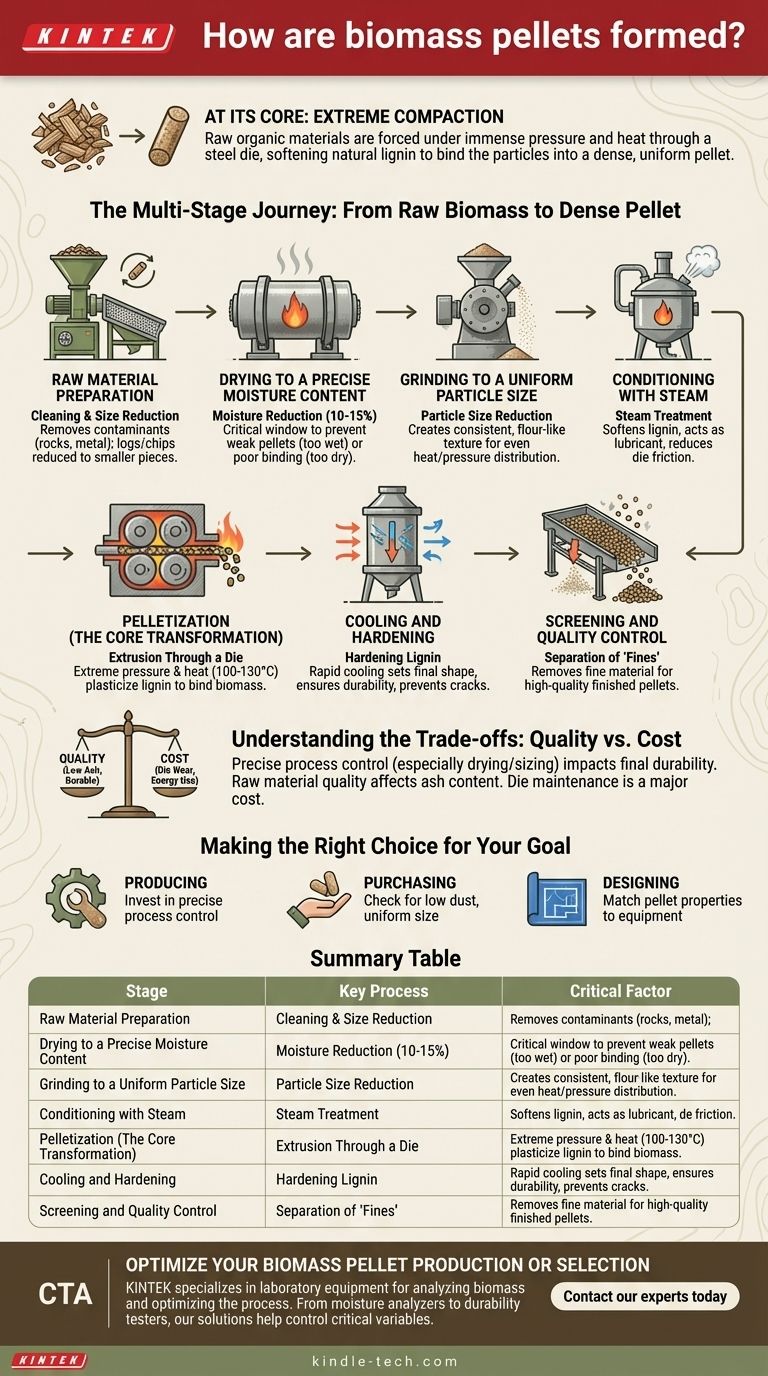
At its core, biomass pellet formation is a process of extreme compaction. Raw organic materials, like wood chips or sawdust, are forced under immense pressure and heat through a steel mold, known as a die. This process heats the natural lignin within the biomass, which acts as a glue, binding the compressed particles together into a dense, uniform pellet as it cools.
The quality of a biomass pellet is not determined by a single action, but by a precise, multi-stage engineering process. Understanding each stage—from drying the raw material to cooling the final product—is essential for anyone looking to produce, purchase, or utilize biomass energy effectively.
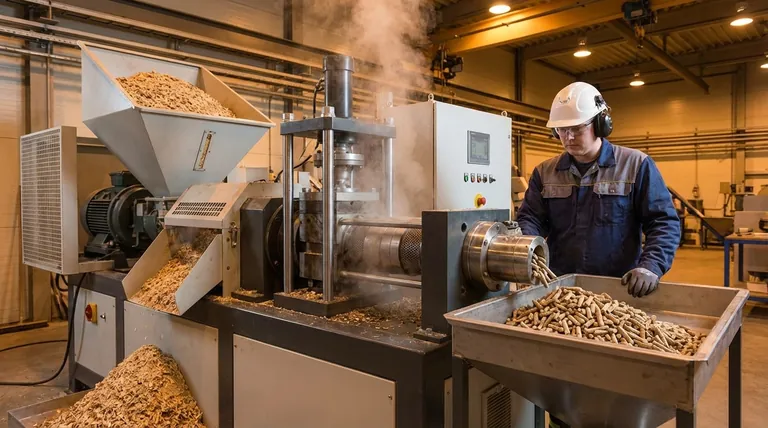

The Multi-Stage Journey: From Raw Biomass to Dense Pellet
Creating a high-quality, energy-dense pellet is a journey of transformation. Each step is carefully controlled to ensure the final product has the desired characteristics of durability, low moisture, and high energy content.
Stage 1: Raw Material Preparation
The process begins with the feedstock, which can range from sawdust and wood shavings to agricultural residues. This raw material is first cleaned to remove contaminants like rocks or metal, which could damage the machinery.
If the source material is large, like logs or wood chips, it is fed into a chipper or hammer mill to reduce its size. The goal is to create smaller, more manageable pieces for the next stages.
Stage 2: Drying to a Precise Moisture Content
This is one of the most critical steps. Raw biomass often has a moisture content of 40-60%. For effective pelletization, this must be reduced to a narrow window of 10-15%.
If the material is too wet, steam will get trapped in the die, creating weak or broken pellets. If it's too dry, there isn't enough moisture to help soften the lignin, resulting in poor binding and excessive friction. Large industrial rotary dryers are typically used for this purpose.
Stage 3: Grinding to a Uniform Particle Size
After drying, the material is sent through a hammer mill a second time. This fine-grinding step reduces the particles to a consistent, flour-like texture.
This uniformity is crucial. A consistent particle size ensures that heat and pressure are distributed evenly within the die, leading to a denser, more durable pellet. It also maximizes the surface area for the lignin to bind effectively.
Stage 4: Conditioning with Steam
Before entering the pellet mill, the ground material is "conditioned." It is mixed with dry steam in a conditioner or mixer.
This step may seem counterintuitive after intensive drying, but it serves two key purposes. The steam slightly raises the temperature and moisture content, which softens the lignin and makes the material more pliable. This acts as a lubricant, reducing friction and wear on the pellet mill's die and rollers.
Stage 5: Pelletization (The Core Transformation)
This is where the pellet is formed. The conditioned feedstock is fed into the pellet mill. Inside, rollers press the material with extreme force, pushing it through the holes of a thick, circular steel die.
The combination of intense pressure and friction generates temperatures of 100-130°C (212-266°F). This heat plasticizes the lignin, turning it into a natural adhesive that binds the biomass particles together as they are extruded through the die holes.
Stage 6: Cooling and Hardening
Pellets exit the die extremely hot (around 70-90°C) and relatively soft. They are immediately transported to a counter-flow cooler.
The cooling process is essential for hardening the lignin, which sets the pellet's final shape and gives it the mechanical durability needed for transport and storage. Rapid cooling prevents cracks and ensures a stable final product.
Stage 7: Screening and Quality Control
The final step is to screen the cooled pellets. This process separates the finished pellets from any fine material or dust, known as "fines".
High-quality production aims for minimal fines. The finished, screened pellets are then ready for storage in silos or packaging in bags for distribution.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Quality vs. Cost
The pelletization process is a balance of precision and efficiency. Deviations at any stage can significantly impact the final product, leading to common pitfalls.
The Critical Role of Raw Material Quality
The "garbage in, garbage out" principle applies directly to pellet production. Using biomass with high bark content, dirt, or other contaminants will result in pellets with high ash content. High-ash pellets burn less efficiently and can cause maintenance issues in boilers and stoves.
Moisture Content: The Narrow Window of Success
Achieving the correct moisture content is a constant operational challenge. Over-drying wastes energy and creates brittle pellets, while under-drying leads to blockages in the die and low-durability products. Consistent monitoring is key.
Die Wear and Maintenance Costs
The extreme pressure and friction inherent in pelletization cause significant wear on the pellet mill's die and rollers. This is a primary operational cost. The choice of raw material and proper conditioning are critical for minimizing this wear and extending the life of the machinery.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the formation process empowers you to assess pellet quality and optimize its use.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality pellets: Invest in precise process control, especially for drying and particle size, as these have the greatest impact on final pellet durability.
- If your primary focus is purchasing pellets for a boiler or stove: Examine the pellets for low dust content (fines) and uniform size; these are indicators of a well-controlled manufacturing process and predict better performance.
- If your primary focus is designing a biomass energy system: Acknowledge that pellet properties like ash content and durability are direct results of the production process and must be matched to your equipment's specifications.
By recognizing that a biomass pellet is an engineered product, you can better predict its performance and ensure the success of your energy goals.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Critical Factor |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Cleaning & Size Reduction | Removal of contaminants |
| 2. Drying | Moisture Reduction | Achieving 10-15% moisture content |
| 3. Grinding | Particle Size Reduction | Creating a uniform, flour-like texture |
| 4. Conditioning | Steam Treatment | Softening lignin for binding |
| 5. Pelletization | Extrusion Through a Die | High pressure (100-130°C) |
| 6. Cooling | Hardening | Rapid cooling for durability |
| 7. Screening | Quality Control | Separation of fines from finished pellets |
Optimize Your Biomass Pellet Production or Selection
Understanding the precise engineering behind pellet formation is key to achieving high efficiency and low operational costs. Whether you are producing pellets or specifying them for a boiler system, the right equipment and consumables are critical for success.
KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables for analyzing biomass and optimizing the pelletization process. From moisture analyzers to durability testers, our solutions help you control the critical variables that define pellet quality.
Ready to achieve superior pellet quality and performance? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Lab Plastic PVC Calender Stretch Film Casting Machine for Film Testing
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
People Also Ask
- How does a hydraulic hot press machine work? Unlock Precision in Material Bonding and Forming
- What advantages does a hot press offer over cold pressing? Enhance Sulfide Solid-State Electrolyte Performance
- What is the function of a laboratory hydraulic hot press in the assembly of solid-state photoelectrochemical cells?
- What does a hydraulic heat press do? Achieve Industrial-Scale, Consistent Pressure for High-Volume Production
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in all-solid-state battery fabrication? Enhancing Ion Conductivity



















