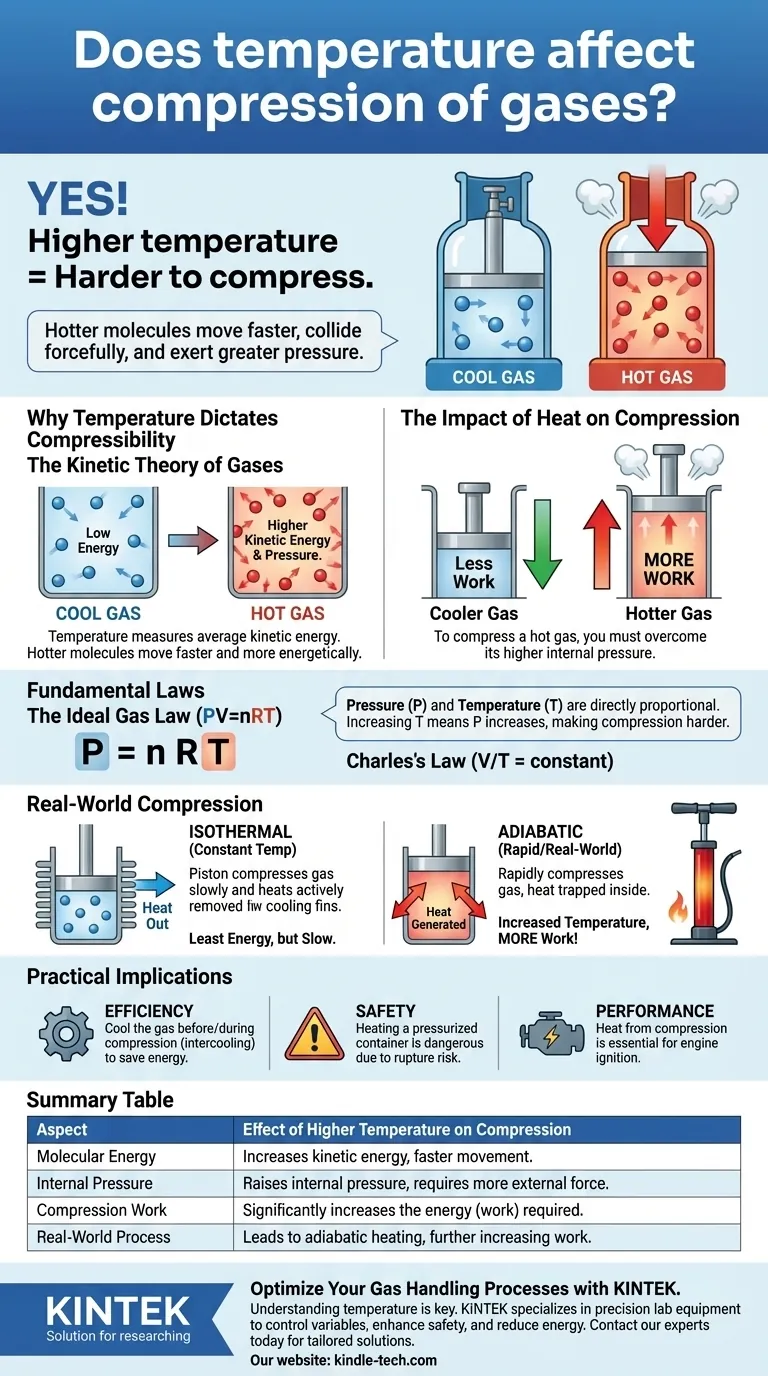
Yes, temperature has a direct and critical effect on the compression of gases. A gas at a higher temperature is significantly harder to compress than the same gas at a lower temperature. This is because temperature is a measure of the kinetic energy of the gas molecules; hotter molecules move faster, collide more forcefully with the walls of their container, and therefore exert a greater pressure that must be overcome.
The core principle is that compressing a gas requires work to overcome the pressure exerted by its molecules. Since a hotter gas exerts more pressure at a given volume, it requires more work to compress.

Why Temperature Dictates Compressibility
To understand the relationship between temperature and compression, we must look at the behavior of gas molecules. This is explained by the kinetic theory of gases.
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
Temperature is a macroscopic measurement of the average kinetic energy of the molecules in a substance. Higher temperatures mean the individual gas molecules are moving faster and more energetically.
A cool gas has molecules with lower average kinetic energy, meaning they move more slowly. A hot gas has molecules with higher average kinetic energy, causing them to move much faster.
Pressure as a Result of Molecular Collisions
The pressure a gas exerts is the result of countless molecules colliding with the walls of their container. Each collision imparts a small amount of force.
When molecules are hotter and moving faster, they strike the container walls more frequently and with greater force, resulting in higher pressure.
The Impact of Heat on Compression
Compressing a gas means forcing its molecules into a smaller volume. To do this, you must apply an external pressure that is greater than the internal pressure of the gas.
Because a hot gas naturally exerts a higher internal pressure, you must apply a significantly greater external force to compress it to the same volume as a cooler gas.
The Fundamental Laws at Play
This relationship isn't just theoretical; it's precisely described by fundamental gas laws that form the basis of thermodynamics.
The Ideal Gas Law (PV=nRT)
The Ideal Gas Law is the unifying equation: Pressure (P) × Volume (V) = moles of gas (n) × gas constant (R) × Temperature (T).
This equation shows that pressure and temperature are directly proportional. If you hold the volume constant and increase the temperature (T), the pressure (P) must also increase. This confirms why a hotter gas is harder to compress—it starts at or builds to a higher pressure.
Charles's Law (V/T = constant)
Charles's Law states that for a fixed amount of gas at constant pressure, the volume is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
While this describes expansion upon heating, its inverse is equally true for compression. To maintain a constant pressure while reducing volume, you would have to proportionally reduce the temperature.
Practical Realities and Key Trade-offs
In real-world applications, the process of compression itself introduces a critical complication: heat.
The Idealized Case: Isothermal Compression
Isothermal compression assumes the temperature of the gas is held perfectly constant throughout the process.
To achieve this, you would need to actively and continuously remove the heat that is generated by the act of compression. This process requires the least amount of energy (work) but is often slow and impractical.
The Real-World Case: Adiabatic Compression
In nearly all rapid compression scenarios, such as in an engine cylinder or a bike pump, the process is closer to adiabatic. This means no heat is allowed to escape the system.
All the energy you put into compressing the gas increases its internal energy, causing a rapid and significant rise in temperature. This is why a tire pump gets hot during use.
The Consequence: Increased Work Required
This adiabatic heating works against you. As you compress the gas, its temperature rises, which in turn increases its internal pressure even more.
You are now fighting against a continuously increasing opposing force. This is why real-world compression always requires more work than the theoretical, constant-temperature ideal. Multi-stage compressors with intercoolers are used in industry specifically to combat this effect.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this relationship is crucial for efficiency, safety, and performance in any system that involves compressed gases.
- If your primary focus is industrial efficiency: Cooling the gas before and during compression (a process known as intercooling) will dramatically reduce the energy required to compress it.
- If your primary focus is safety: Recognize that heating a sealed, pressurized container is extremely dangerous because the internal pressure will rise proportionally with temperature, creating a risk of rupture.
- If your primary focus is engine performance: The heat generated during the compression stroke of an internal combustion engine is essential for igniting the fuel-air mixture, converting that thermal energy into mechanical work.
Ultimately, temperature is not a passive variable but an active participant in the work of compressing a gas.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Effect of Higher Temperature on Compression |
|---|---|
| Molecular Energy | Increases kinetic energy, making molecules move faster. |
| Internal Pressure | Raises the gas's internal pressure, requiring more external force to compress. |
| Compression Work | Significantly increases the energy (work) required for compression. |
| Real-World Process | Leads to adiabatic heating, further increasing resistance and work needed. |
Optimize Your Gas Handling Processes with KINTEK
Understanding the critical relationship between temperature and gas compression is key to efficiency, safety, and performance in any laboratory or industrial setting. Whether you are designing a new system or optimizing an existing one, managing thermal effects is paramount.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables that help you control these variables. From temperature-controlled environments to efficient compression systems, our solutions are designed to enhance your workflow's safety and reduce energy consumption.
Let us help you achieve superior results. Contact our experts today via our contact form to discuss how our tailored solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs and challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Air Valve Applications
- Ball Press Mold for Lab
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
People Also Ask
- Why are PTFE beakers required for hafnium metal ICP-OES validation? Ensure Pure Sample Dissolution
- Why is Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) preferred as a lining material for reactors? Ensure Maximum Chemical Resistance
- What is a sustainable solution to reduce plastic waste? A Guide to the Waste Hierarchy
- Why is slender PTFE tubing necessary for flow control in multi-channel catalyst aging? Ensure Equal Gas Distribution
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type



















