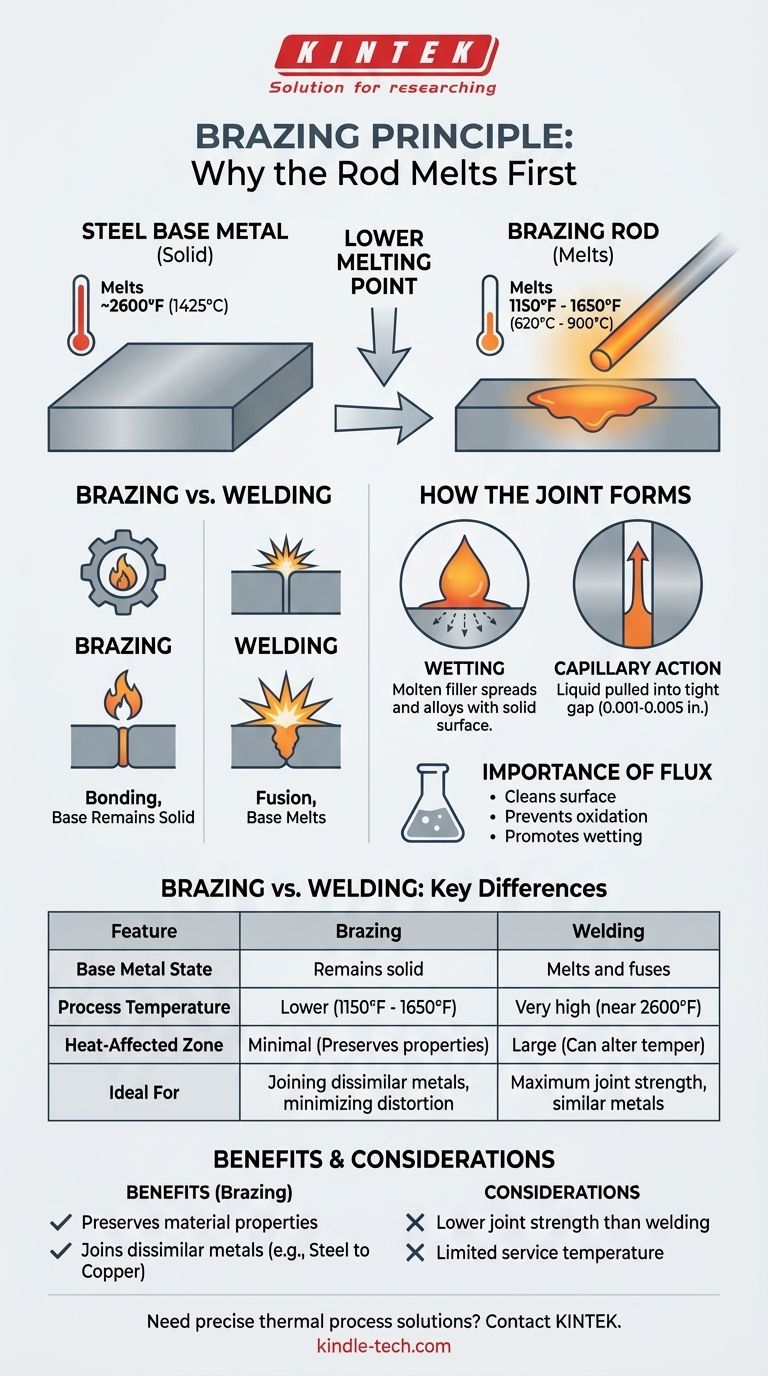
Critically, the brazing rod must have a lower melting temperature than the steel being joined. This is the defining principle of the brazing process. The procedure works by melting a filler metal (the rod) that flows into the gap between the solid, un-melted steel parts, creating a strong metallurgical bond upon cooling.
The fundamental rule of brazing is that the filler metal melts while the base metals remain solid. Therefore, a brazing rod always has a significantly lower melting point than the steel it is joining, allowing it to form a bond without melting or distorting the steel's core structure.

The Core Principle: Why Brazing Relies on a Lower Melting Point
The temperature difference between the filler metal and the base metal is not just a detail—it is the entire basis for the process and what distinguishes it from welding.
Defining Brazing vs. Welding
The key difference between brazing and welding is the state of the base metals during the process.
In welding, the base metals themselves are heated to their melting point and fused together, often with a filler material. The goal is to create a single, continuous piece of metal.
In brazing, only the filler metal melts. The base metals (the steel parts) get very hot but remain well below their melting point. Brazing is a bonding process, not a fusion process.
Understanding Melting Points by the Numbers
To put this in perspective, consider the typical temperatures involved.
A common carbon steel has a melting point around 2600°F (1425°C).
Brazing filler metals for steel, such as bronze or silver alloys, have melting points (technically their liquidus temperature) that are much lower, typically in the range of 1150°F to 1650°F (620°C to 900°C).
This massive temperature gap is what makes the process possible. You can bring the entire assembly to 1700°F, which is hot enough to melt the rod but leaves the steel over 900°F below its melting point.
How the Brazed Joint is Formed
With the base metal remaining solid, the molten filler metal must bond to it through other mechanisms. This happens through two key phenomena.
The Concept of "Wetting"
Wetting is the ability of a liquid to spread across a solid surface. In brazing, the molten filler metal "wets" the surface of the hot steel.
This is not simple adhesion. It is a metallurgical process where the filler metal forms a thin diffusion layer, alloying with the very surface of the steel to create an exceptionally strong and permanent bond.
The Power of Capillary Action
Brazing works best on parts with a very small, controlled gap between them, typically 0.001 to 0.005 inches.
When the filler metal melts, this tight gap pulls the liquid metal into the joint through capillary action. This is the same force that pulls water up a narrow tube, ensuring the entire joint is filled with the bonding alloy.
The Importance of Flux
For wetting to occur, the steel surfaces must be perfectly clean at the atomic level. At brazing temperatures, steel rapidly forms oxides that prevent the filler from bonding.
A flux is applied before heating. It melts at a lower temperature than the brazing rod, acting as a chemical cleaning agent that shields the joint from oxygen and dissolves any existing oxides, preparing the surface for perfect wetting.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Brazing vs. Welding Steel
Because brazing does not melt the base metal, it has distinct advantages and disadvantages compared to welding.
Benefit: Preserving Material Properties
The high heat of welding creates a large heat-affected zone (HAZ) that can alter the steel's temper, hardness, and internal stress, potentially weakening the area around the weld.
Brazing uses significantly less heat, resulting in a much smaller HAZ. This preserves the original properties of the steel, reduces warping, and minimizes residual stress in the final assembly.
Benefit: Joining Dissimilar Metals
Brazing is an excellent method for joining metals with vastly different melting points, such as steel to copper or steel to brass. Attempting to weld these combinations is often impossible, as one metal would vaporize before the other melts.
Limitation: Joint Strength and Service Temperature
A brazed joint's mechanical strength is limited by the strength of the filler metal, which is almost always lower than that of the parent steel. While a properly designed brazed joint is extremely strong, it will not achieve the full, 100% parent metal strength that a high-quality weld can.
Furthermore, a brazed assembly cannot be used in applications where the service temperature approaches the melting point of the filler metal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct process requires you to understand your primary objective for the joint.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength comparable to the base metal: Choose welding, as it fuses the parent materials directly.
- If your primary focus is minimizing heat distortion and preserving the steel's properties: Brazing is the superior choice due to its lower process temperature.
- If you need to join steel to a different metal like copper or brass: Brazing is the most effective and common method for the task.
Understanding this fundamental temperature relationship empowers you to select the right joining process for the integrity and performance of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Brazing | Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Base Metal State | Remains solid | Melts and fuses |
| Process Temperature | Lower (1150°F - 1650°F) | Very high (near steel's 2600°F melting point) |
| Heat-Affected Zone | Minimal, preserves steel properties | Large, can alter temper and hardness |
| Ideal For | Joining dissimilar metals, minimizing distortion | Maximum joint strength, fusing similar metals |
Need to join metals without compromising their integrity? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for precise thermal processes like brazing. Our expertise ensures you achieve strong, reliable joints while preserving your material's properties. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's metal joining needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Precision Machined Yttrium Stabilized Zirconia Ceramic Rod for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Rod for High Temperature Applications
- Professional Cutting Tools for Carbon Paper Cloth Diaphragm Copper Aluminum Foil and More
People Also Ask
- Why tungsten is not used in heating devices? The Critical Role of Oxidation Resistance
- What is the melting point of tungsten? Discover the Metal That Withstands Extreme Heat
- Can tungsten be used as a heating element? Unlocking Extreme Heat for High-Temperature Applications
- What are heating elements with tungsten? Unlock Extreme Heat for Vacuum & Industrial Processes
- Why tungsten is not used as heating element? Discover the critical role of oxidation resistance.











