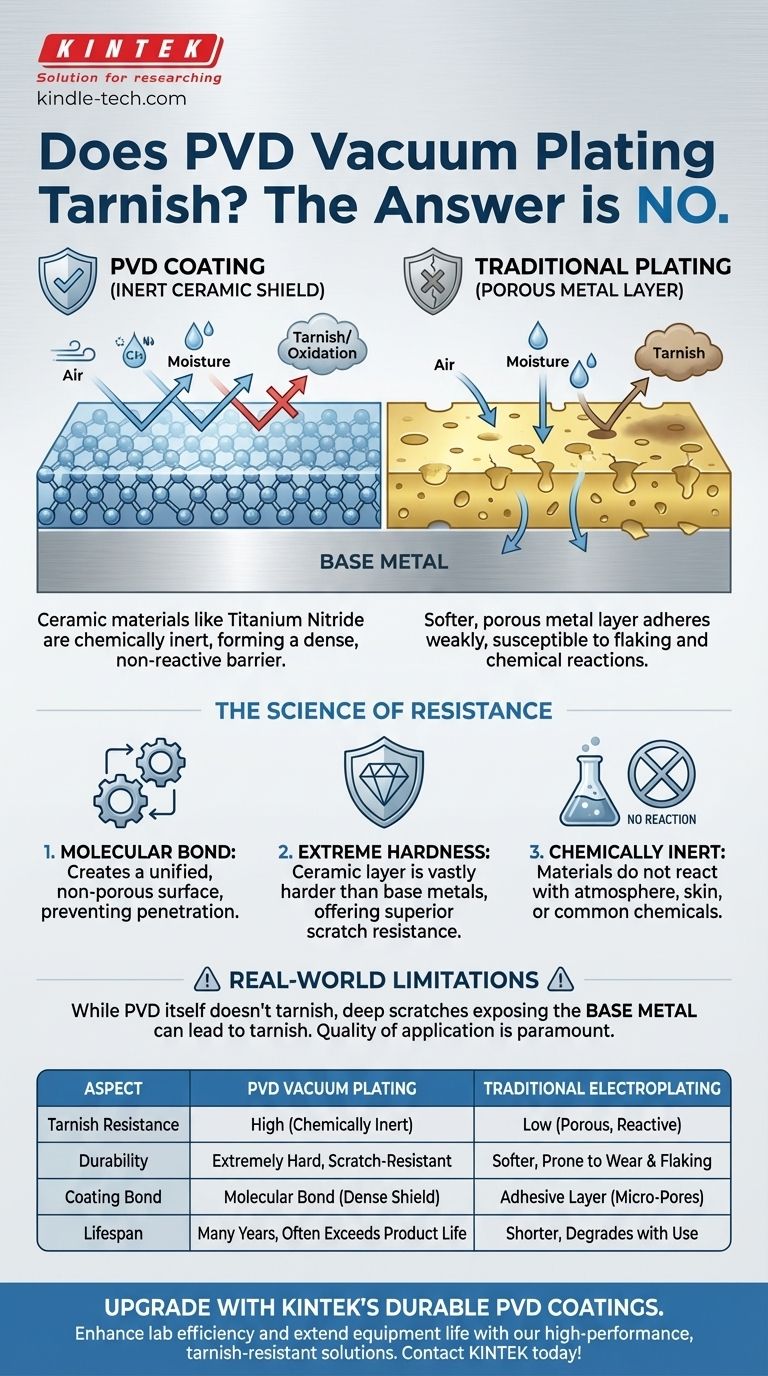
No, as a rule, PVD vacuum plating does not tarnish. The materials used in the PVD process, such as titanium nitride, are chosen specifically for their inert and non-reactive properties. This creates a hard, dense barrier that protects the underlying metal from the atmospheric and chemical exposure that causes traditional tarnish.
The core reason PVD coatings resist tarnish is that they are not a simple layer of metal; they are a micro-thin ceramic bonded to the base metal at a molecular level, forming a chemically stable shield.

What Exactly is PVD Coating?
To understand why PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) is so resilient, you must first understand that it is fundamentally different from traditional plating methods.
A Layer of Vapor, Not Paint
The PVD process takes place in a high-tech vacuum chamber. A solid, high-purity material (like titanium or zirconium) is vaporized into a plasma of atoms and ions.
This vapor is then deposited onto the object being coated, forming a new, bonded surface layer that is incredibly dense and hard.
The Materials Make the Difference
The most common materials used for decorative PVD coatings are titanium nitride, zirconium nitride, and chromium nitride.
These are not metals in the traditional sense; they are ceramics. This is critical because ceramics are known for their extreme hardness and chemical stability.
How It Differs from Traditional Plating
Traditional electroplating uses a wet chemical bath to deposit a thin layer of metal, like gold or silver. This layer is softer, more porous, and adheres less strongly than a PVD coating.
Because of this, traditional plating is far more susceptible to flaking, scratching, and chemical reactions (tarnishing).
The Science Behind Why PVD Resists Tarnish
The durability of PVD isn't an accident; it's a direct result of the physics and chemistry involved in the process.
An Inert, Non-Reactive Barrier
Tarnish is a chemical reaction, typically oxidation, that occurs when a reactive metal is exposed to air, moisture, and oils.
The ceramic materials used in PVD are chemically inert. They simply do not react with the elements in the atmosphere, your skin, or common chemicals.
A True Molecular Bond
Unlike a coating that merely sits on top of the surface, PVD creates a molecular bond with the base metal.
This creates a unified surface that is incredibly dense and non-porous. There are no microscopic holes for moisture or air to penetrate and attack the metal underneath.
Superior Hardness and Scratch Resistance
PVD coatings are significantly harder than the base metals they cover and vastly harder than traditional gold or silver plating.
This exceptional scratch resistance is crucial. A coating can only prevent tarnish as long as it remains intact, and PVD's hardness ensures it stands up to daily wear and tear.
Understanding the Real-World Limitations
While PVD is a superior technology, no coating is indestructible. Understanding its limitations is key to managing expectations.
The Base Metal Still Matters
The PVD coating itself will not tarnish. However, if the coating is compromised by a deep gouge or scratch that exposes the underlying base metal (such as brass or copper), that exposed metal can then tarnish.
Quality of Application is Paramount
The effectiveness of a PVD coating is highly dependent on the quality of the application process.
A poorly executed PVD process can result in poor adhesion or an uneven layer, making it more susceptible to damage and failure over time.
Wear and Tear is Inevitable
Over many years of extreme, abrasive wear—such as on a bracelet that constantly rubs against a desk—the PVD coating can eventually wear thin.
This is a process of gradual abrasion, not chemical tarnishing. For most applications, this lifespan is measured in many years, often exceeding the life of the product itself.
Making the Right Choice for Durability
Your decision should be based on your primary goal for the item, whether it's jewelry, a watch, or fixtures.
- If your primary focus is maximum longevity for a daily-wear item: PVD is the superior choice, offering unparalleled resistance to scratches, corrosion, and tarnish.
- If your primary focus is the appearance of a precious metal with high durability: PVD-coated stainless steel provides the look of gold or rose gold with scratch resistance that far exceeds actual gold plating.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible cost for occasional-wear items: Traditional electroplating is cheaper but requires the understanding that it will degrade and potentially tarnish much faster.
Ultimately, choosing PVD is an investment in a surface engineered for lasting visual integrity and performance.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD Vacuum Plating | Traditional Electroplating |
|---|---|---|
| Tarnish Resistance | High (chemically inert ceramic layer) | Low (porous, reactive metal layer) |
| Durability | Extremely hard and scratch-resistant | Softer, prone to wear and flaking |
| Coating Bond | Molecular bond for a dense, non-porous shield | Adhesive layer with potential for micro-pores |
| Lifespan | Many years, often exceeding product life | Shorter, degrades with exposure and use |
Upgrade your lab’s capabilities with durable, tarnish-resistant PVD coatings from KINTEK!
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including advanced PVD coating solutions. Our coatings provide a hard, chemically inert barrier that protects your instruments and components from wear, corrosion, and tarnish—ensuring long-lasting accuracy and reliability in your laboratory workflows.
Whether you're coating precision tools, sample holders, or specialized fixtures, KINTEK’s PVD technology delivers unmatched durability and performance. Contact us today to learn how our solutions can enhance your lab’s efficiency and extend the life of your critical equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition process? Unlock Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is meant by vapor deposition? A Guide to Atomic-Level Coating Technology
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is plasma in CVD process? Lowering Deposition Temperatures for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- What materials are deposited in PECVD? Discover the Versatile Thin-Film Materials for Your Application



















