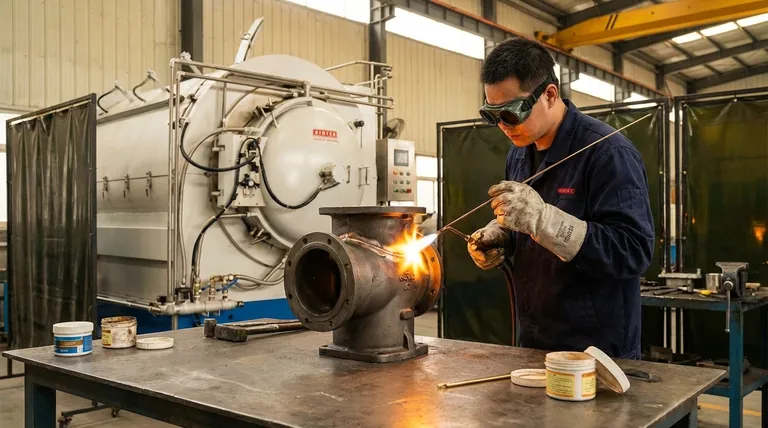
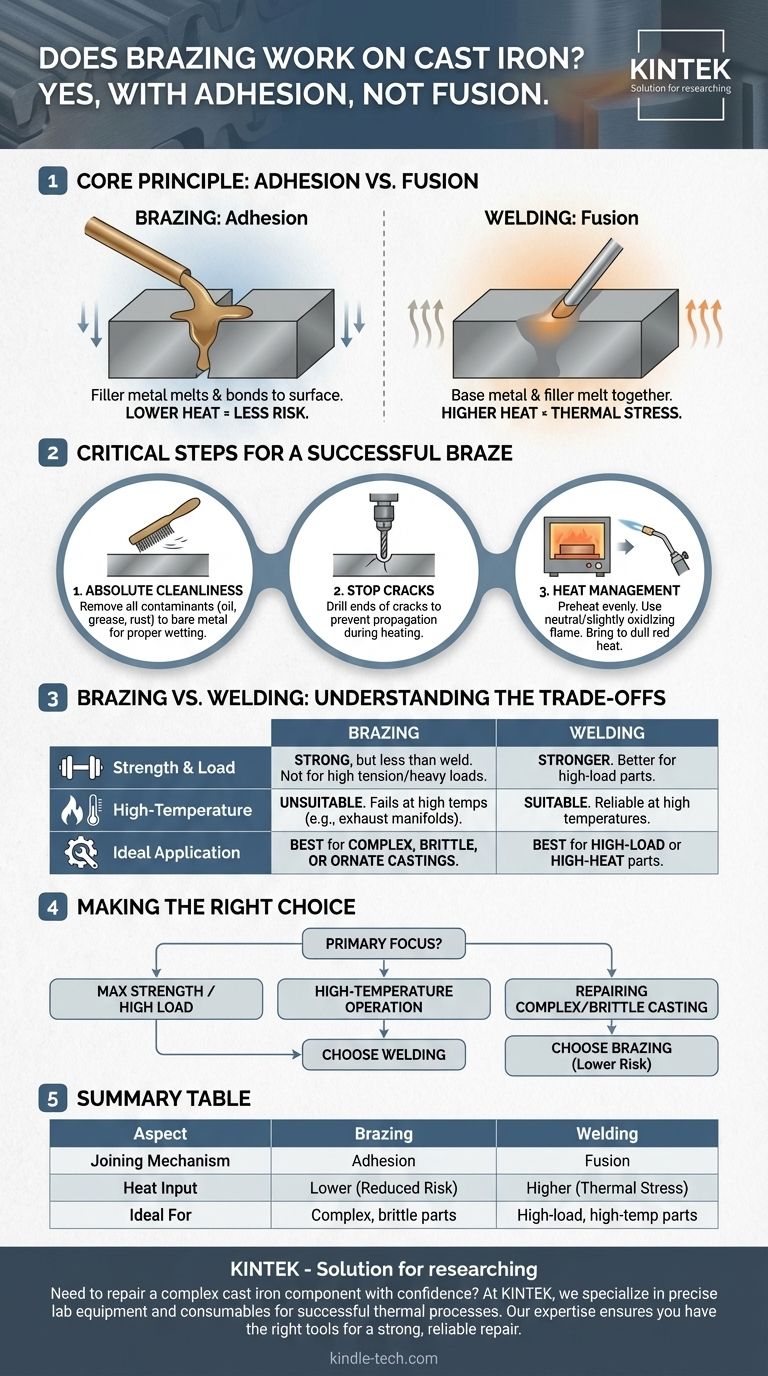
Yes, brazing is a common and effective method for joining or repairing cast iron. It is often referred to as "braze welding" and is particularly useful for complex castings or types of iron that are difficult to weld, as it puts significantly less thermal stress on the base metal.
The core principle to understand is that brazing joins cast iron using adhesion, not fusion. A filler metal with a lower melting point flows onto and bonds with the cast iron's surface without actually melting the iron itself, making it a lower-heat, lower-risk alternative to true welding.

How Brazing Works on Cast Iron
Traditional welding melts both the base metal and the filler rod, fusing them into a single, continuous piece. Brazing works on a different principle that is often better suited to the brittle nature of cast iron.
The Role of Adhesion
In brazing, only the filler metal (typically a bronze or brass alloy rod) melts. This molten filler is drawn into the prepared joint by capillary action, where it adheres to the surfaces of the cast iron, acting like a very strong metallic glue.
Why This Protects the Casting
Cast iron is sensitive to rapid heating and cooling, which can cause cracking. Because brazing occurs at a much lower temperature than welding, it minimizes the thermal shock to the part. This drastically reduces the risk of the repair process causing new cracks to form.
Critical Steps for a Successful Braze
Proper preparation and heat management are not optional; they are essential for creating a strong, lasting bond on cast iron.
Absolute Cleanliness is Non-Negotiable
The success of the braze depends entirely on the filler metal's ability to "wet" and adhere to the cast iron surface. Any oil, grease, rust, or other contaminants will prevent this bond from forming, leading to a failed joint. The surface must be cleaned down to bare, bright metal.
Stop Cracks from Spreading
When repairing a crack, it is a standard practice to drill a small hole at each visible end of the fracture. This relieves the stress concentration at the tip of the crack and prevents it from propagating further during the heating process.
Managing Heat: Preheating and Flame Control
The part must be heated evenly to prevent stress. For larger castings, preheating the entire piece in a furnace is the ideal method. During the process, a neutral or slightly oxidizing flame is used to bring the joint area to a dull red heat before applying the filler rod.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Brazing vs. Welding
Choosing between brazing and welding requires an objective look at the demands that will be placed on the finished part. Brazing is an excellent tool, but it has clear limitations.
Strength and Load Bearing
A properly executed braze is strong, but it is not as strong as a true weld. The strength is in the filler material itself and its bond to the surface. For parts subjected to high tension or heavy structural loads, a proper fusion weld will provide a more robust repair.
High-Temperature Applications
The filler metals used for brazing have a significantly lower melting point than cast iron. This makes brazing completely unsuitable for parts that operate at high temperatures, such as exhaust manifolds or internal engine components, as the brazed joint will fail.
When Brazing is the Superior Choice
Brazing shines when repairing complex, ornate, or "hard-to-weld" types of cast iron. Its lower heat input makes it the ideal choice for parts where the risk of cracking from a full welding procedure is unacceptably high and the part is not under extreme load or heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Repair
Use the application of the part to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength for a high-load part: A proper fusion welding procedure is the more appropriate choice.
- If your part operates at high temperatures: Brazing is unsuitable and will fail; welding is the only reliable option.
- If your primary focus is repairing a complex or brittle casting not under heavy load: Brazing is an excellent, lower-risk method that minimizes the chance of further damage.
By understanding these principles, you can confidently choose the right method to reliably repair your cast iron components.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Brazing on Cast Iron |
|---|---|
| Joining Mechanism | Adhesion (filler metal bonds to surface) |
| Heat Input | Lower, reducing thermal stress and cracking risk |
| Ideal For | Complex, brittle, or hard-to-weld castings |
| Strength | Strong, but not as strong as a fusion weld |
| Temperature Limit | Unsuitable for high-temperature applications (e.g., exhaust manifolds) |
Need to repair a complex cast iron component with confidence?
Brazing offers a controlled, lower-heat alternative to traditional welding, minimizing the risk of damaging your valuable castings. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for successful thermal processes. Our expertise ensures you have the right tools for a strong, reliable repair.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of brazing welding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Source
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What is brazing in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Joint Quality and Efficiency



















