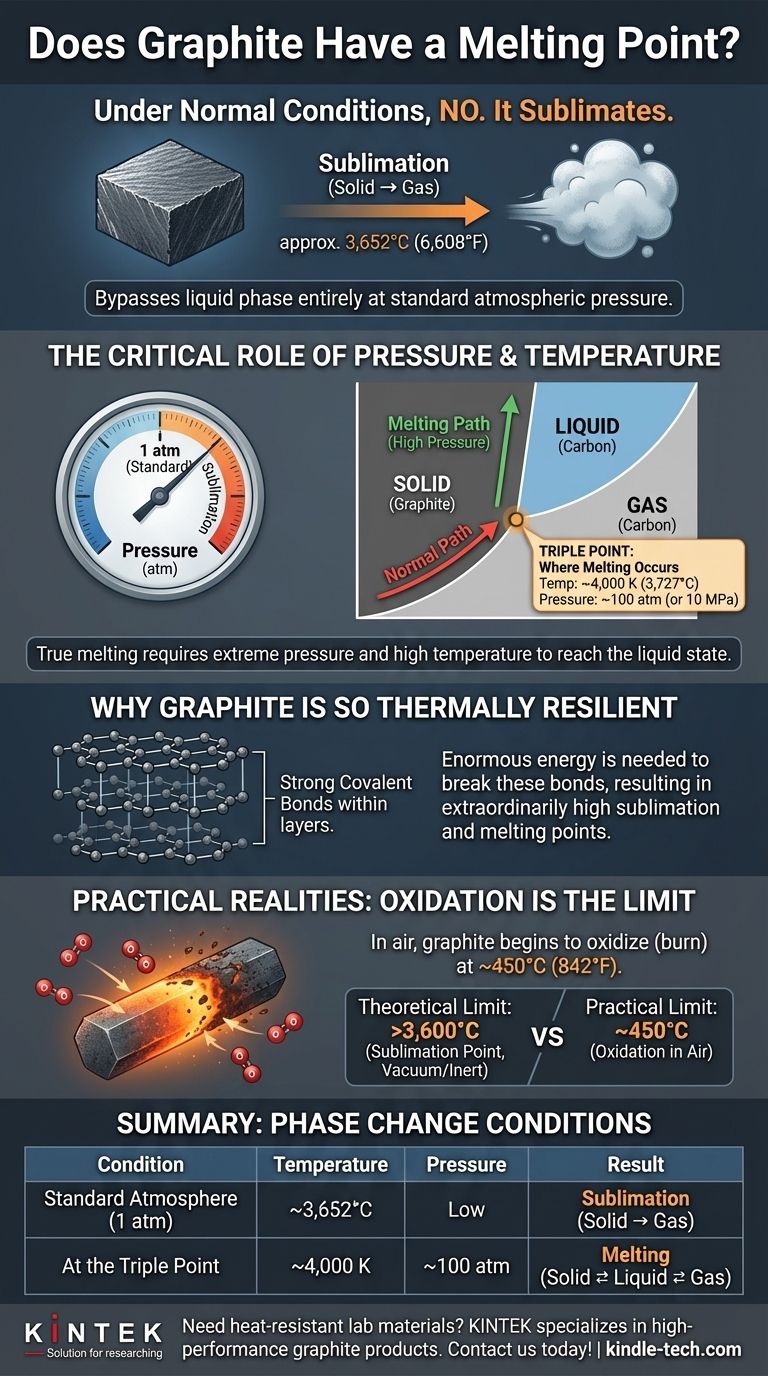
Under normal conditions, graphite does not melt. Instead of turning into a liquid, it bypasses that phase entirely and sublimates—turning directly from a solid into a gas at approximately 3,652°C (6,608°F). For graphite to truly melt into a liquid state, it must be subjected to both extremely high temperatures and immense pressure.
The concept of a single "melting point" for graphite is misleading. Its state of matter is a direct function of two variables: temperature and pressure. While it can melt under specific, extreme conditions, its defining characteristic for nearly all practical purposes is its incredibly high sublimation point.

The Critical Role of Pressure and Temperature
The question of whether graphite melts introduces one of the most fundamental principles of materials science: the state of a substance (solid, liquid, or gas) is not determined by temperature alone. Pressure is an equally critical factor.
Sublimation: The Standard Behavior
At the standard atmospheric pressure we experience every day (1 atm), heating graphite will not produce a liquid.
The strong bonds holding the carbon atoms together require a massive amount of energy to break. At 1 atm, the energy required is so high that the atoms gain enough kinetic energy to fly apart directly into a gaseous state, a process called sublimation.
The Graphite Phase Diagram
A phase diagram is a map that shows a substance's physical state at different combinations of temperature and pressure. For graphite, this map reveals why we don't see it melt.
Our everyday experience exists along the very bottom of this map, at low pressure. To find liquid carbon, you must move up the map to a region of much higher pressure.
Finding the Triple Point
The triple point is the specific combination of temperature and pressure where the solid, liquid, and gaseous phases of a substance can all exist in equilibrium. This is the minimum condition under which true melting can occur.
For graphite, the triple point is estimated to be around 4,000–4,500 Kelvin (3,727–4,227 °C) and at pressures of 100 atmospheres (or 10 MPa). These are not conditions found in any normal environment.
Why Graphite Is So Thermally Resilient
Graphite's extreme resistance to heat is rooted in its atomic structure. Understanding this structure explains why it behaves so differently from materials like ice or metal.
The Strength of Covalent Bonds
Graphite consists of layers of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. Within each layer, every carbon atom is bonded to three others by incredibly strong covalent bonds.
These bonds are among the strongest in nature and require an enormous amount of thermal energy to break apart, which is why graphite's sublimation and melting points are so extraordinarily high.
Energy Required for Phase Change
To melt or sublimate a substance, you must supply enough energy to overcome the forces holding its atoms or molecules together.
Because graphite's covalent bonds are so stable, the energy input needed is immense, making it one of the most heat-resistant materials known to man. This property makes it ideal for applications like crucibles for melting metals, furnace linings, and rocket nozzles.
Common Pitfalls and Practical Realities
While graphite's theoretical properties are impressive, real-world applications introduce other limitations that are often more important than its sublimation point.
Theoretical Limit vs. Practical Limit
The sublimation temperature of over 3,600°C is a theoretical maximum that is only relevant in a vacuum or an inert (non-reactive) atmosphere.
In most industrial or engineering contexts, other factors will cause the material to fail long before it reaches this temperature.
The Critical Flaw: Oxidation
Graphite's biggest vulnerability is oxygen. In the presence of air, graphite will begin to oxidize (effectively, burn) at temperatures as low as 450°C (842°F).
Therefore, for any high-temperature application, the primary concern is not melting or sublimation, but preventing the material from reacting with its environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding how graphite behaves under heat is key to using it effectively or simply appreciating its unique properties.
- If your primary focus is a high-temperature industrial application: You must account for oxidation. The practical temperature limit is determined by the surrounding atmosphere, not the sublimation point.
- If you are a student of chemistry or materials science: The key insight is that graphite's melting point exists only at its triple point, requiring both high temperature (~4,000 K) and high pressure (~100 atm).
- If you just need a simple, definitive answer: At normal pressure, graphite sublimates directly into a gas; it does not melt.
Ultimately, graphite's behavior is a powerful illustration that a material's properties are dictated by its fundamental structure and its interaction with the environment.
Summary Table:
| Condition | Temperature | Pressure | Resulting Phase Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Atmosphere (1 atm) | ~3,652°C (6,608°F) | Low | Sublimation (Solid → Gas) |
| At the Triple Point | ~4,000 K (3,727°C) | ~100 atm | Melting (Solid ⇄ Liquid ⇄ Gas) |
Need a heat-resistant material for your lab? Graphite's exceptional properties make it ideal for high-temperature applications like furnace linings and crucibles. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including graphite products designed for durability and precision. Let our experts help you select the right materials for your specific thermal processing needs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and find the perfect solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why graphite is used in furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment & Energy Efficiency
- Can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking its extreme 3,600°C potential in inert environments
- Why is graphite used in furnaces? For Extreme Heat, Purity, and Efficiency
- What temperature can graphite withstand? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential
- What is the temperature range of a graphite furnace? Unlock up to 3000°C for advanced materials processing.



















