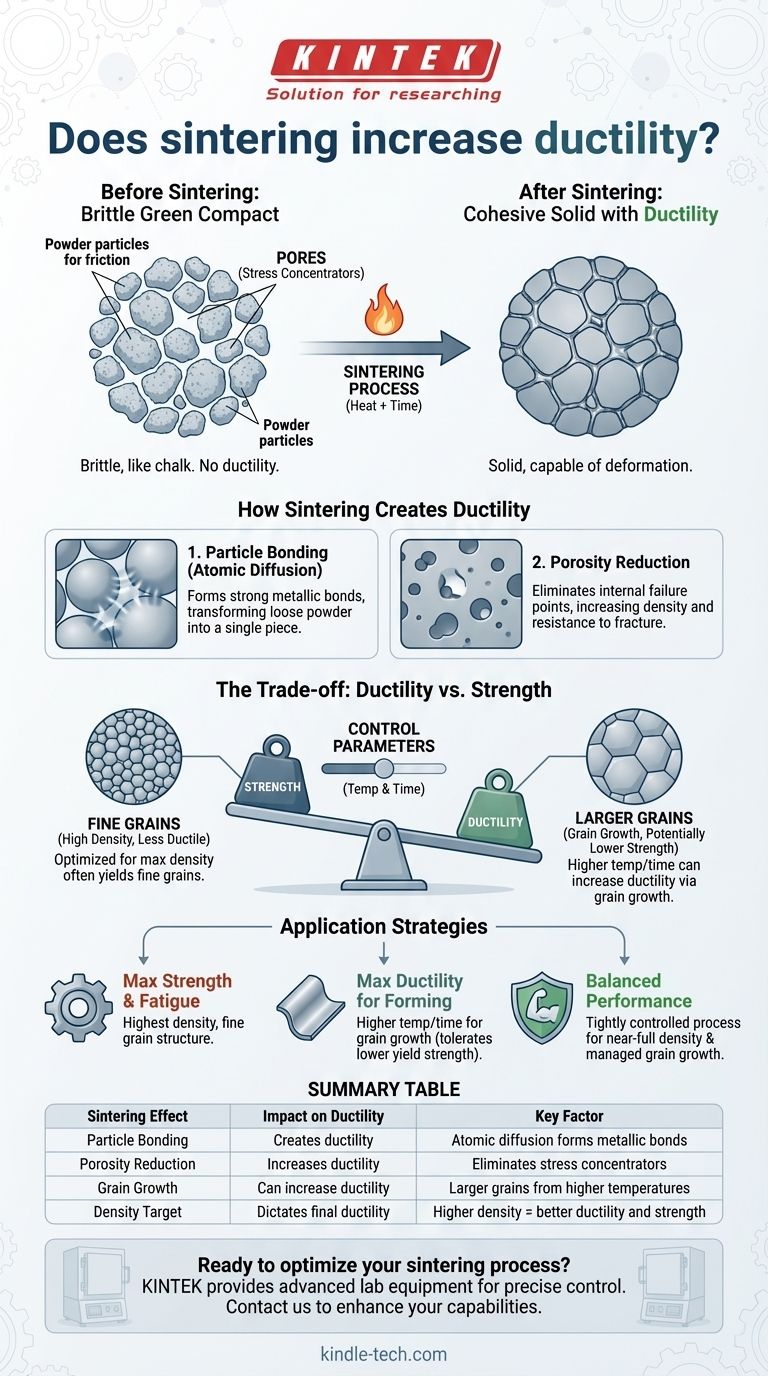
Yes, fundamentally, the sintering process is what creates ductility in a component made from powdered material. An unsintered, or "green," part is extremely brittle and possesses virtually no ductility; sintering transforms it into a cohesive solid that can deform under stress.
Sintering imparts ductility by bonding individual particles and eliminating internal pores. However, the final level of ductility is a direct result of the specific sintering parameters used, which often involves a critical trade-off between ductility, density, and strength.

The Role of Sintering in Creating Ductility
To understand how sintering affects ductility, you must first understand the state of the material before the process begins.
From Brittle Powder to Cohesive Solid
A part formed by pressing metal powder is known as a "green compact." While it holds its shape, the particles are only held together by mechanical friction.
This green part has no meaningful ductility. If you try to bend it, it will fracture instantly, much like a piece of chalk.
Sintering, which heats the material below its melting point, facilitates atomic diffusion between these particles. This creates strong metallic bonds, transforming the loose powder collection into a single, solid piece of material capable of plastic deformation (ductility).
How Porosity Reduction Impacts Ductility
The primary goal of sintering is to reduce and eliminate the empty spaces, or pores, between the powder particles.
These pores are internal defects that act as stress concentrators. When a load is applied, stress multiplies at the edges of these pores, providing perfect initiation points for cracks.
By removing pores and increasing the material's density, sintering eliminates these internal failure points. This drastically increases the material's ability to resist fracture, a property closely related to ductility.
The Link to Final Microstructure
The sintering process directly dictates the final microstructure of the material, including its grain size and the distribution of any remaining pores.
It is this final microstructure that governs all mechanical properties. A well-sintered part with minimal porosity and strong inter-particle bonds will be a ductile and strong component.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Ductility vs. Strength
While sintering introduces ductility, the degree of ductility can be manipulated, and it rarely exists in isolation from other properties.
The Inverse Relationship
In most metals, there is an inverse relationship between strength and ductility. Processes that make a metal significantly stronger often make it less ductile, and vice-versa.
Sintering is no exception. While it increases both strength and ductility from the baseline of a green compact, optimizing for one often comes at the expense of the other.
The Effect of Sintering Parameters
You can control the final properties by adjusting the sintering temperature and time.
Higher temperatures or longer sintering times can lead to grain growth, where smaller grains merge into larger ones. Larger grains can sometimes increase ductility but typically reduce the material's overall strength.
Conversely, parameters optimized for maximum density and strength often aim to create a fine-grained structure, which may result in slightly lower ductility compared to an over-sintered, large-grained part.
The Primary Goal: Density
Remember that the main objective of sintering is to create a dense body. Increasing density almost always increases strength, toughness, and durability.
The final ductility is often a consequence of the process chosen to achieve the target density. A part that is 99% dense will be dramatically more ductile and stronger than one that is only 90% dense.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your approach to sintering should be dictated by the end-use application of the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and fatigue resistance: You should optimize the sintering process for the highest possible density with a fine, uniform grain structure.
- If your primary focus is maximizing ductility for forming operations: You may use higher temperatures or longer times to encourage some grain growth, provided you can tolerate a potential decrease in yield strength.
- If your primary focus is a balanced performance profile: You must use a tightly controlled process to achieve near-full density while carefully managing grain growth to get the desired blend of strength and ductility.
By mastering the sintering process, you can engineer the material's microstructure to achieve the precise properties your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Effect | Impact on Ductility | Key Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Bonding | Creates ductility | Atomic diffusion forms metallic bonds |
| Porosity Reduction | Increases ductility | Eliminates stress concentrators |
| Grain Growth | Can increase ductility | Larger grains from higher temperatures |
| Density Target | Dictates final ductility | Higher density = better ductility and strength |
Ready to optimize your sintering process for the perfect balance of ductility and strength?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables that help you achieve precise control over sintering parameters. Whether you're working with metal powders for high-strength components or need to maximize ductility for forming operations, our solutions ensure you get the material properties your application demands.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and deliver consistent, high-quality results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics
- How does a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace facilitate the high densification of Al-30%Sc alloys?
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve high-density NTC ceramics with superior stability.



















